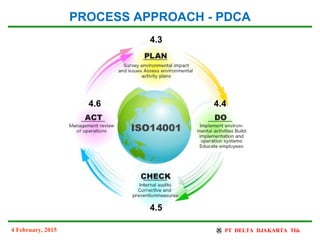
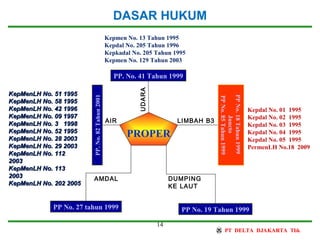
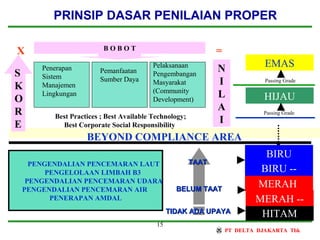
The document provides background information on ISO 14001:2004, an international standard for environmental management systems (EMS). It discusses the history and development of EMS standards beginning in 1973. Key aspects of ISO 14001:2004 include establishing an environmental policy, identifying environmental impacts, setting objectives and targets, training employees, documenting the system, conducting management reviews, and continually improving the EMS. Certification to ISO 14001:2004 can provide benefits such as reduced waste costs, energy and material savings, and an improved public image.