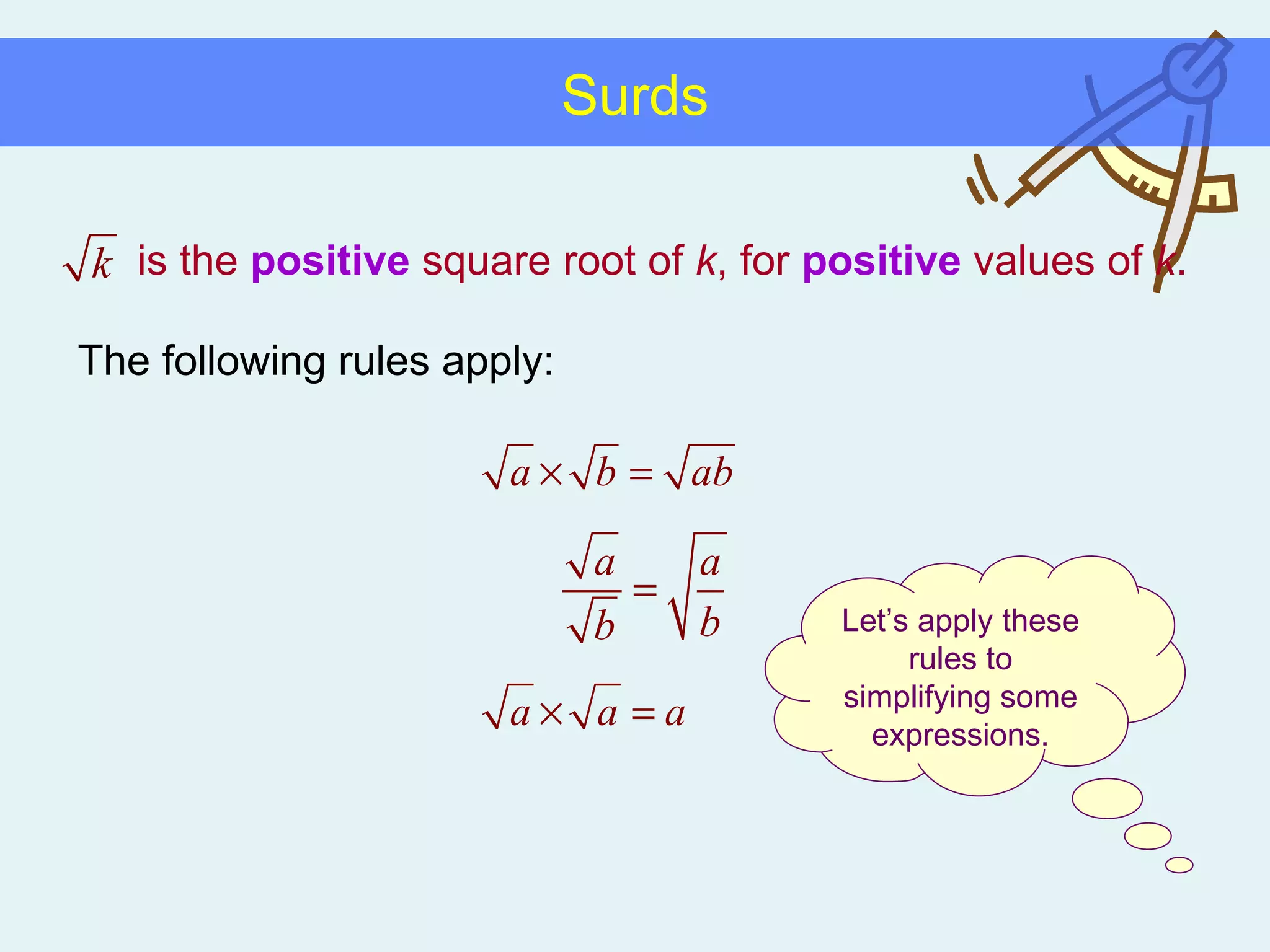
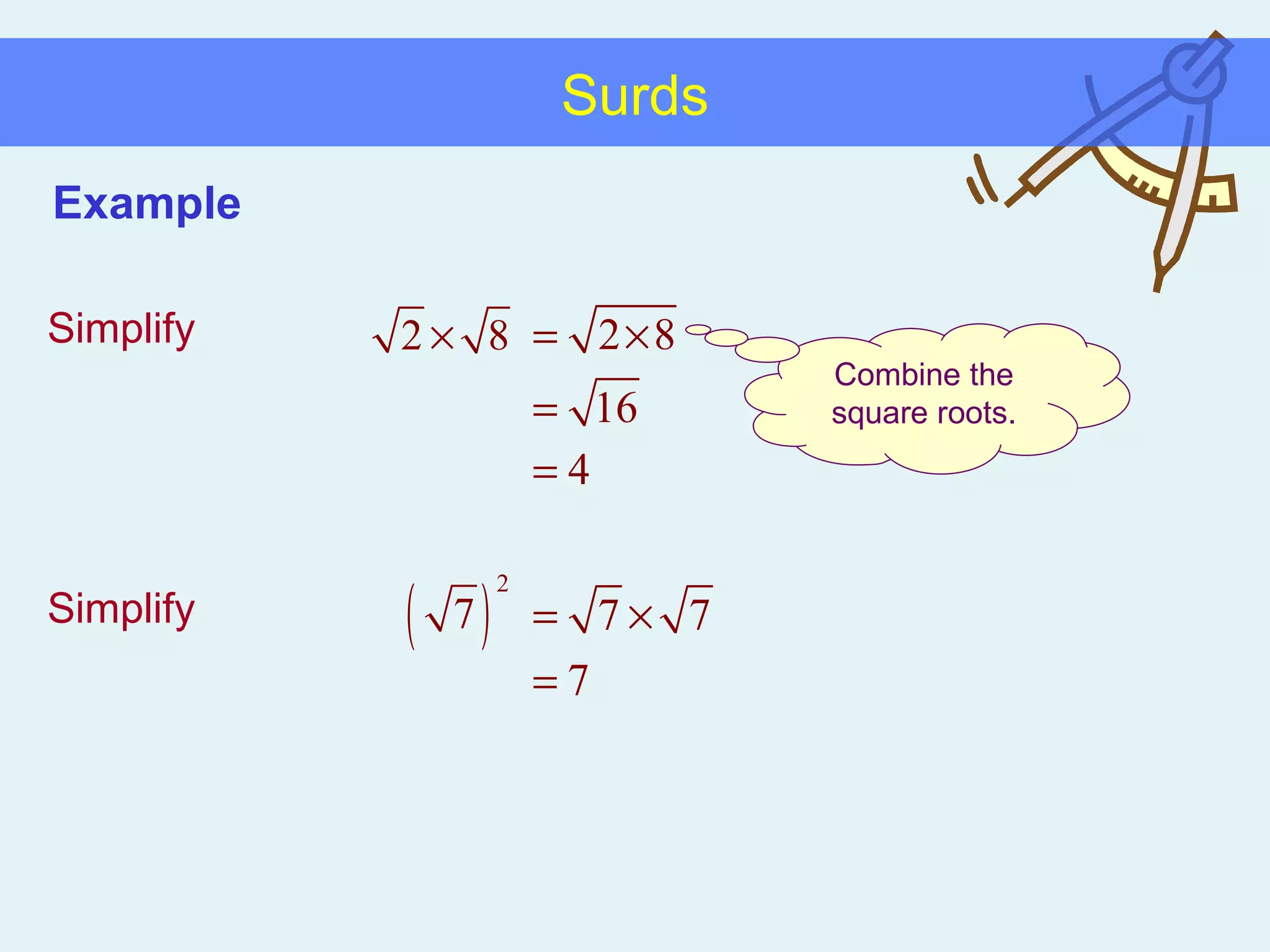
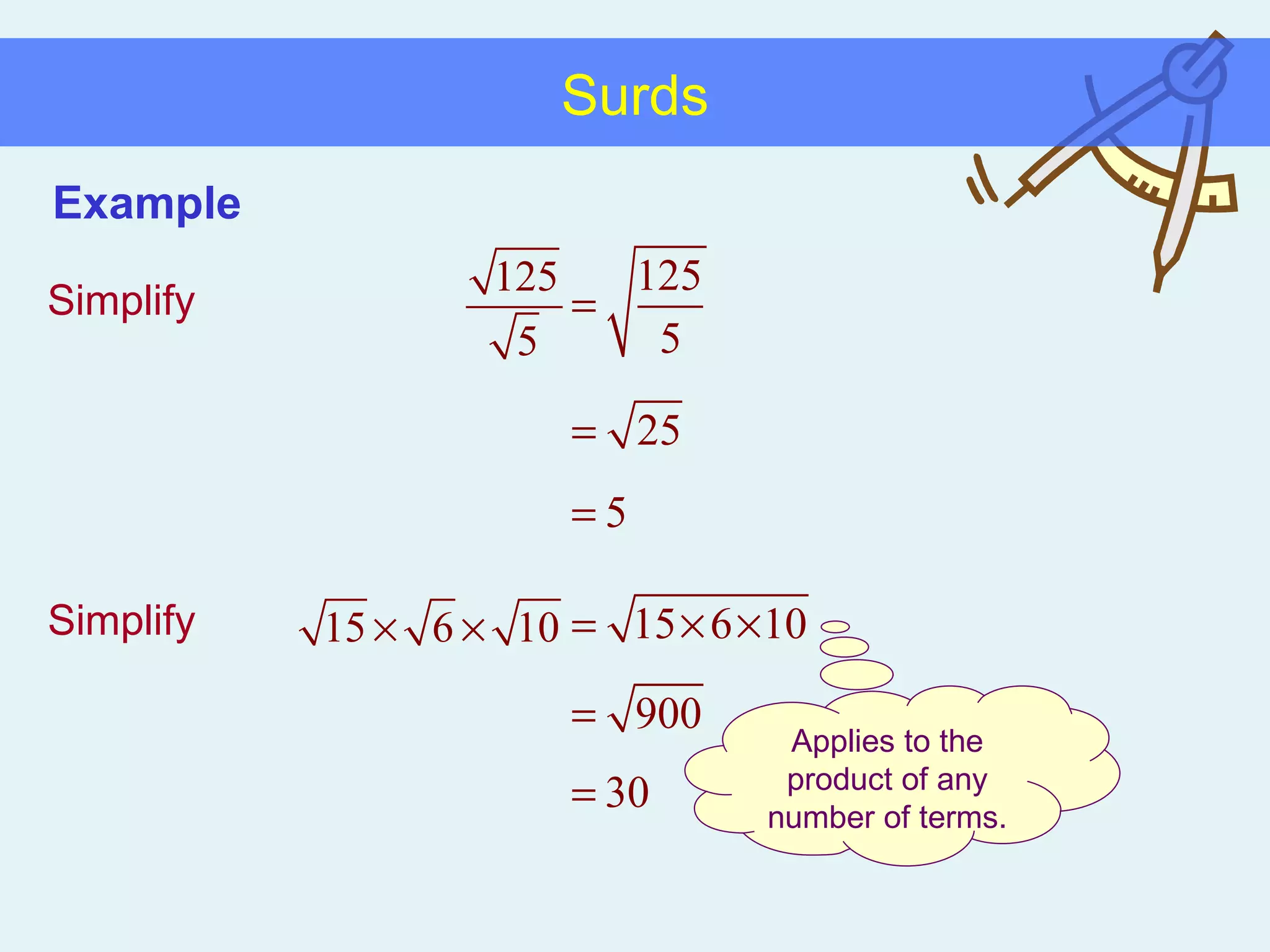
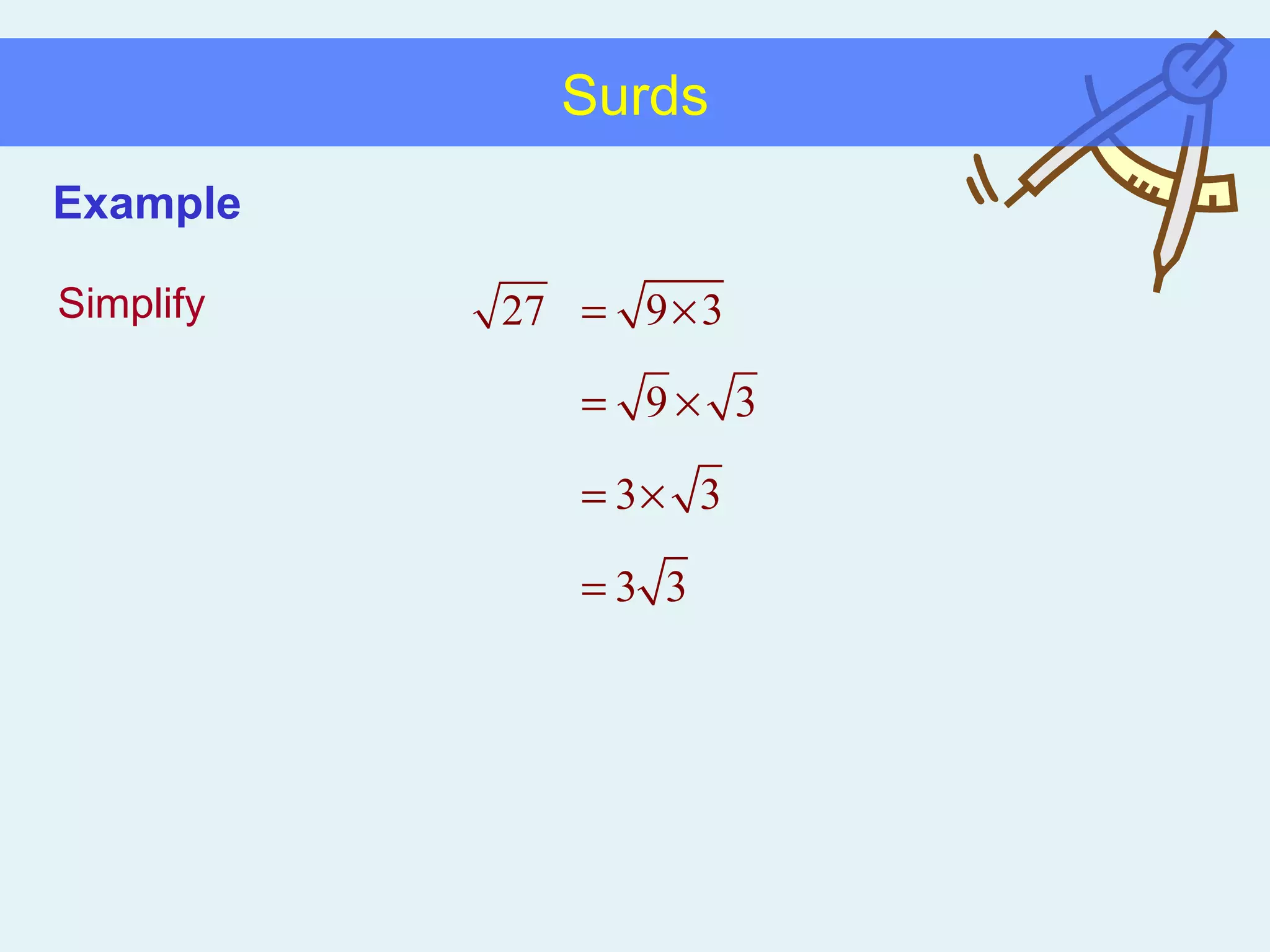
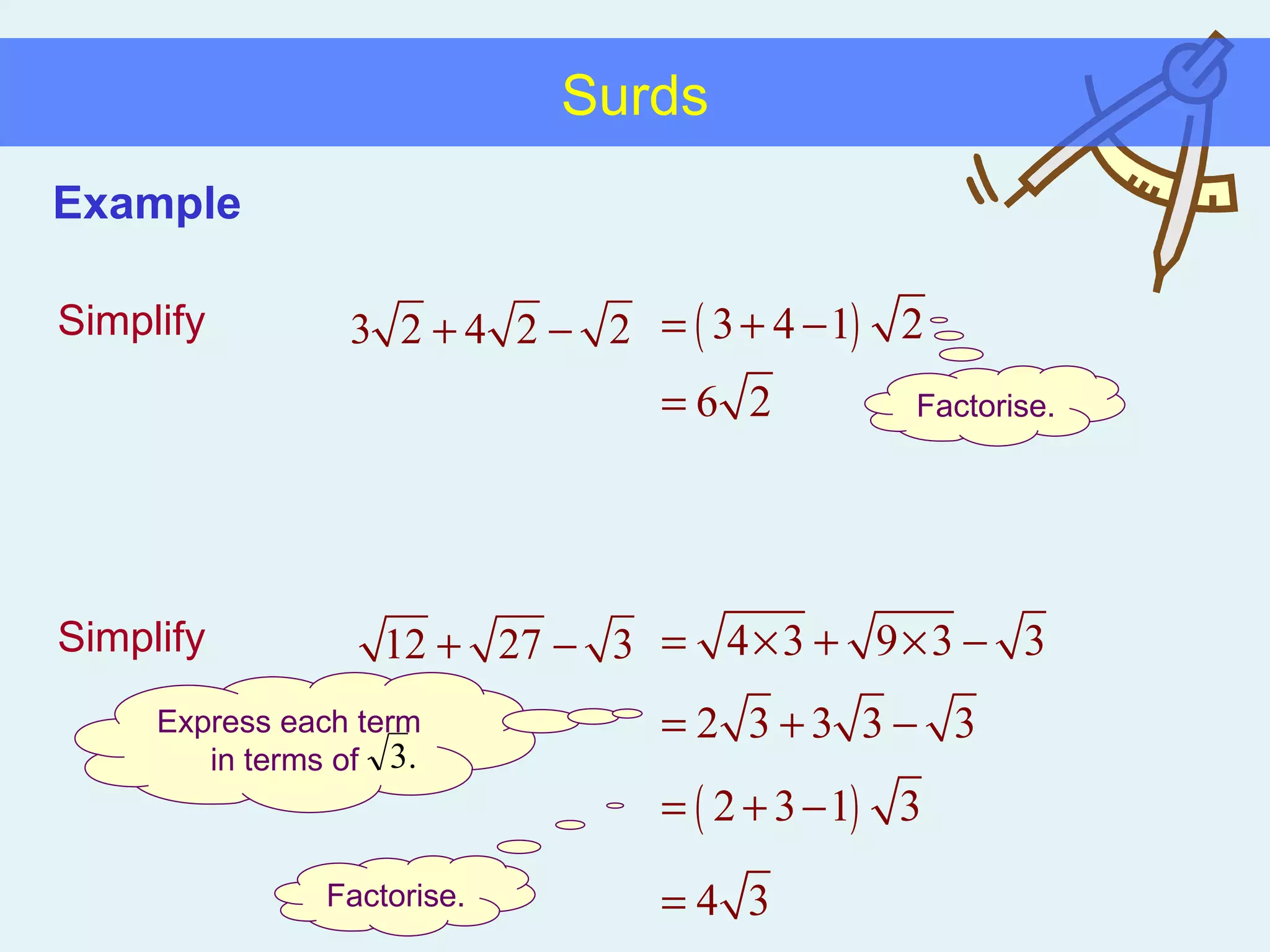
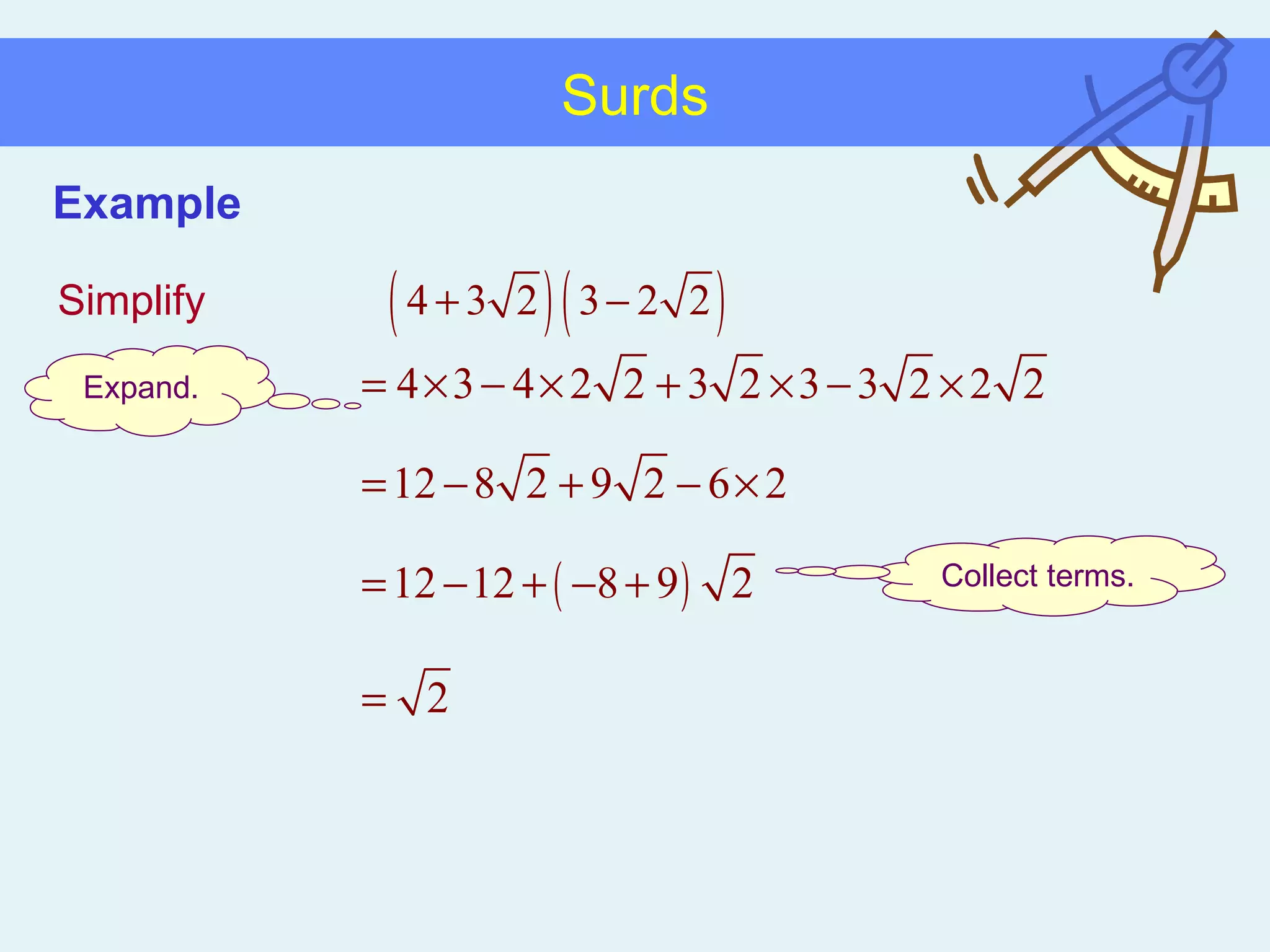
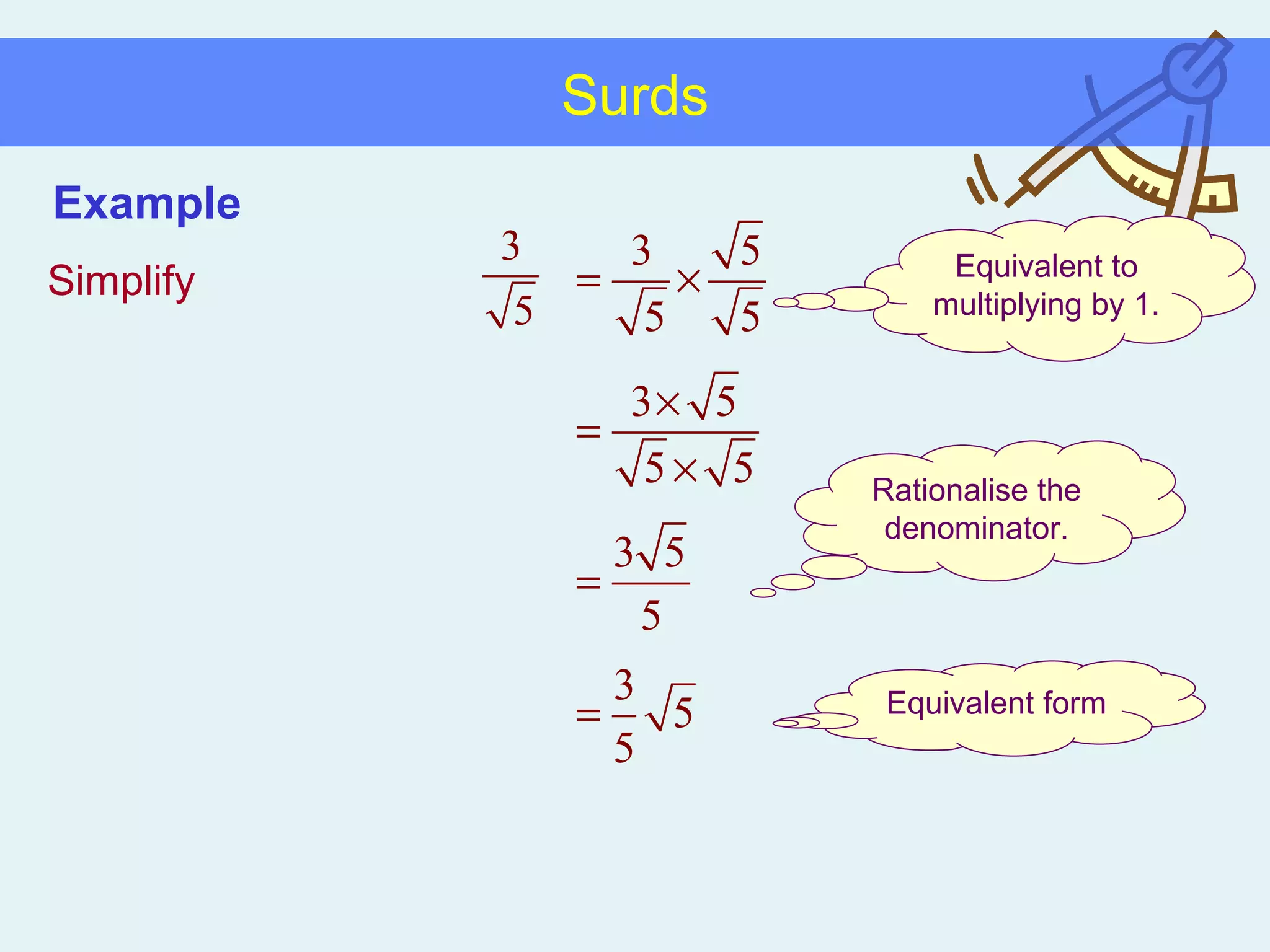
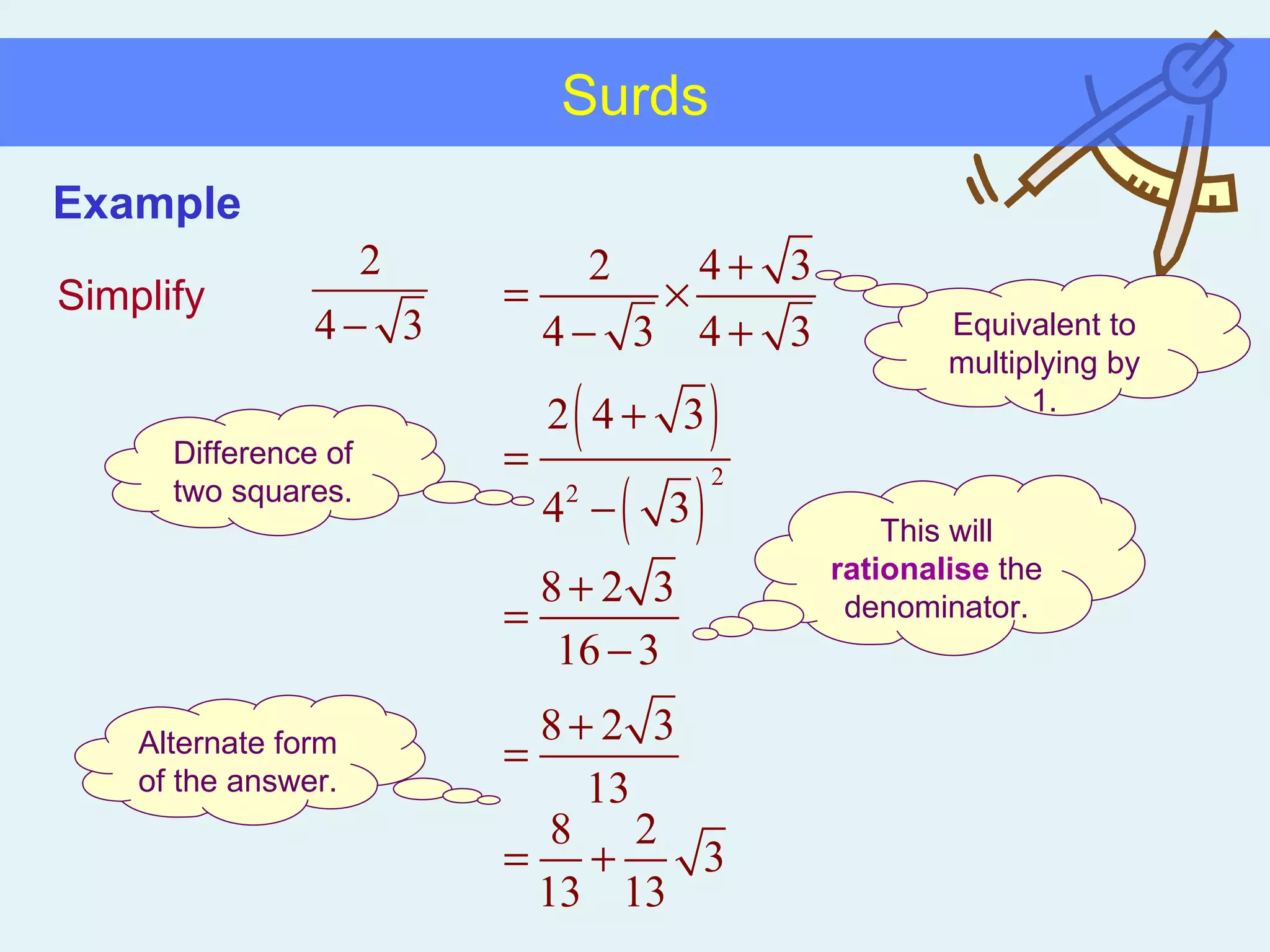
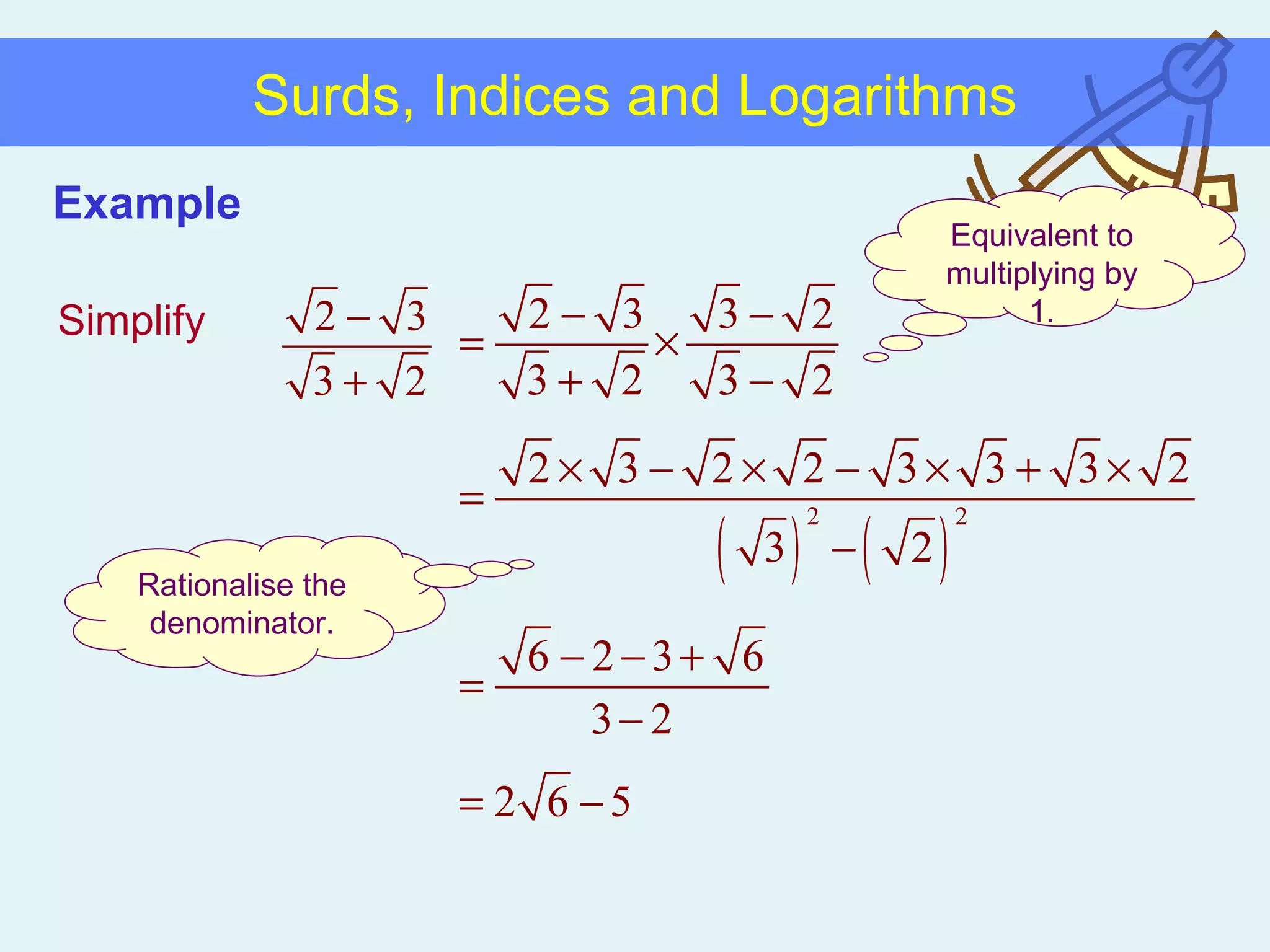
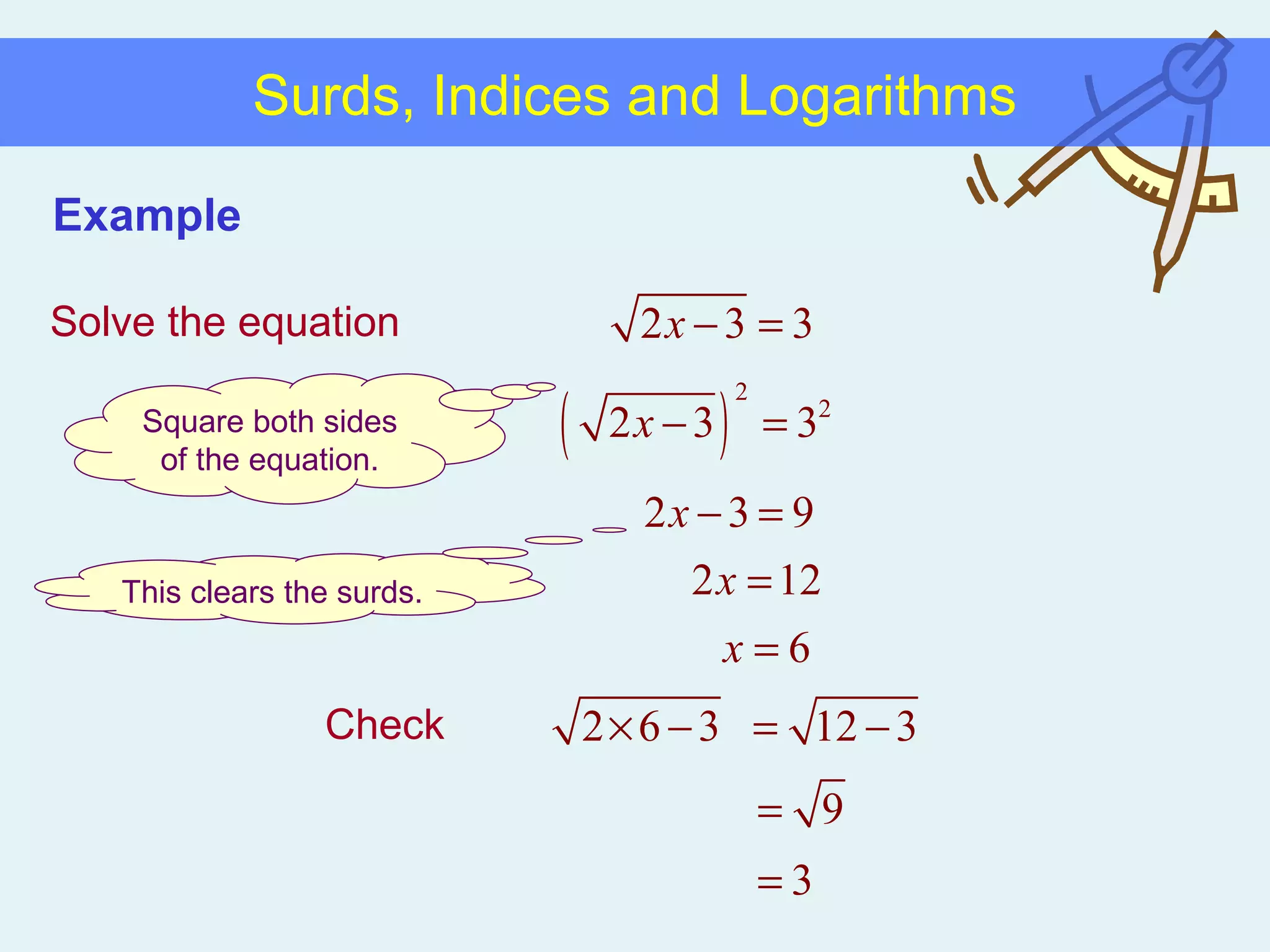
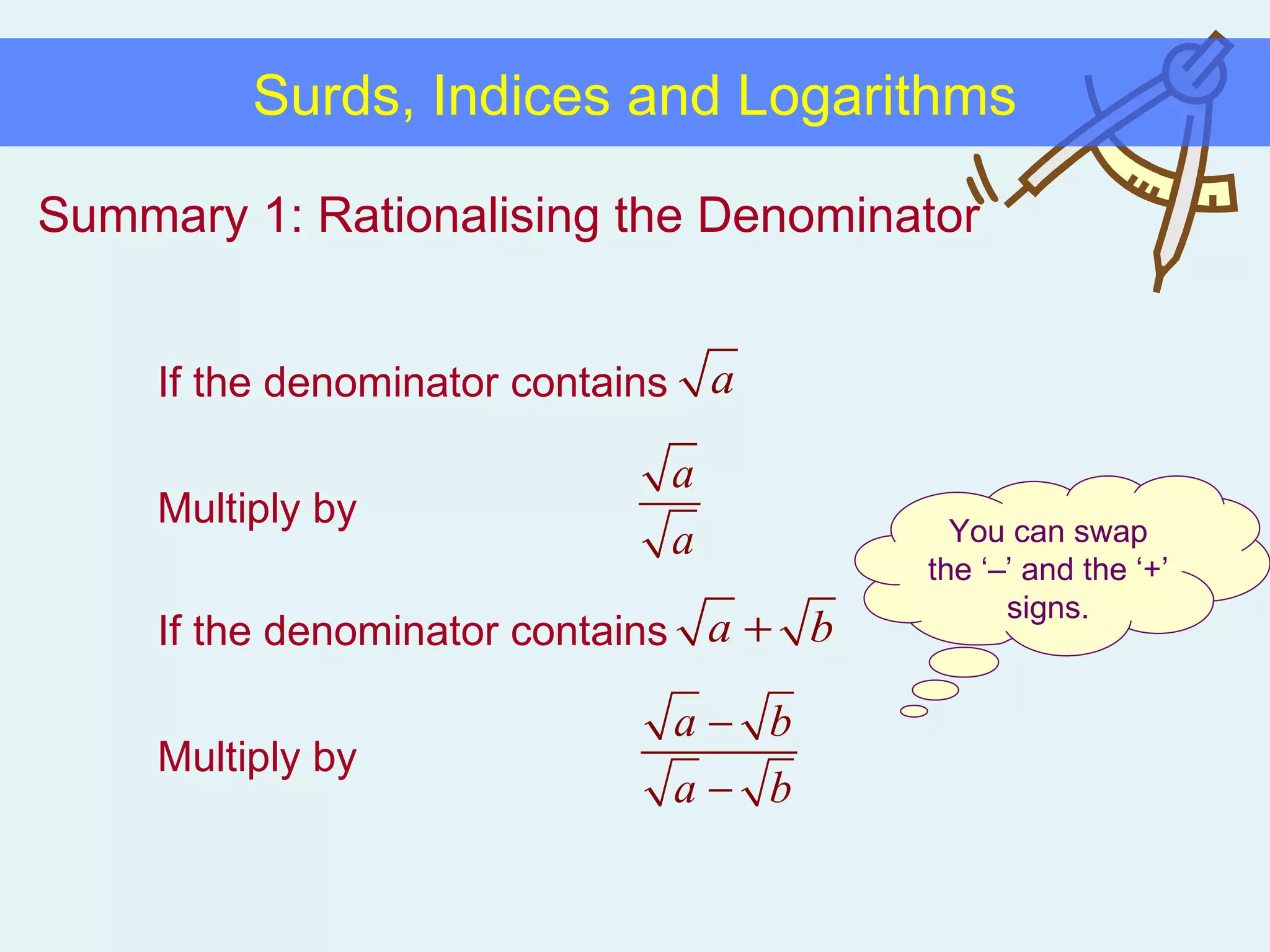
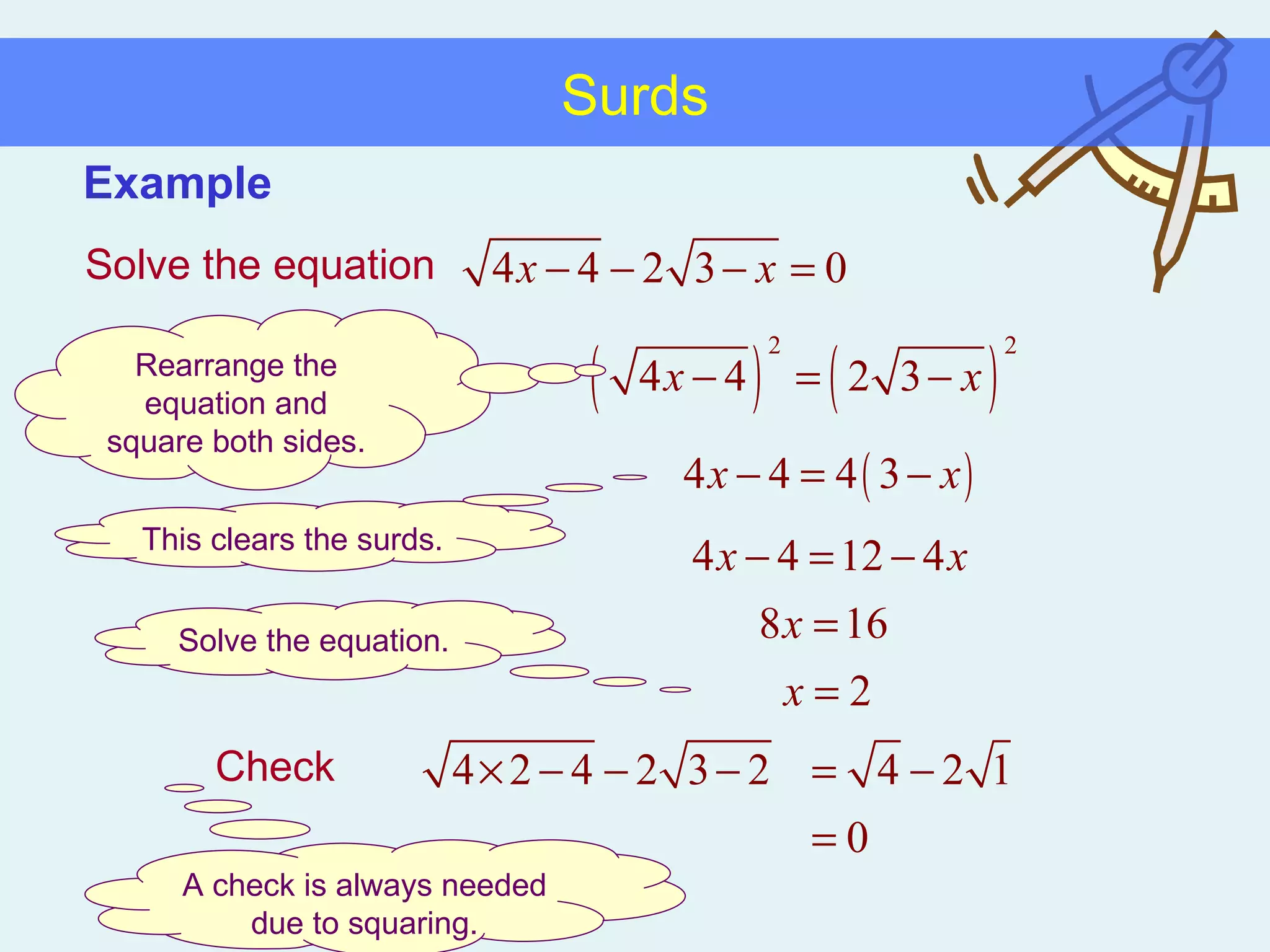
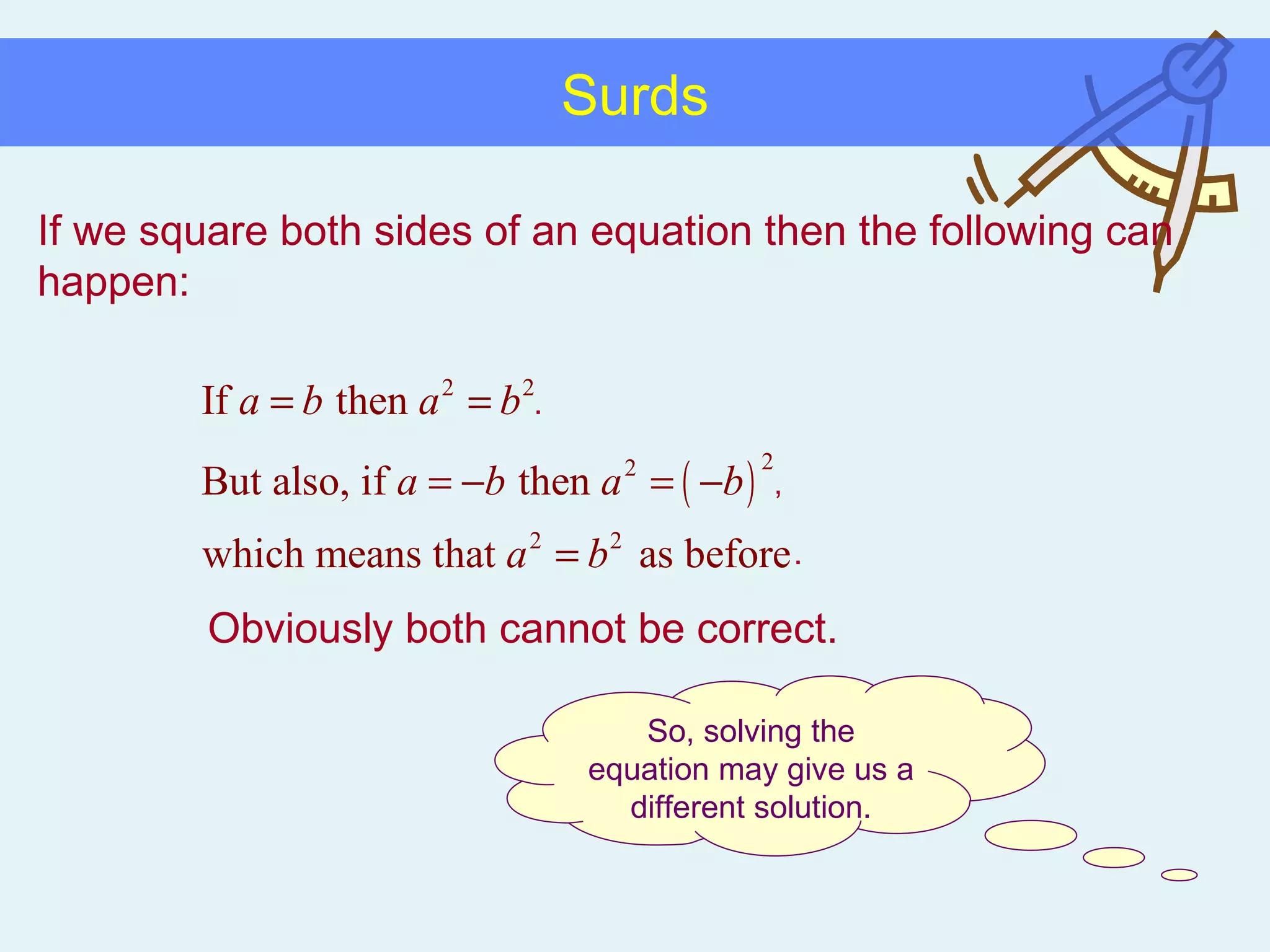
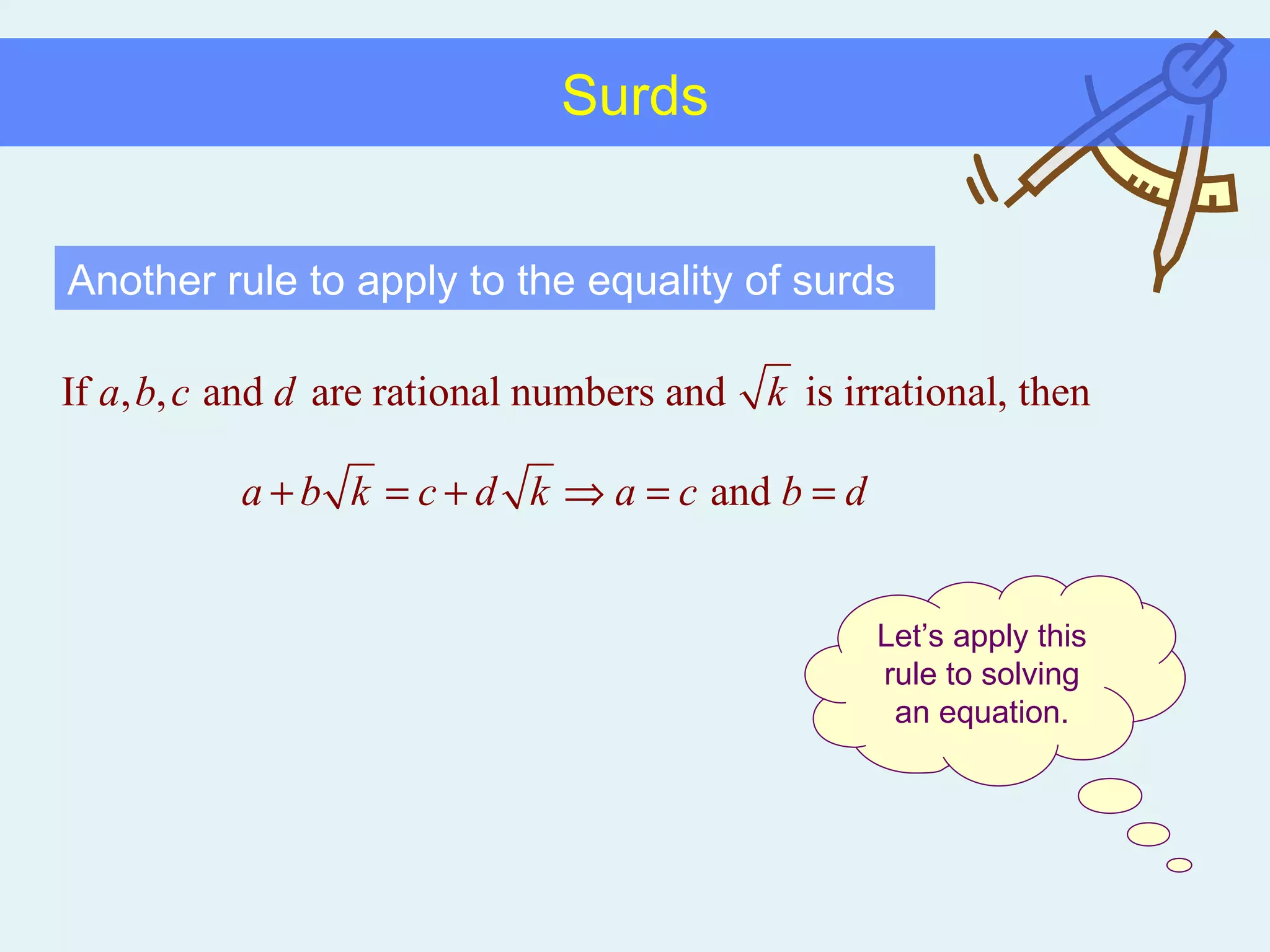
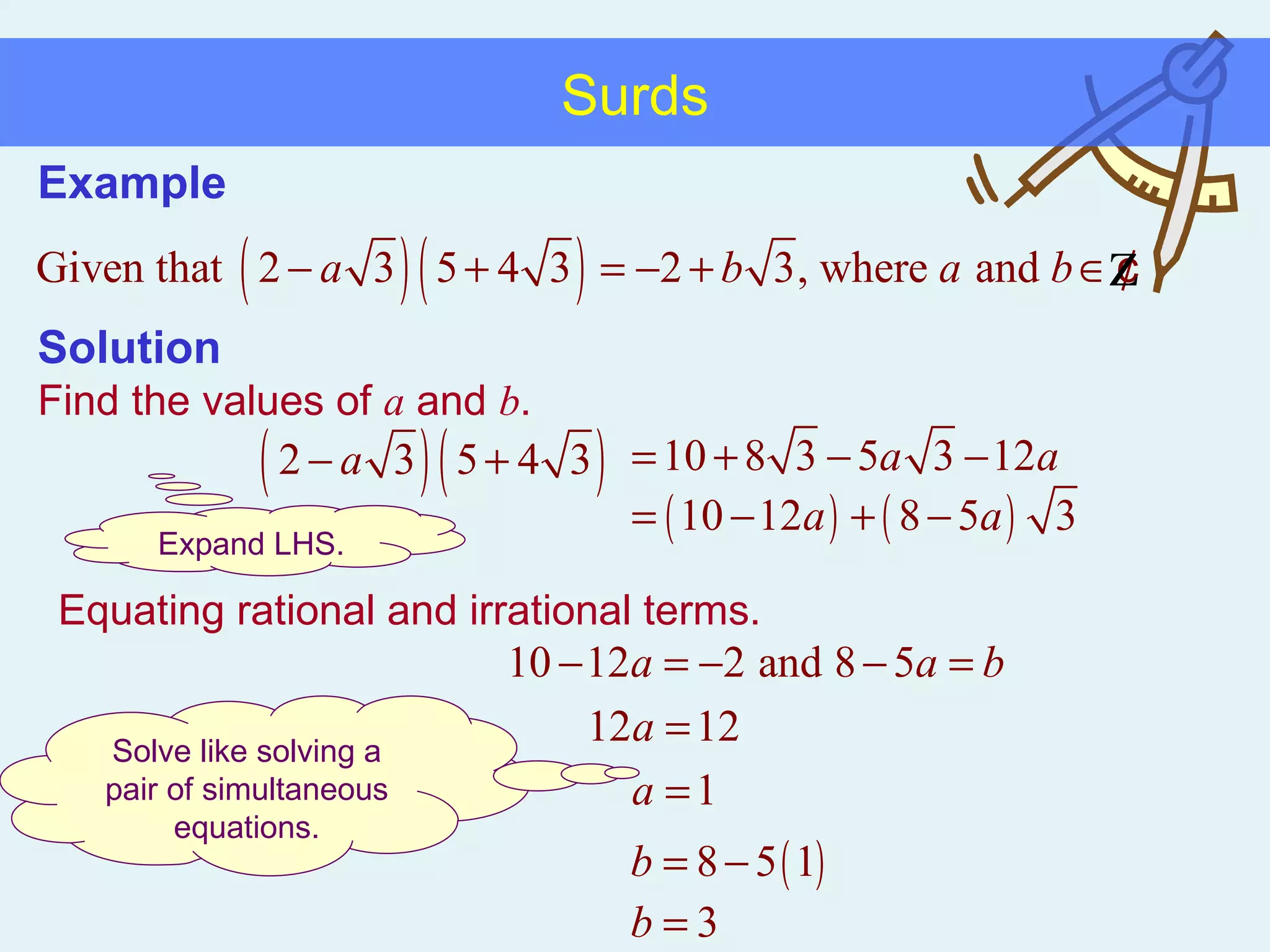
This document discusses working with surds, which are expressions involving square roots. It provides rules for multiplying, dividing, adding, subtracting, and simplifying surds. Some key rules covered are combining like terms under a square root, rationalizing denominators by multiplying the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator, and squaring both sides of an equation to clear surds before solving. Examples are provided to demonstrate applying these rules to simplify expressions and solve equations involving surds.