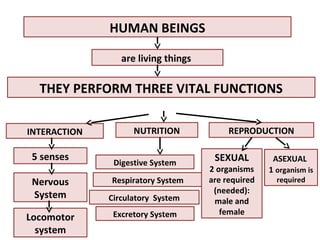
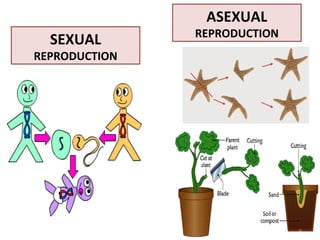
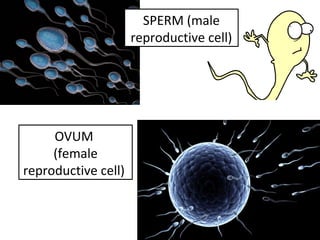
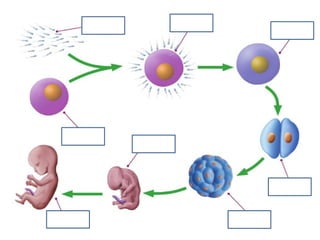
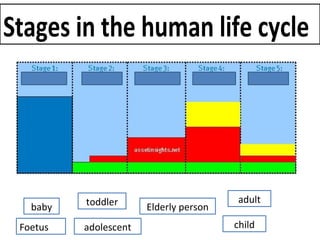
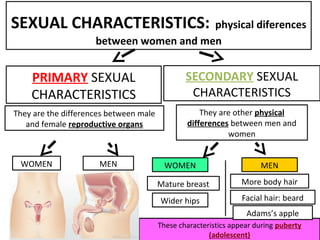
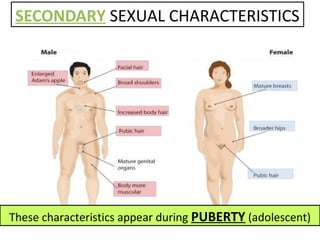
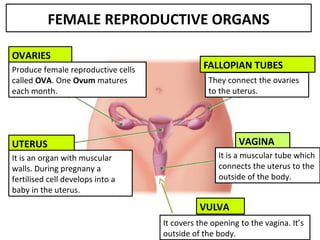
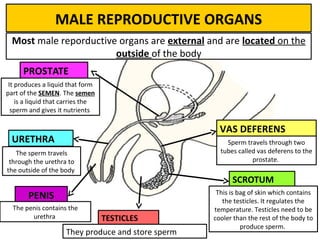
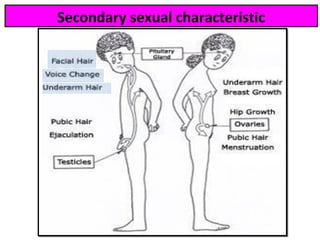
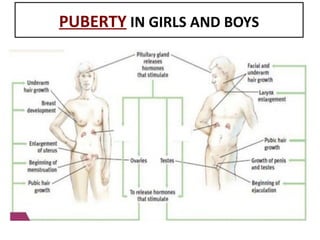
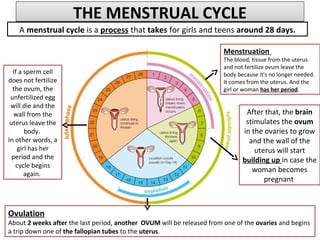
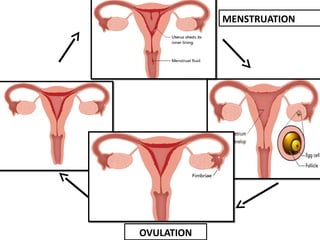
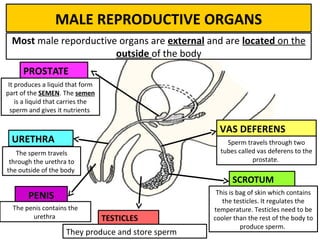
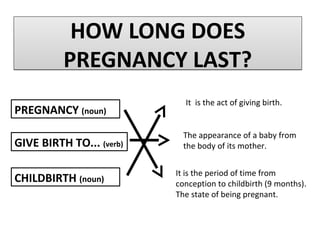
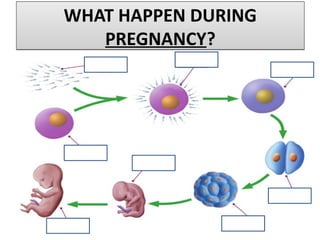
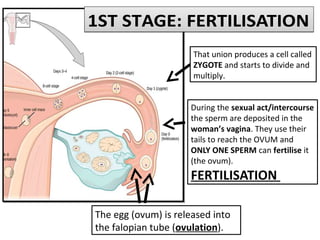
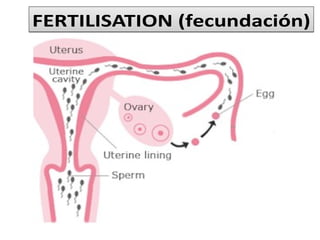
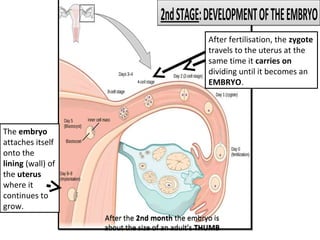
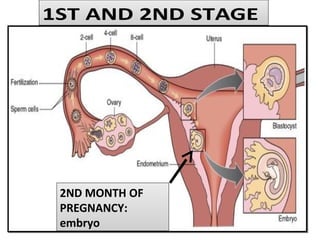
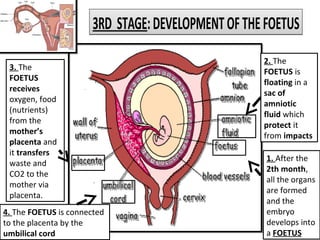
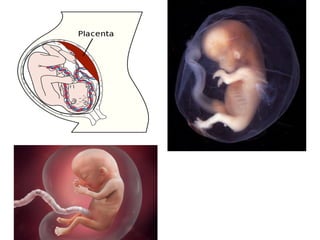
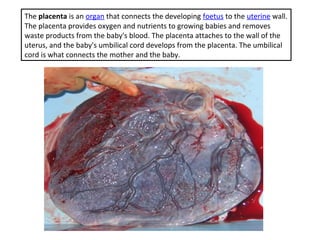
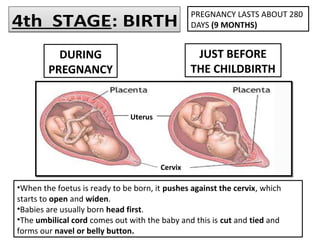
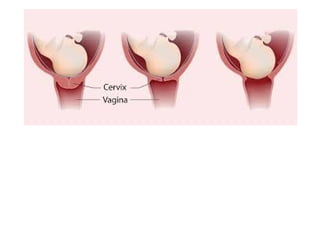
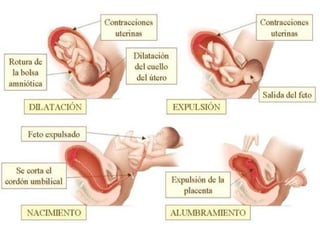
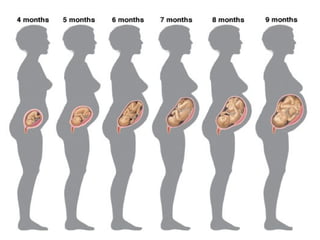
Human beings reproduce sexually, requiring both a male and female. The document outlines the process of human reproduction from fertilization through birth. It describes how sperm and eggs are produced, how they unite during sexual intercourse to form a zygote, and the development stages of the embryo and fetus as it grows over nine months in the uterus until birth. The male and female reproductive systems and changes during puberty are also explained.