Embed presentation
Downloaded 84 times




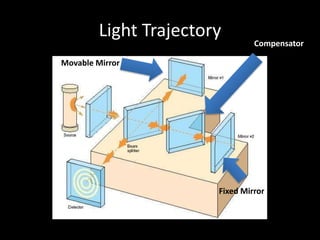


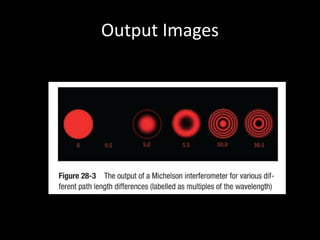
The Michelson interferometer uses a laser light source that is split by a beam splitter into two beams. One beam reflects off a fixed mirror and the other reflects off a movable mirror before recombining at the detector. By moving the movable mirror, the path length of one beam can be varied, causing the beams to interfere constructively or destructively at the detector and creating bright or dark fringes. This allows very small changes in distance or wavelength to be measured precisely.







