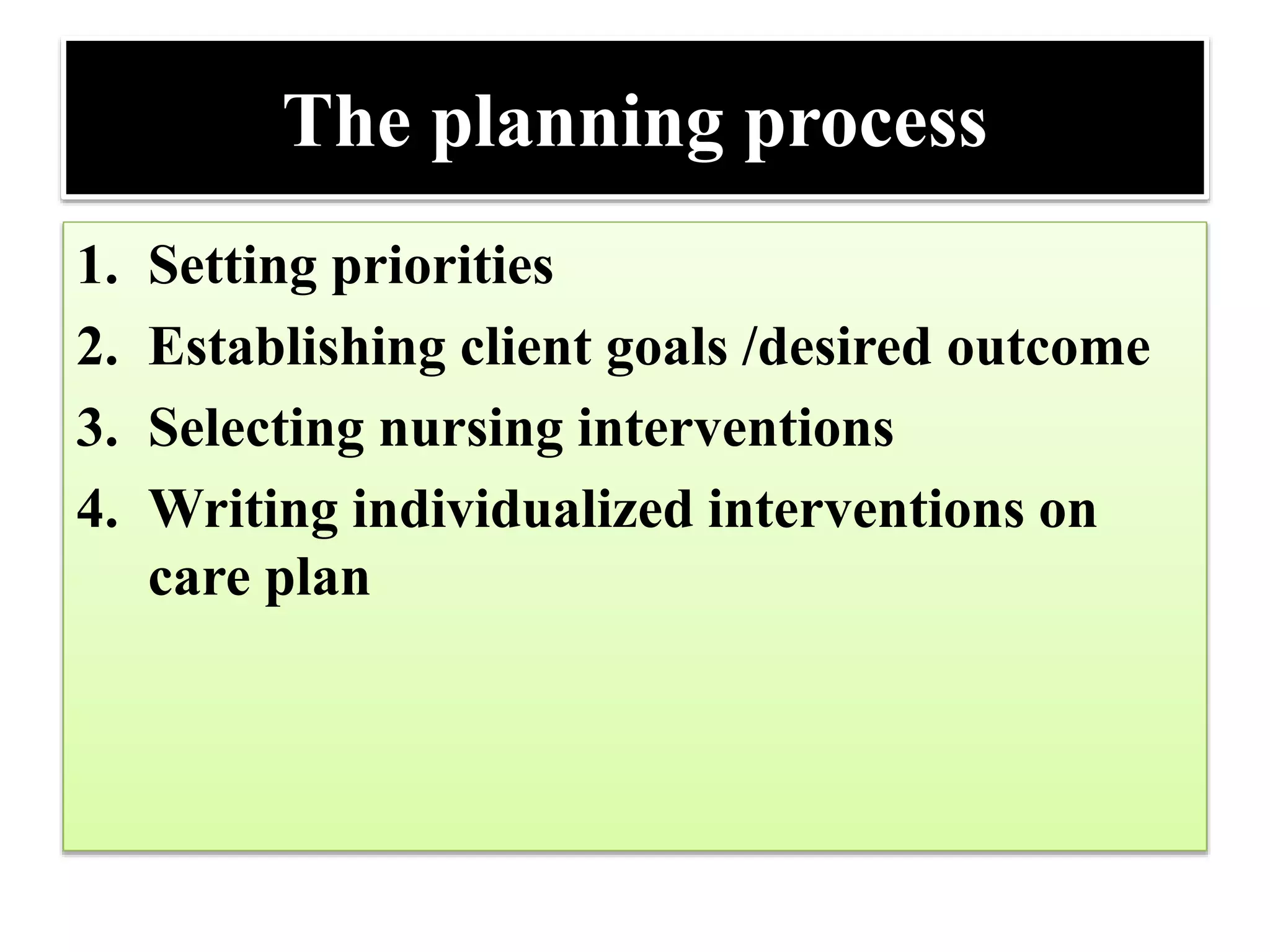
The planning phase of the nursing process involves setting priorities, establishing goals and desired outcomes, and selecting appropriate nursing interventions. Key steps include:
1) Setting priorities by considering factors like the client's health issues, values, and available resources. High priority issues are addressed first.
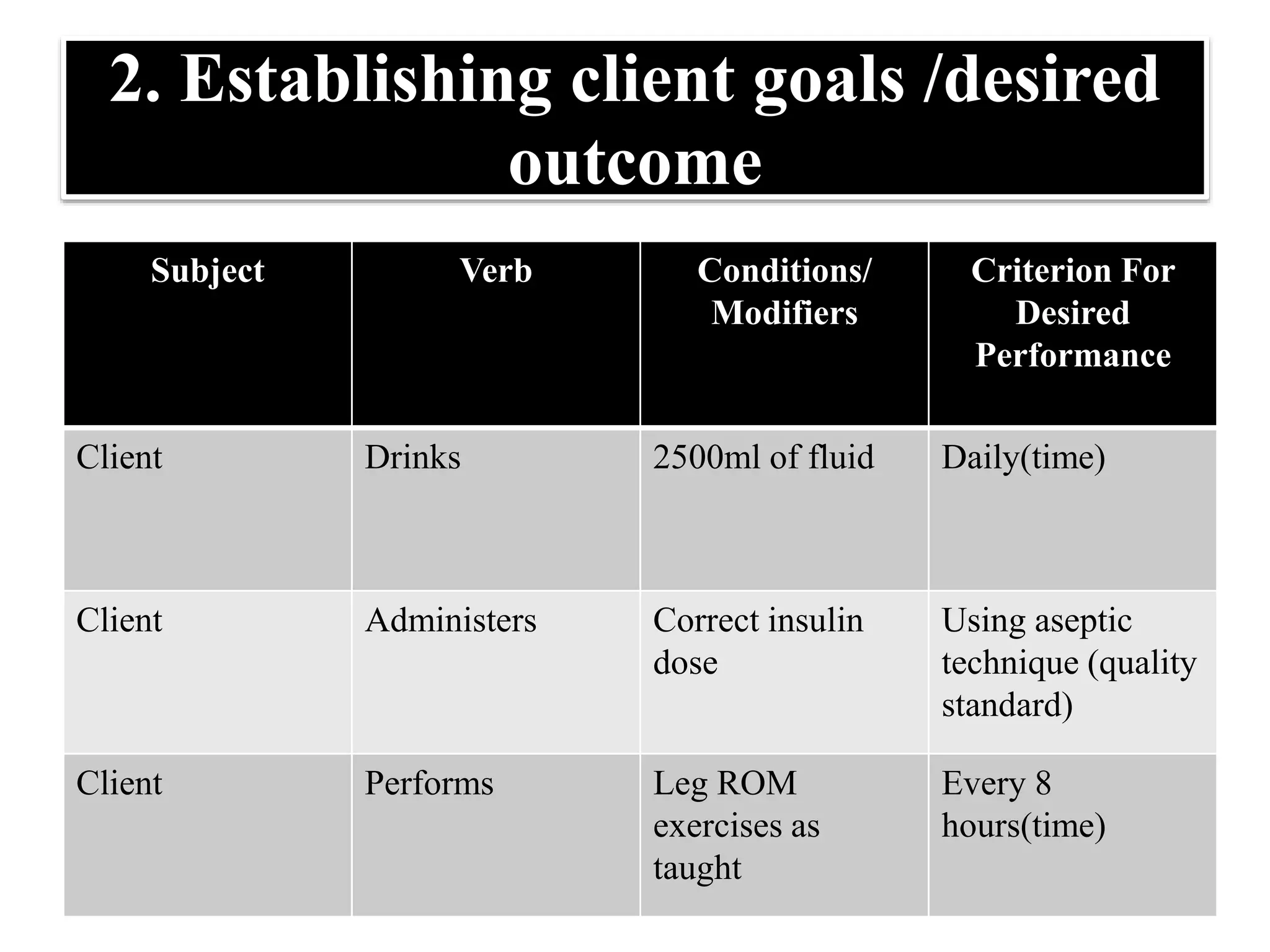
2) Establishing goals and desired outcomes that are client-centered, measurable, realistic and time-limited. Goals provide direction for interventions and criteria for evaluating progress.
3) Selecting nursing interventions that are safe, achievable, congruent with the client's situation, and based on nursing standards. Interventions are then written on the client's individualized care plan.