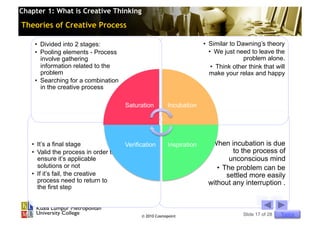
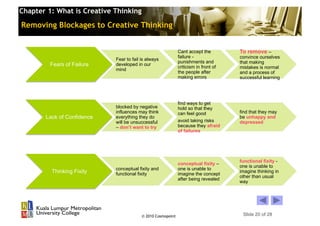
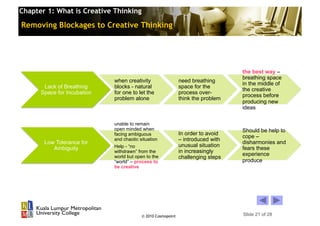
This chapter discusses creative thinking. It defines creative thinking as an ability to imagine new ideas, an attitude of openness, and a process of refinement. The chapter outlines theories of the creative process and characteristics of creative thinking like originality and flexibility. It also discusses myths about creativity and provides strategies for enhancing creative thinking in students, such as removing blockages like fear of failure and lack of confidence. The overall aim is to understand what creative thinking is and how to improve one's creative abilities.