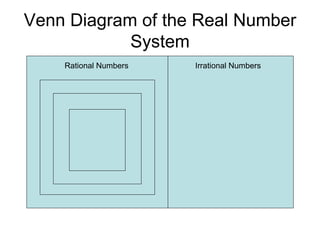
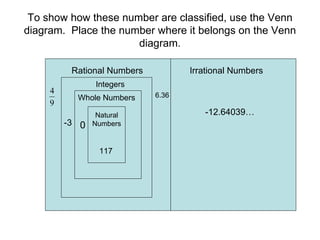
The document discusses the real number system and its subsets. It defines natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, terminating decimals, and repeating decimals. Rational numbers can be expressed as fractions, while irrational numbers are non-terminating and non-repeating decimals. The real number system is represented by a Venn diagram showing the relationships between its subsets. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to classify numbers as rational or irrational.