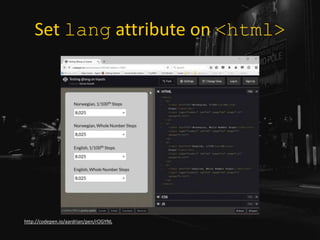
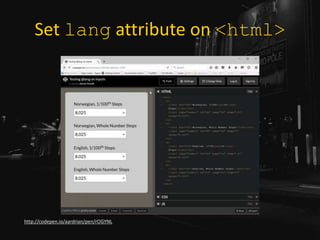
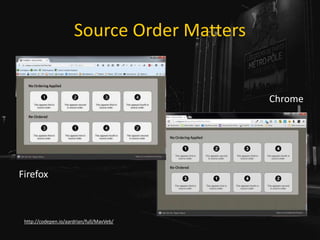
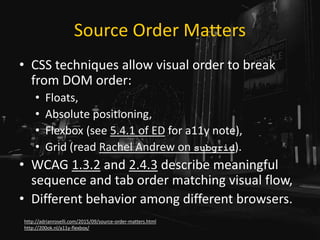
The document is a presentation by Adrian Roselli at WordCamp Europe 2017 focusing on web accessibility (a11y) and emphasizing the importance of incorporating accessibility features in web development. It provides statistics about disabilities, user experience models, and technical tips for enhancing web accessibility, such as proper use of alt text, color contrast, and user stories. The presentation encourages developers to absorb these practices not only for ethical reasons but as a pragmatic necessity in modern web design.










































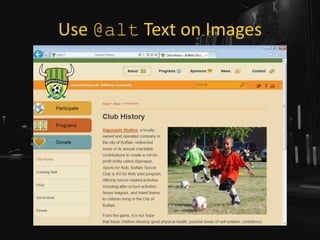
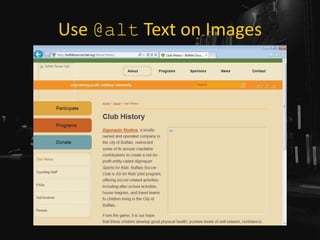


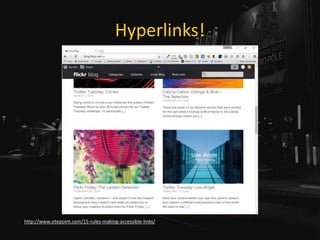


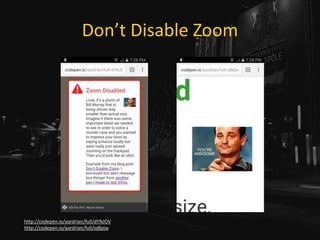
![Use Link Underlines
• You are not Google:
• Users know Google’s layout,
• Users probably don’t visit your site daily.
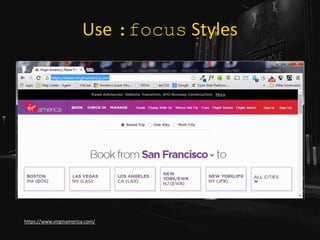
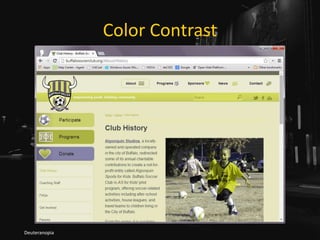
• Relying on color alone will not suffice (WCAG
1.4.1 [A], 1.4.3 [AA]),
• Necessary contrast values:
• 4.5:1 between text and its background for copy,
• 3:1 between text and its background for larger text,
• 3:1 between surrounding text and a hyperlink, plus an
additional visual cue (G183).
http://adrianroselli.com/2014/03/i-dont-care-what-google-did-just-keep.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selfishaccessibility-wordcampeurope-170617080827/85/Selfish-Accessibility-WordCamp-Europe-2017-55-320.jpg)

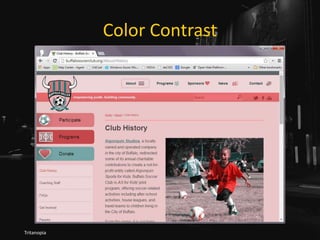
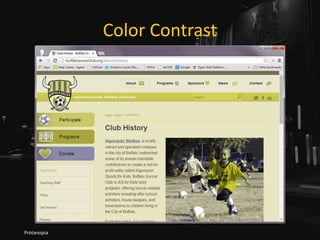










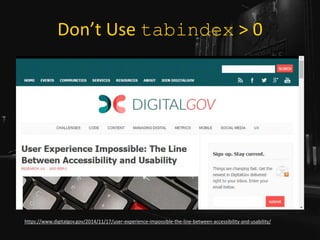

![Maybe Use tabindex=0
• Do you have scrolling content boxes?
• Keyboard users cannot access it.
• Do you have content that displays on hover?
• Keyboard users probably cannot access it.
• A technique:
• <div role="region" aria-label="[if
appropriate]" tabindex="0">
http://adrianroselli.com/2016/02/keyboard-and-overflow.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selfishaccessibility-wordcampeurope-170617080827/85/Selfish-Accessibility-WordCamp-Europe-2017-76-320.jpg)