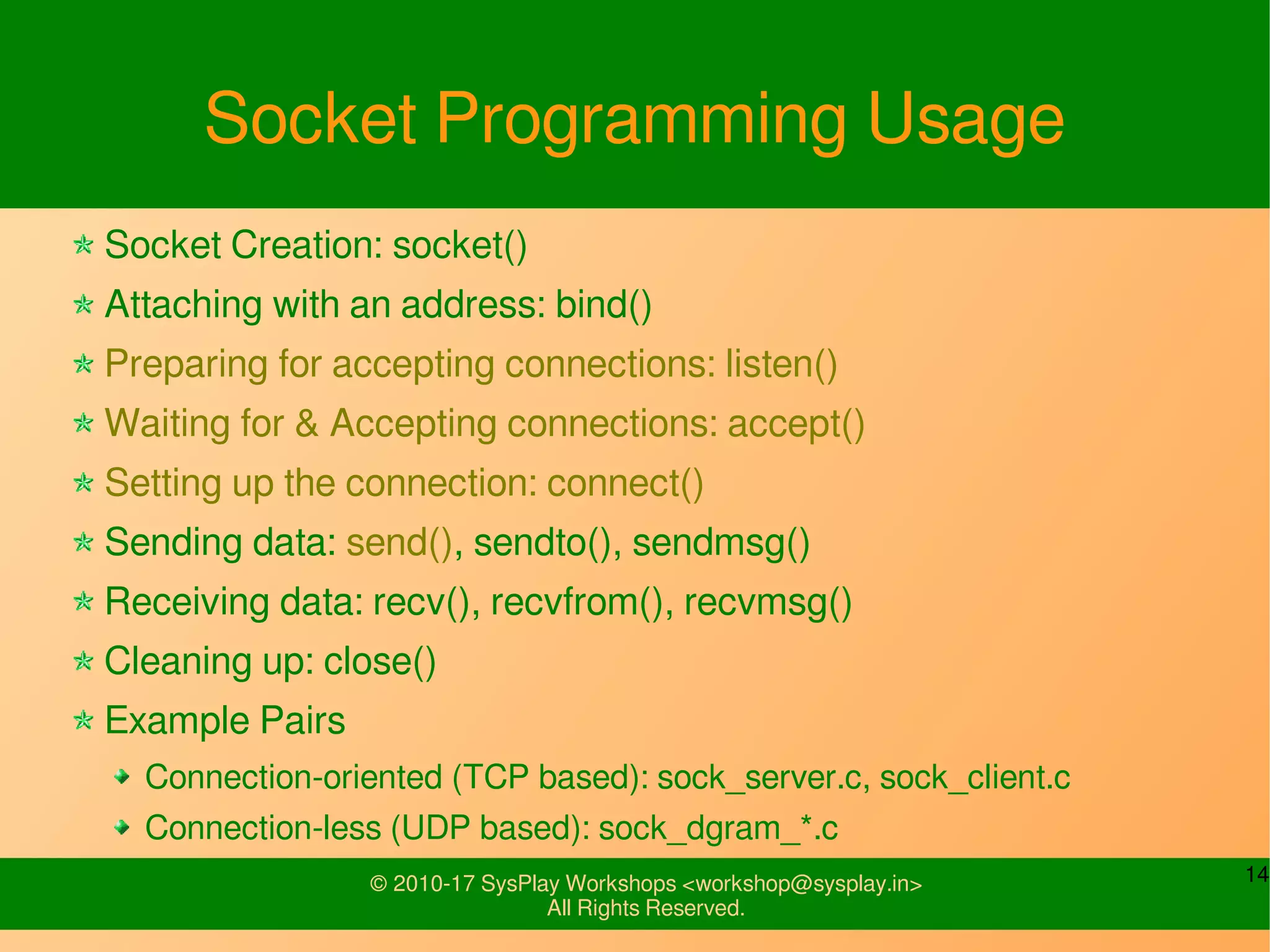
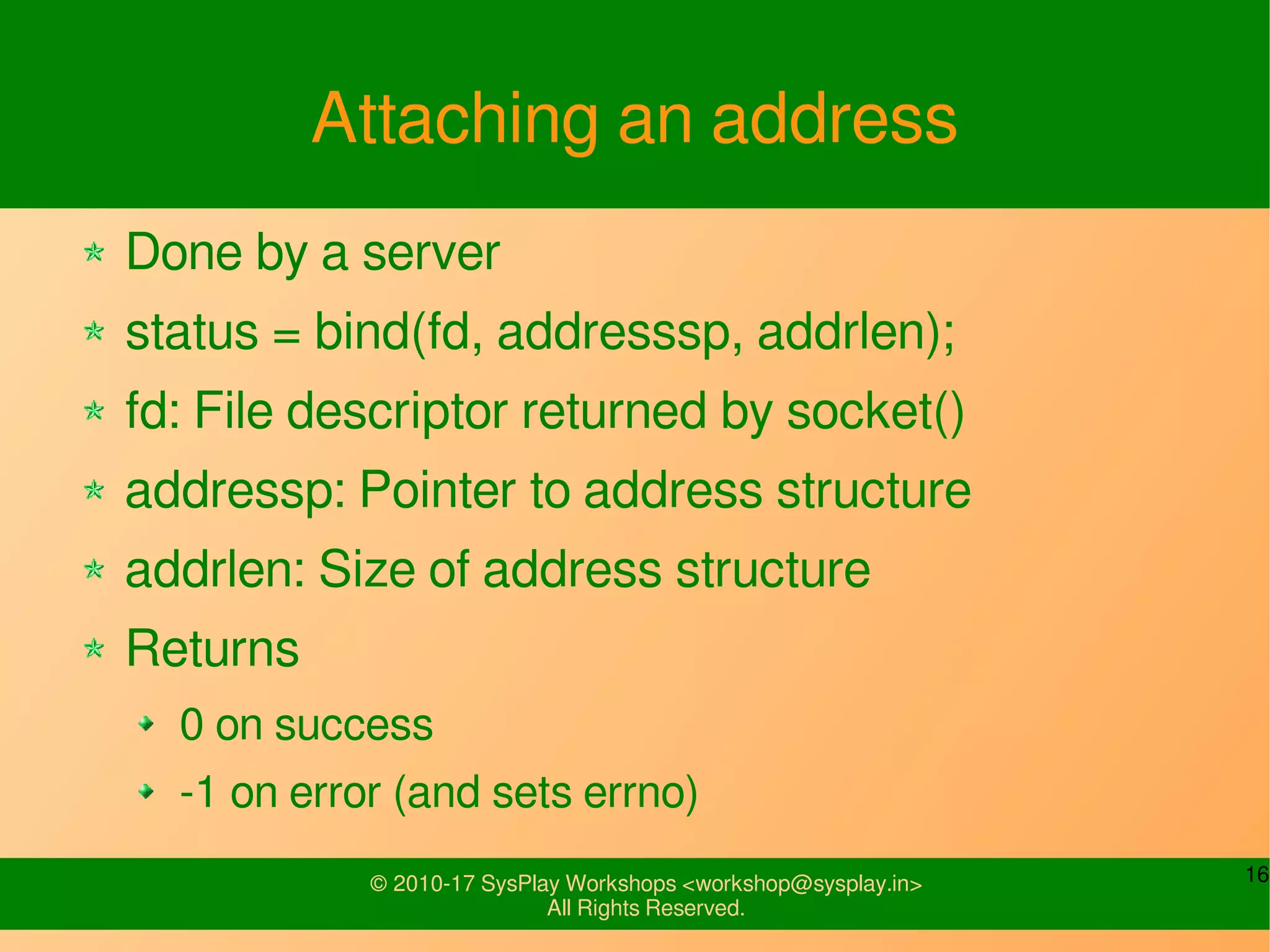
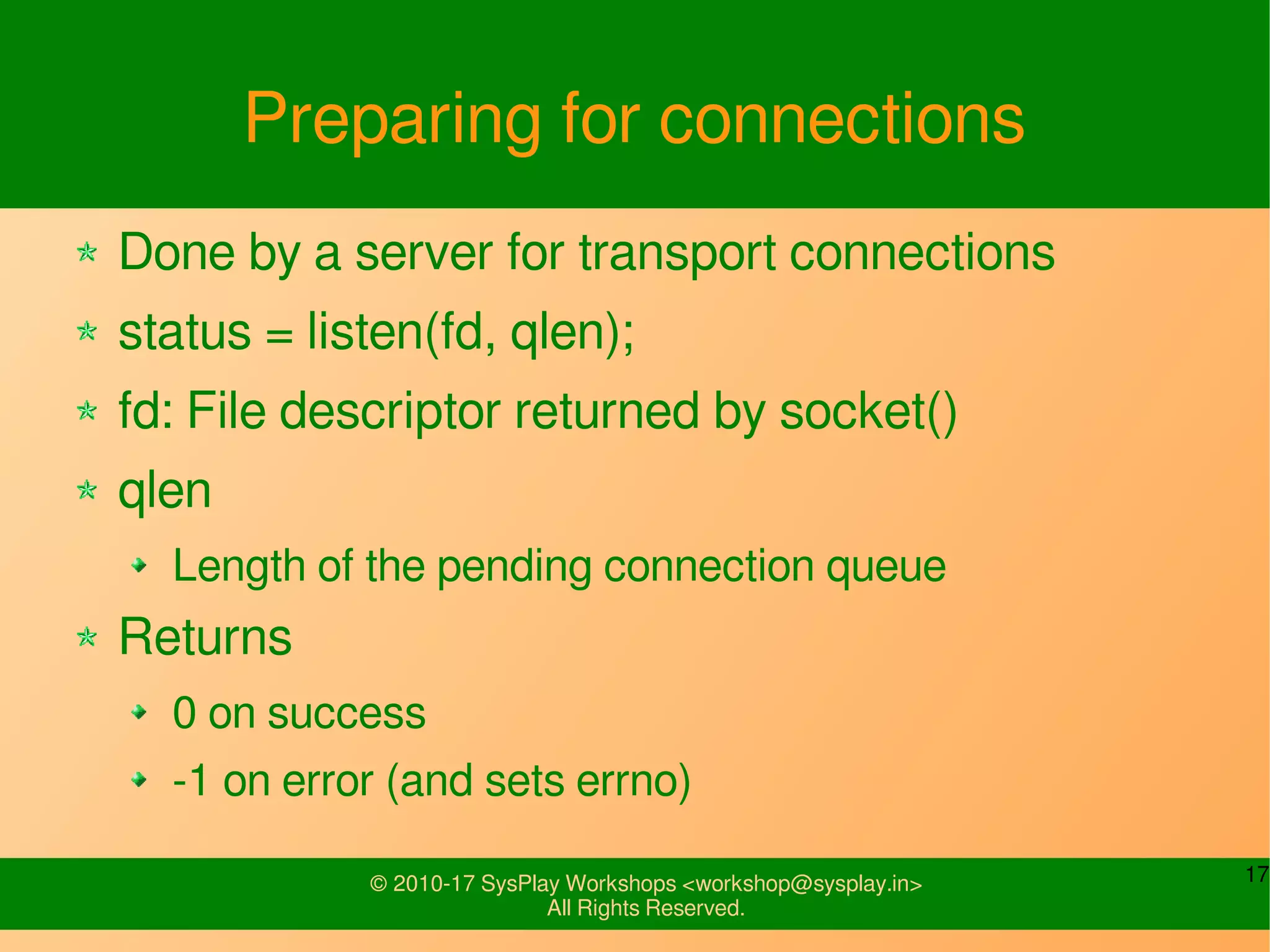
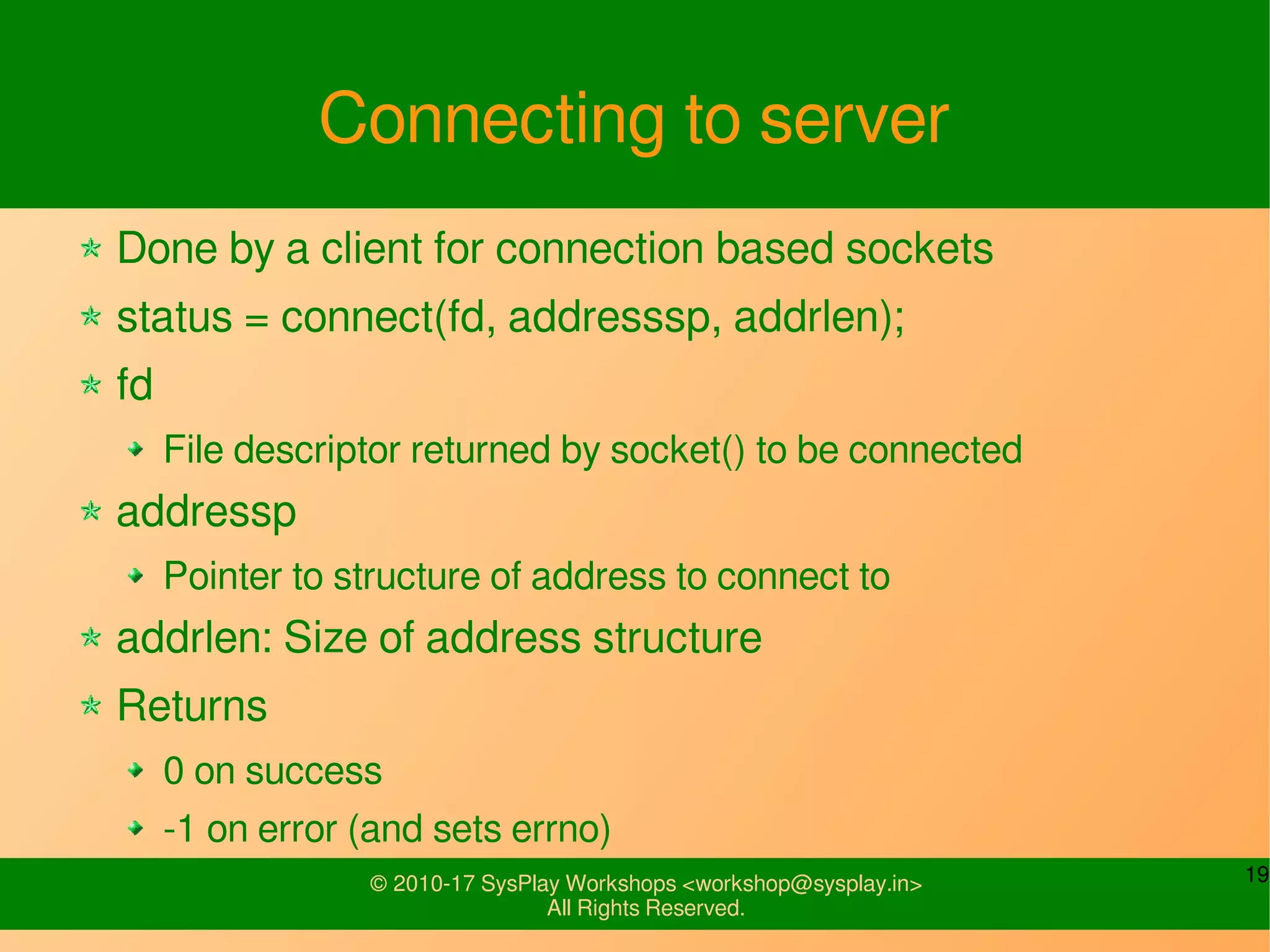
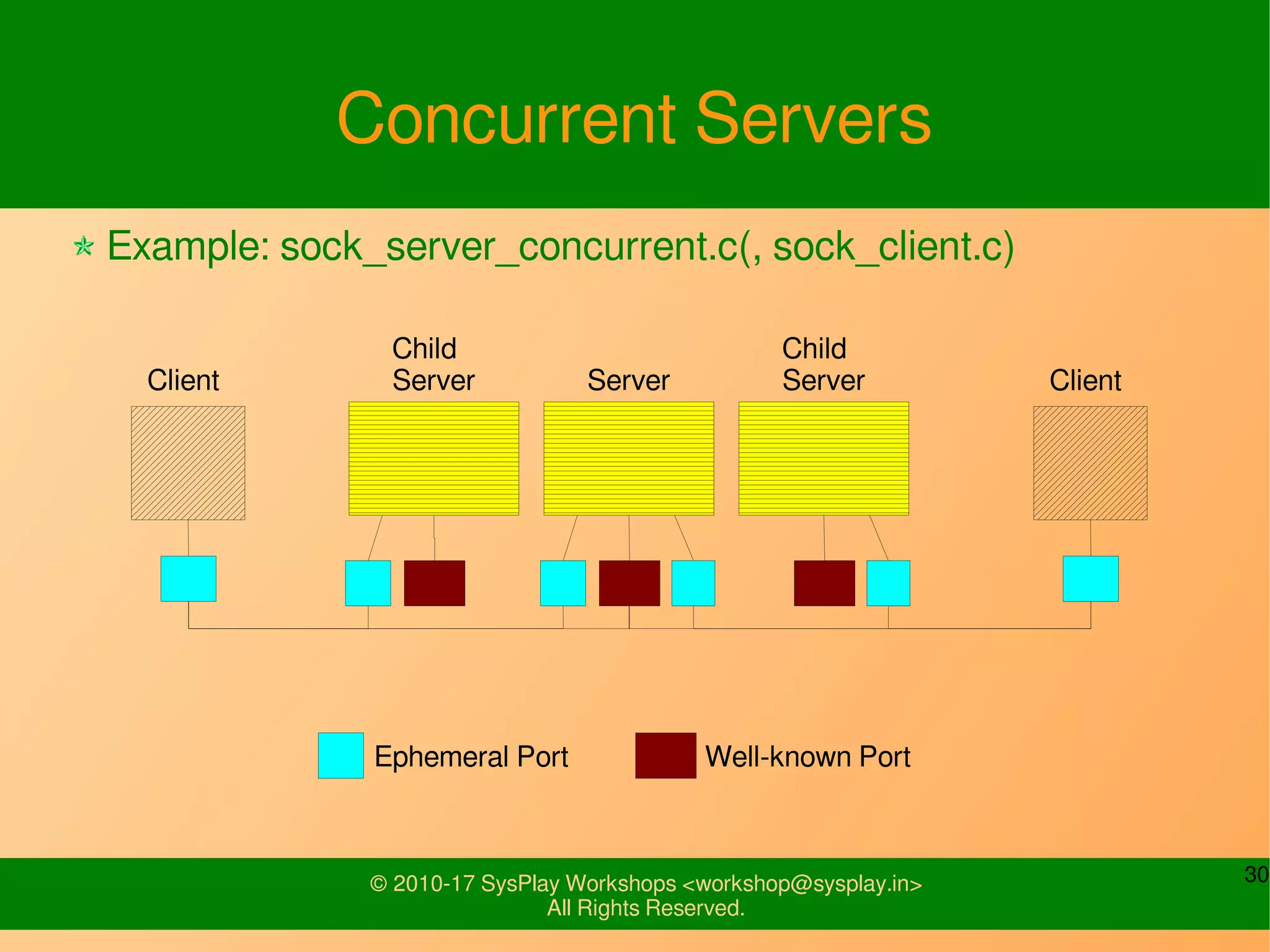
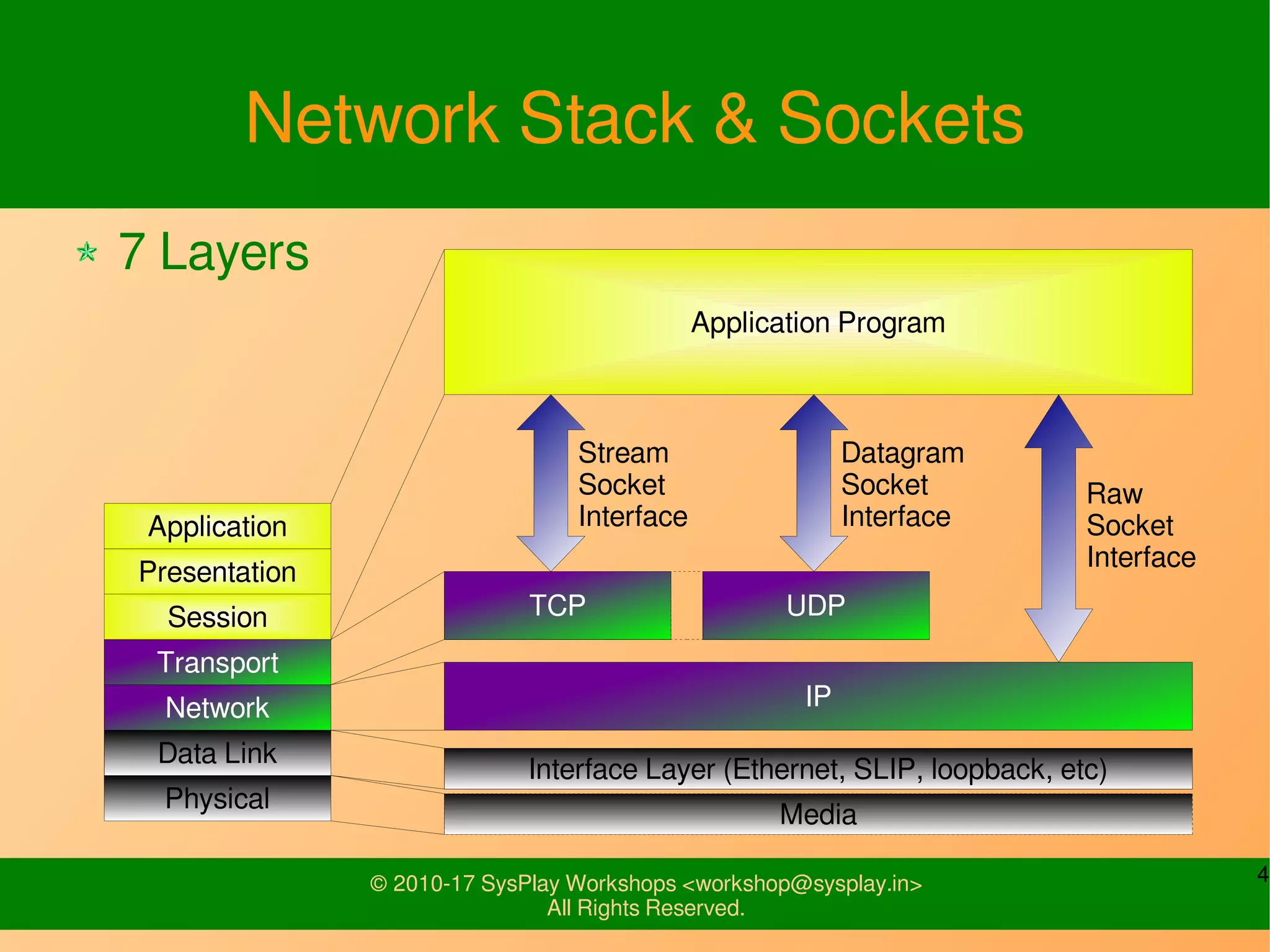
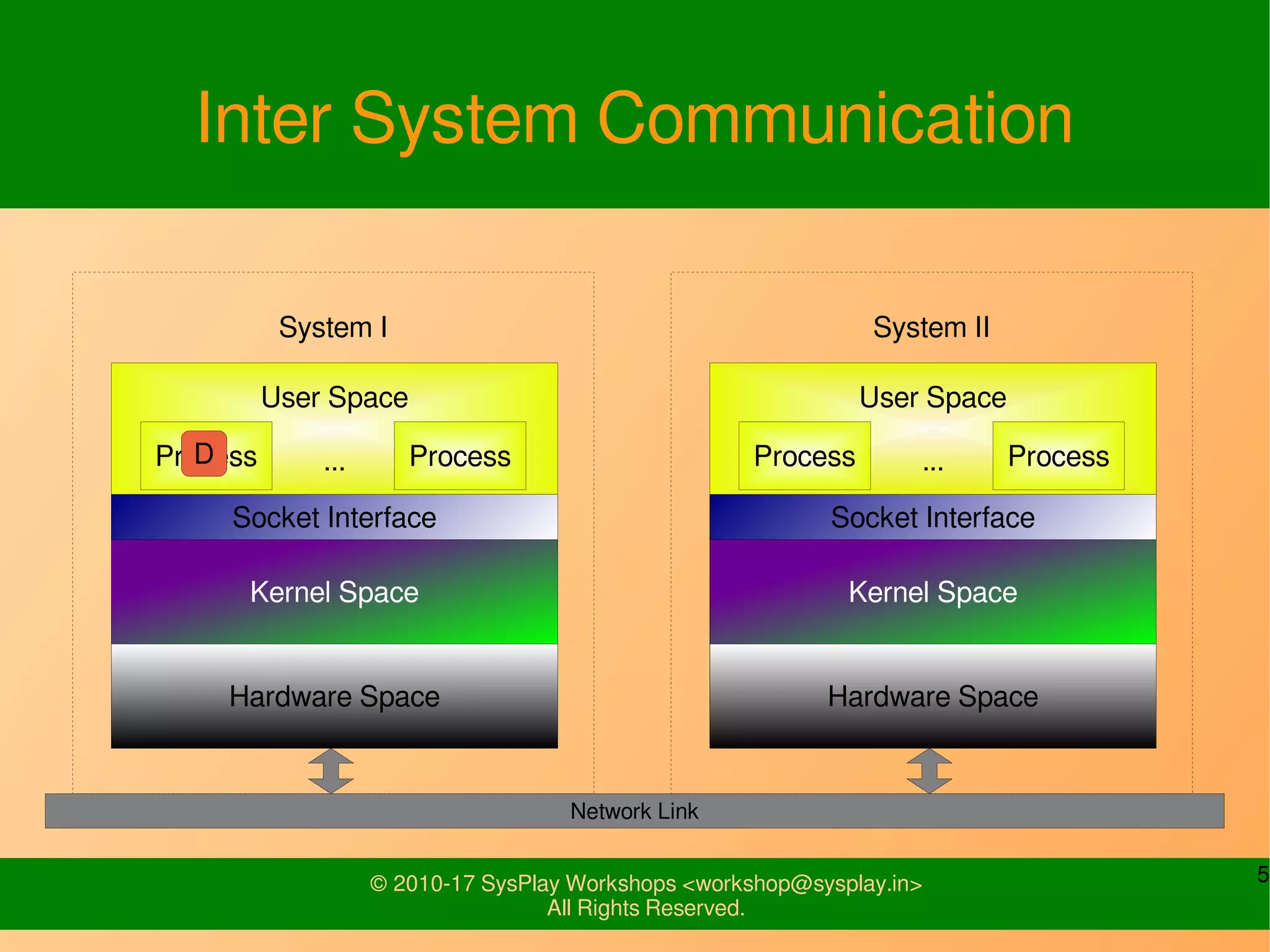
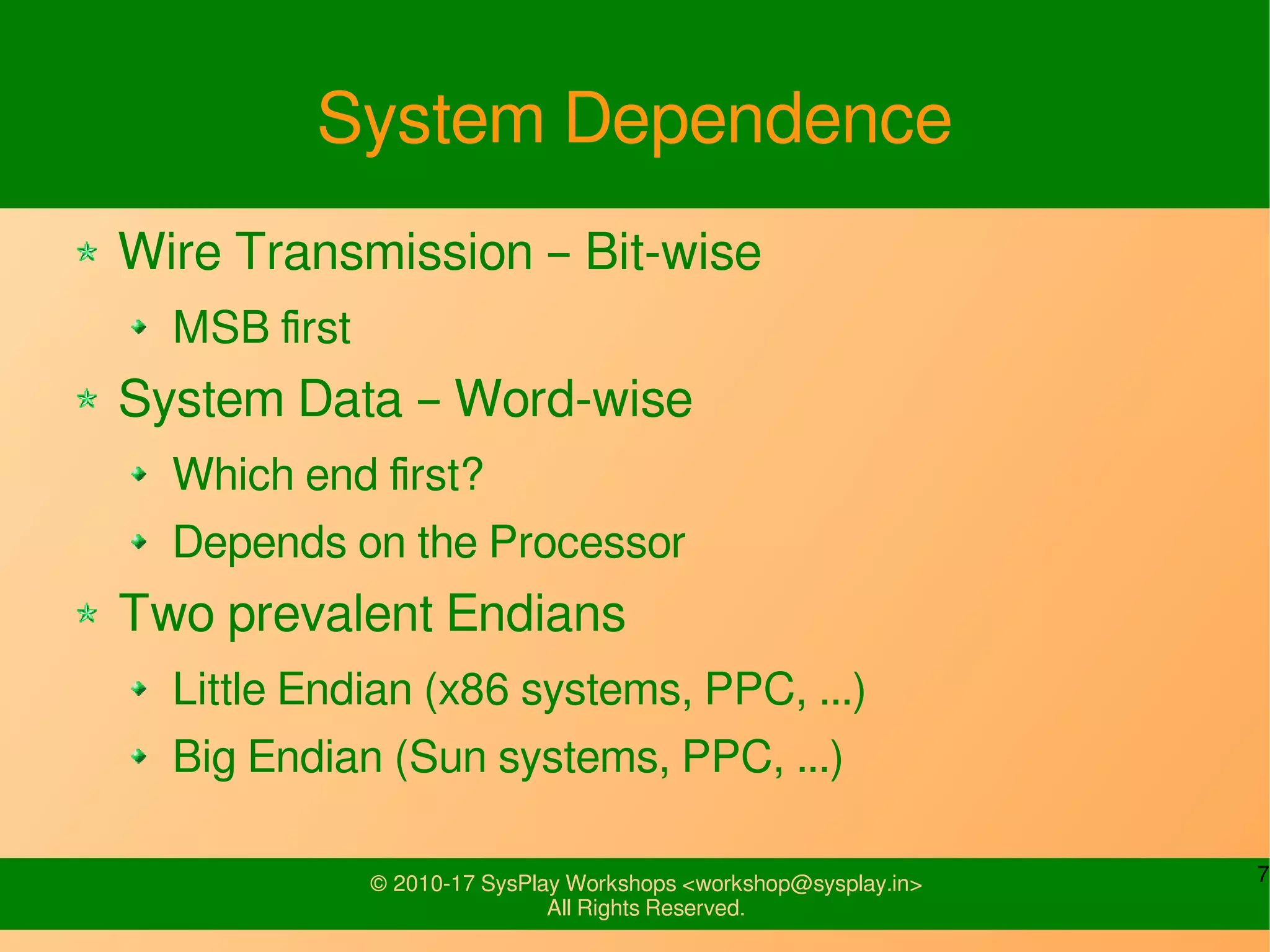
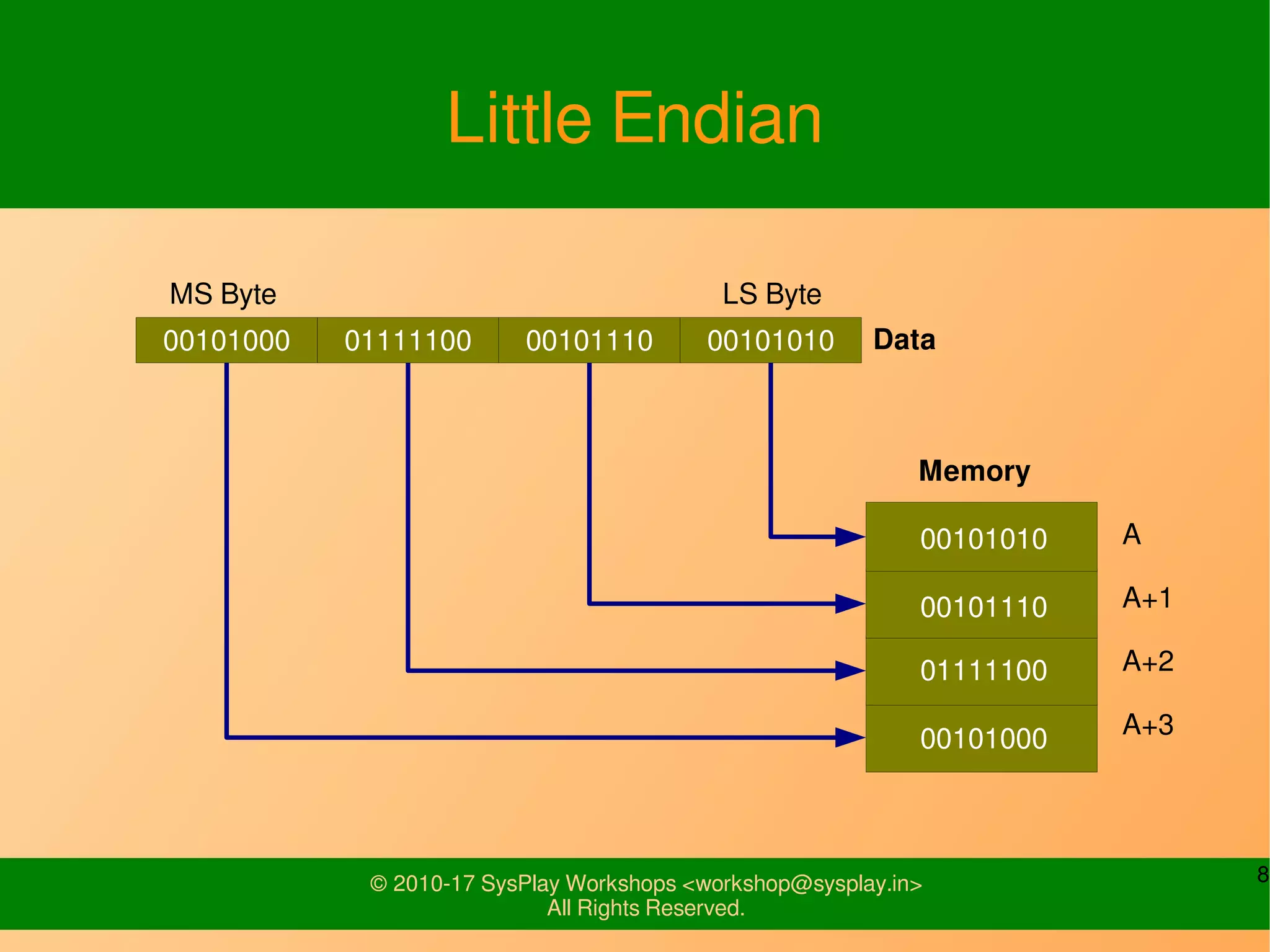
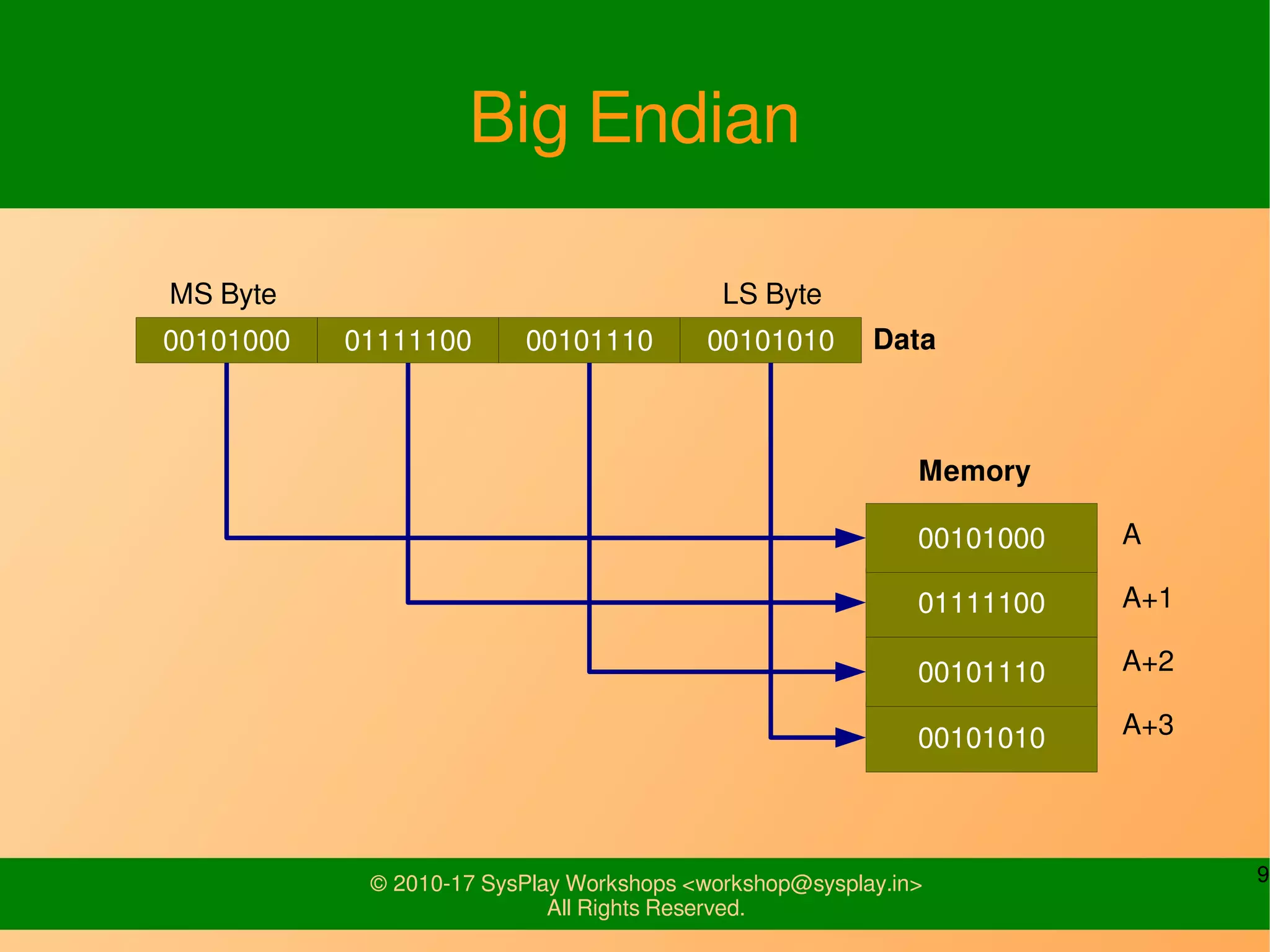
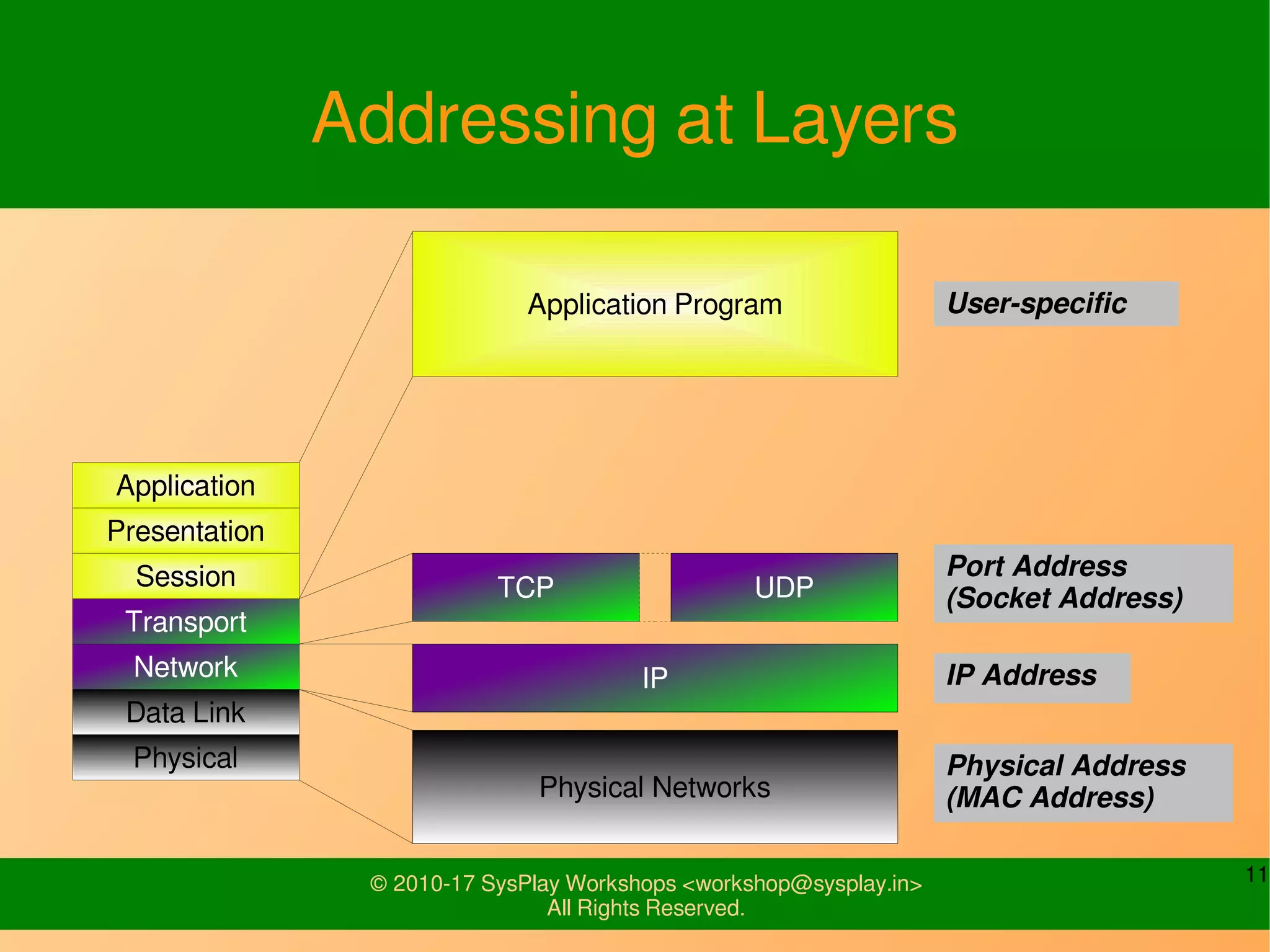
This document discusses Linux network management and socket programming. It covers topics like the network stack and sockets, addressing at different layers, socket programming APIs, client-server concepts and examples. Some key points covered include the seven layer OSI model, TCP and UDP sockets, functions for socket creation, connection establishment, data sending and receiving, and closing sockets. Non-blocking I/O and system calls like select and poll are also discussed.




![12© 2010-17 SysPlay Workshops <workshop@sysplay.in>
All Rights Reserved.
Socket Address
Basic Structure (16 bytes)
struct sockaddr
{
sa_family_t sa_family; // Protocol Family
char sa_data[14]; // Protocol Address
}
typedef unsigned short sa_family_t;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxnetworkmanagement-101013114047-phpapp02/75/Linux-Network-Management-12-2048.jpg)
![13© 2010-17 SysPlay Workshops <workshop@sysplay.in>
All Rights Reserved.
Socket Address ...
With Internet Address
struct sockaddr_in
{
sa_family_t sin_family; // Protocol Family
in_port_t sin_port; // Port Number / Socket Address
struct in_addr sin_addr; // IP Protocol Address
unsigned char sin_zero[8]; // Pad to sizeof(struct sockaddr)
}
typedef uint16_t in_port_t;
struct in_addr { in_addr_t s_addr; }
typedef uint32_t in_addr_t;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxnetworkmanagement-101013114047-phpapp02/75/Linux-Network-Management-13-2048.jpg)