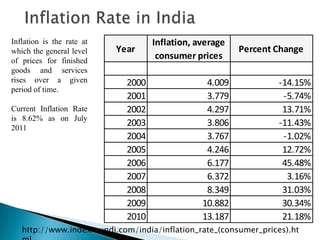
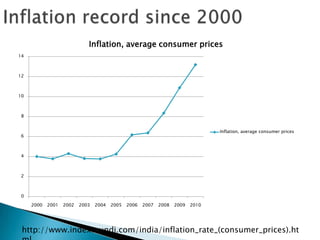
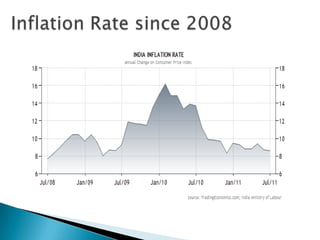
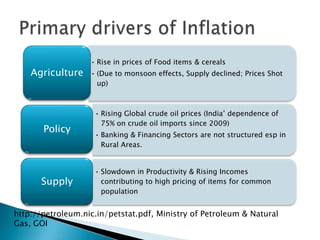
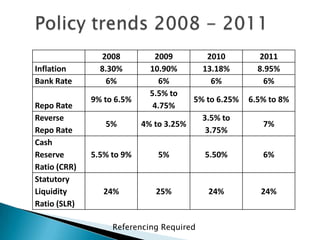
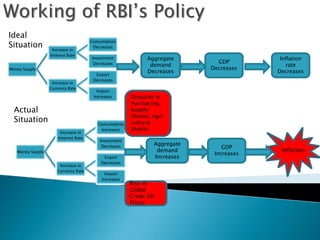
The document contains data on India's inflation rate from 2000 to 2010. Inflation increased substantially from 2006 to 2010, with a peak of 13.18% in 2010. Some key factors that contributed to rising inflation in India over this period included increases in global crude oil prices, as India relies heavily on oil imports; a slowdown in productivity growth; and structural issues in India's banking and rural finance sectors that limit access to credit. Monetary policy tightening by the Reserve Bank of India through higher interest rates and reduced money supply aimed to curb inflation, but other supply-side shocks and global commodity price rises made reducing inflation challenging.