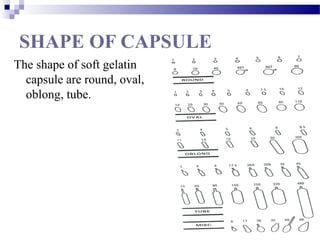
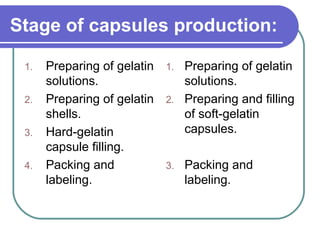
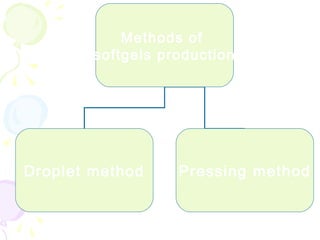
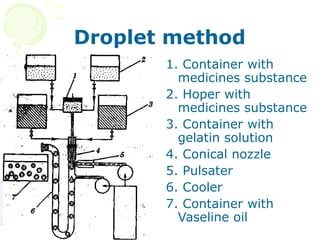
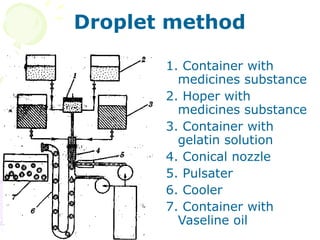
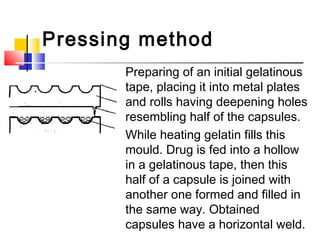
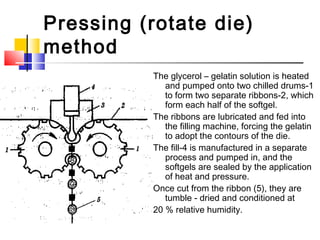
This document discusses soft gelatin capsules. Soft gelatin capsules have soft, gelatin shells that contain liquid or semisolid fill materials. They are formed, filled, and sealed in a single operation using either a droplet or pressing method. Soft gelatin capsules offer advantages over hard capsules like improved bioavailability and enhanced stability. The shells are made of gelatin, plasticizers, preservatives, colors and flavors. Soft gelatin capsules can be used orally or for other routes of administration.