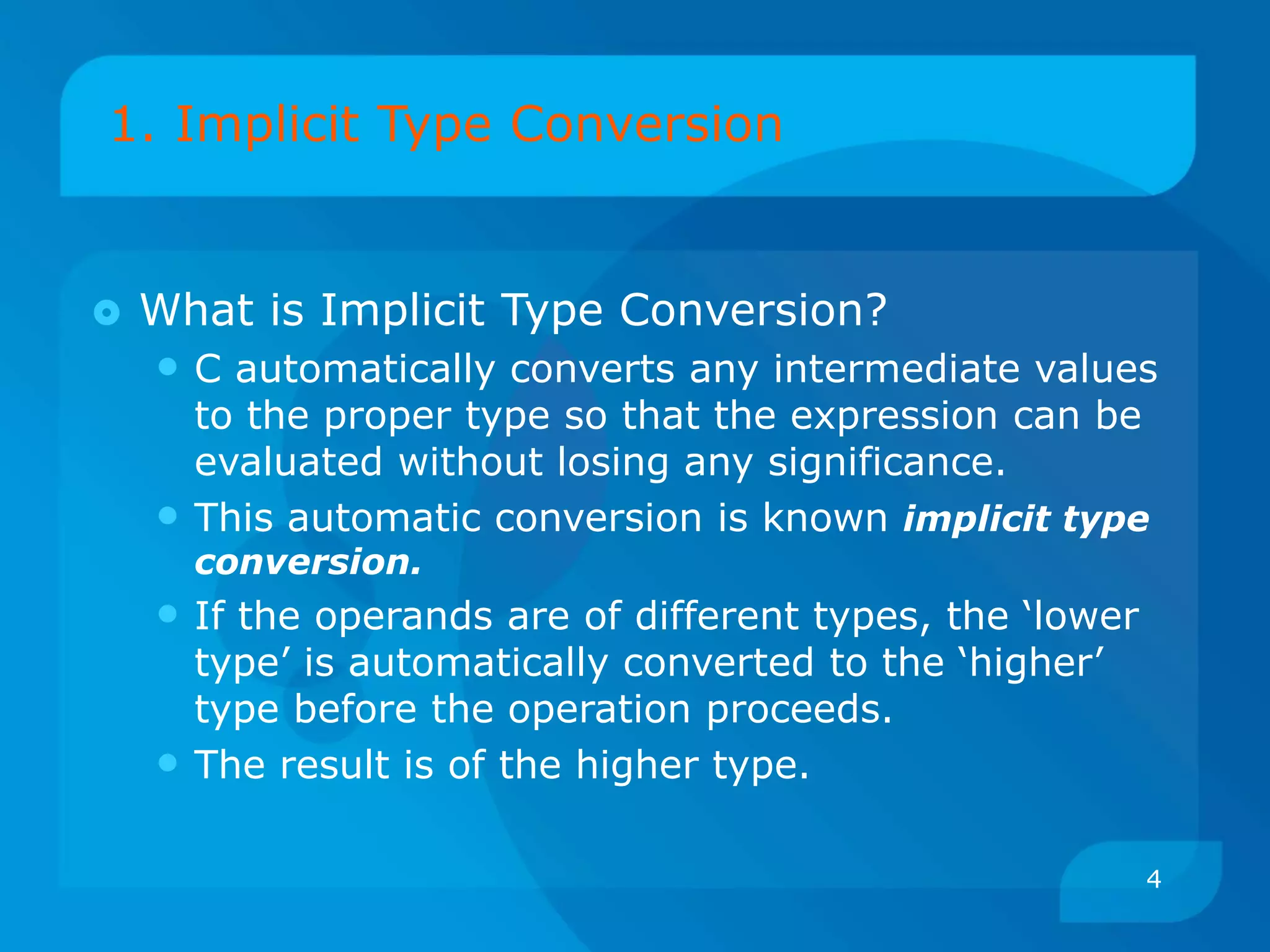
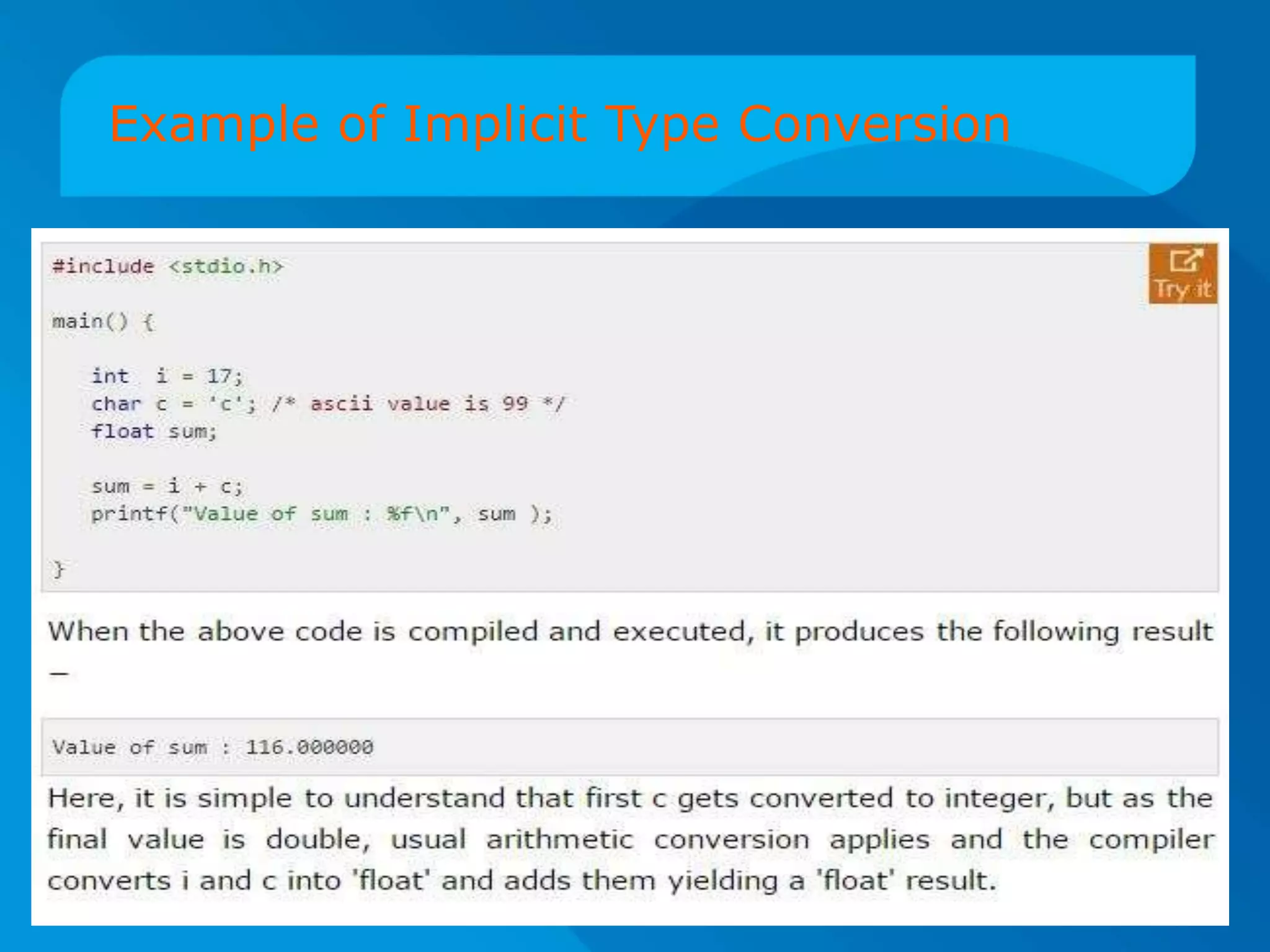
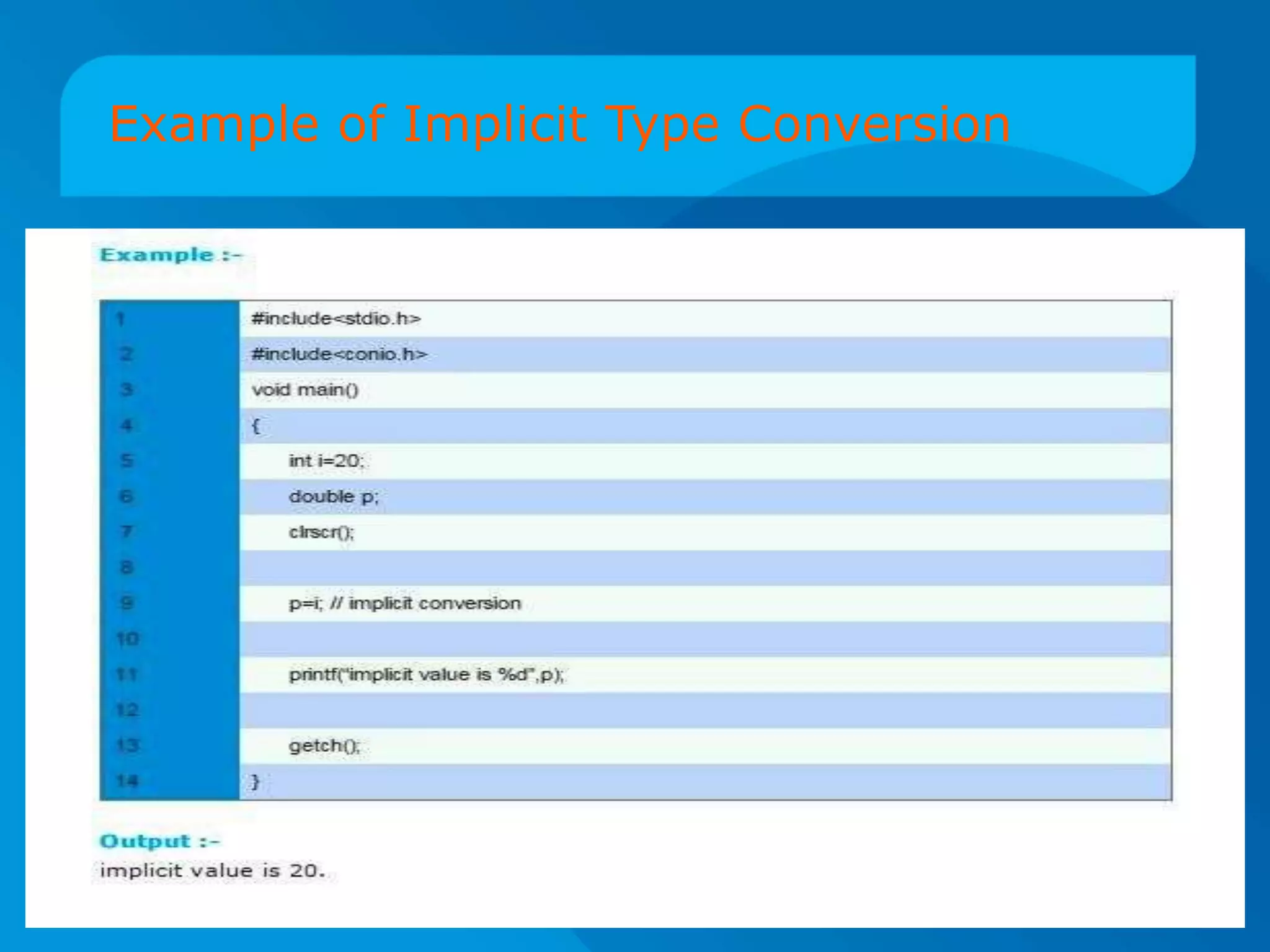
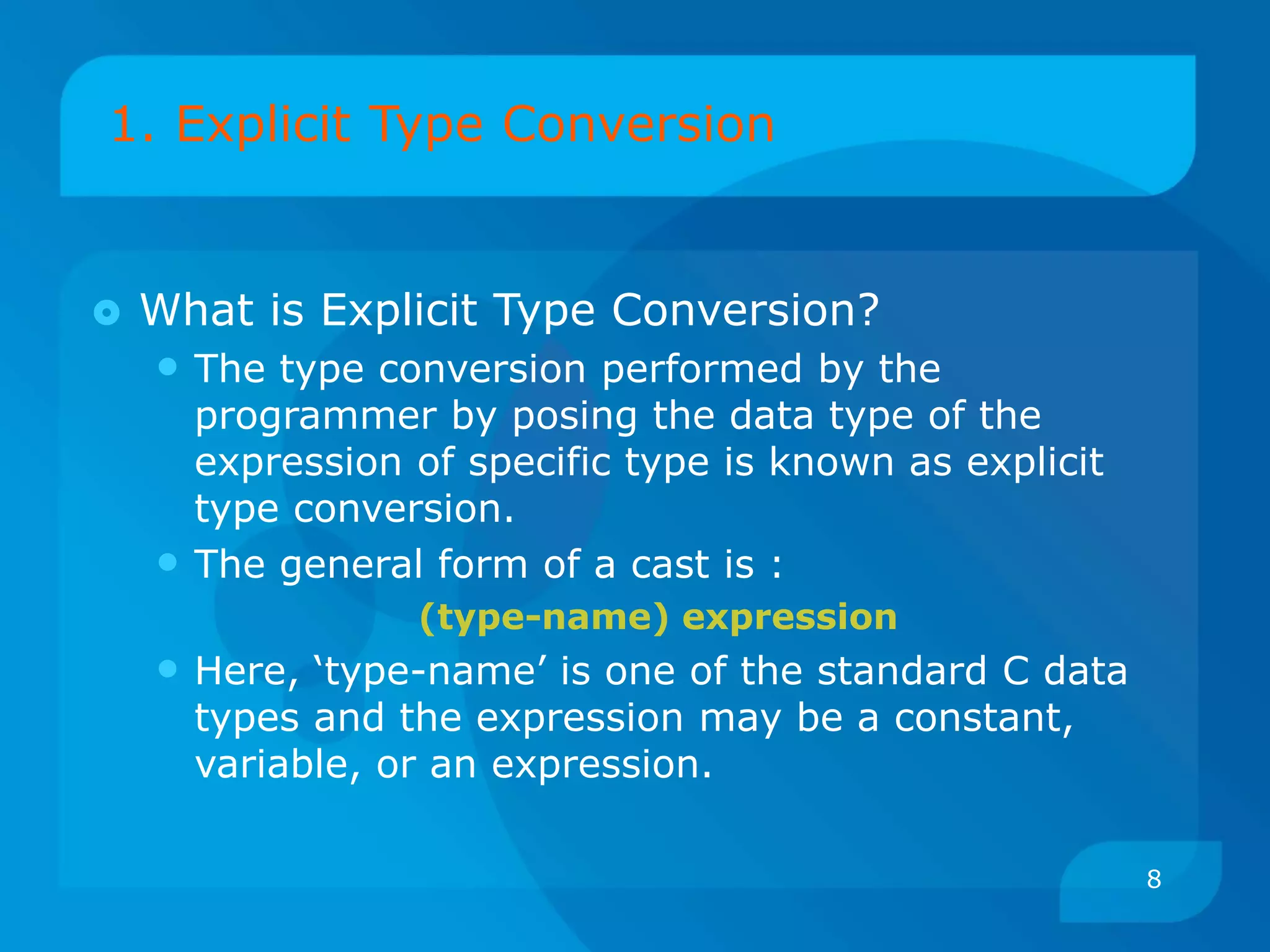
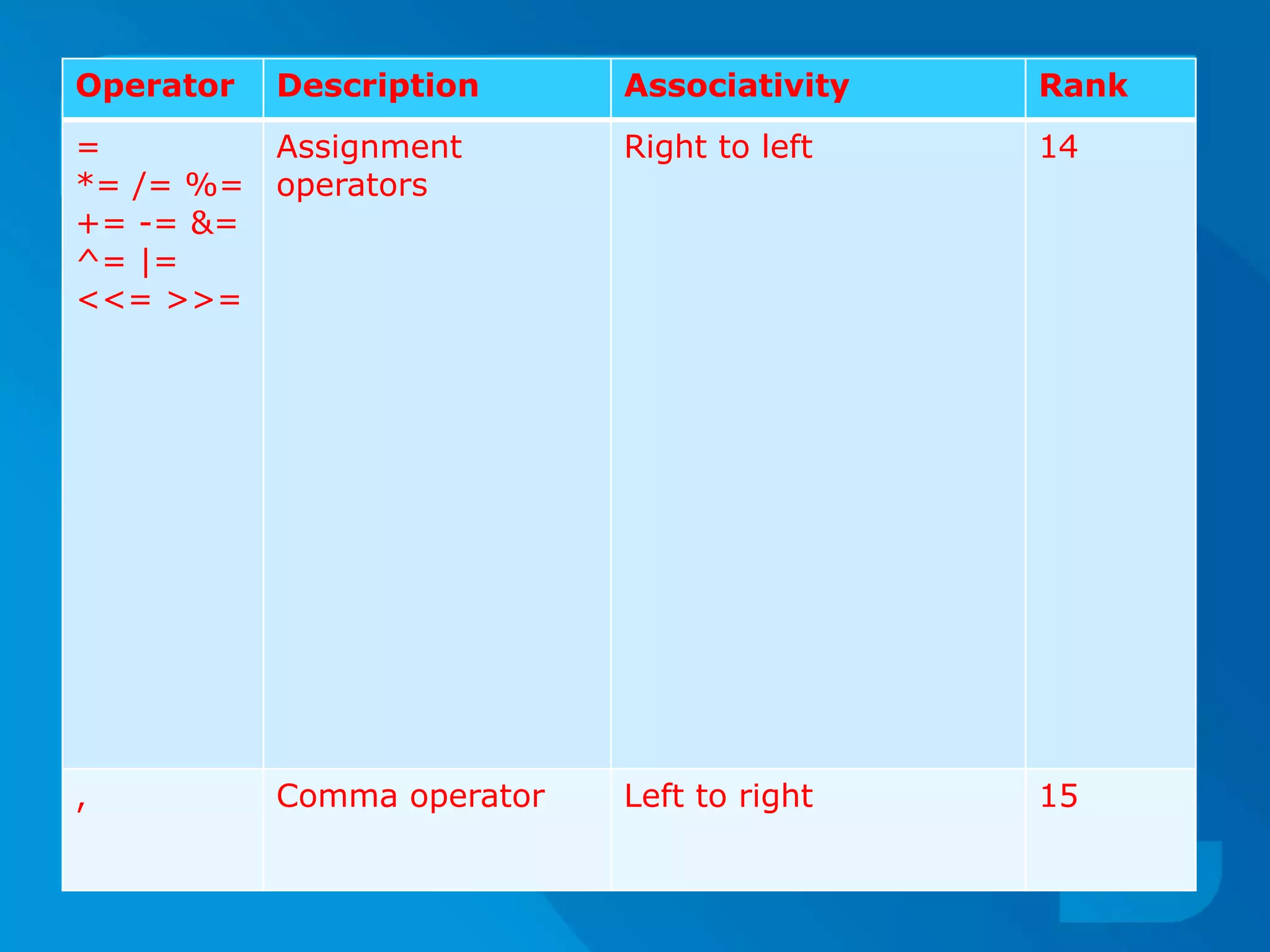
The document discusses type conversion in C programming, covering both implicit and explicit type conversions. It explains how C automatically converts types during operations and demonstrates explicit type casting by the programmer. Additionally, it details operator precedence and associativity rules that dictate the order of operations in expressions.






![14
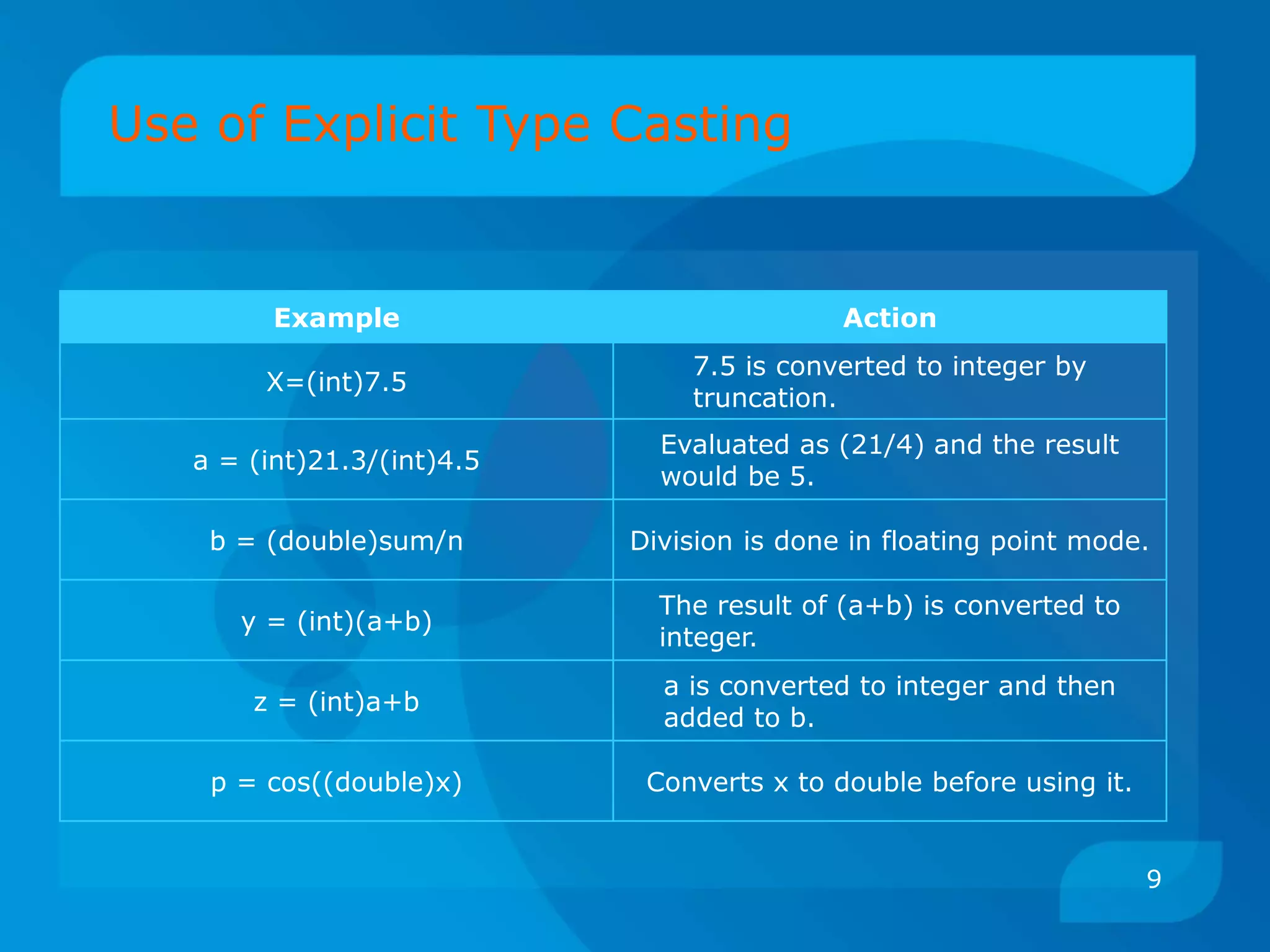
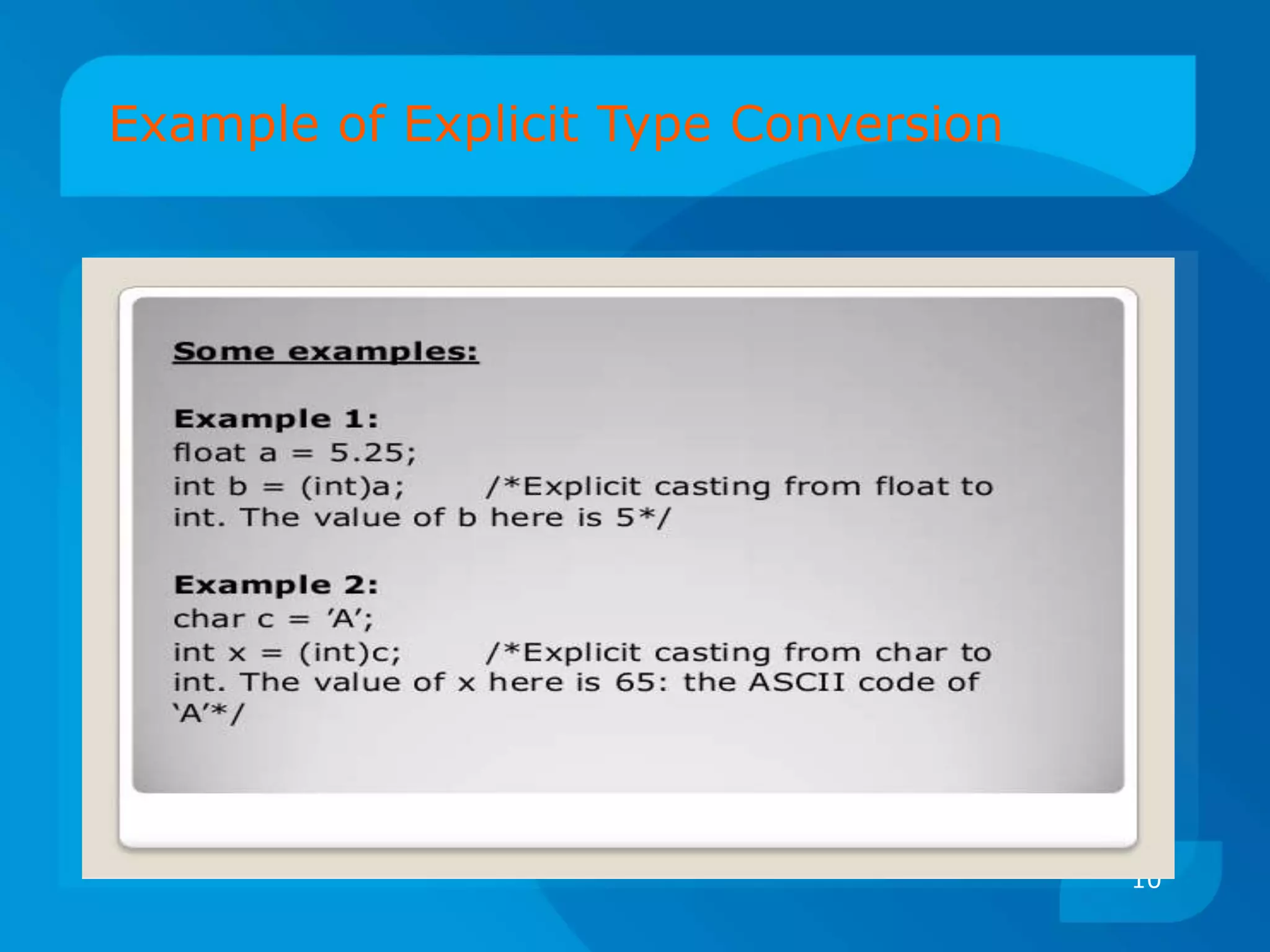
Operator Description Associativity Rank
()
[]
Function call
Array element
reference
Left to right 1
+
-
++
--
!
~
*
&
sizeof
(type)
Unary plus
Unary minus
Increment
Decrement
Logical Negation
Ones complement
Pointer reference
Address
Size of an object
Type cast
Right to left 2
*
/
%
Multiplication
Division
Modulus
Left to right 3
+
-
Addition
Subtraction
Left to right 4
<<
>>
Left shift
Right shift
Left to right 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cpuseminar-151116115630-lva1-app6892/75/Type-Conversion-Precedence-and-Associativity-14-2048.jpg)
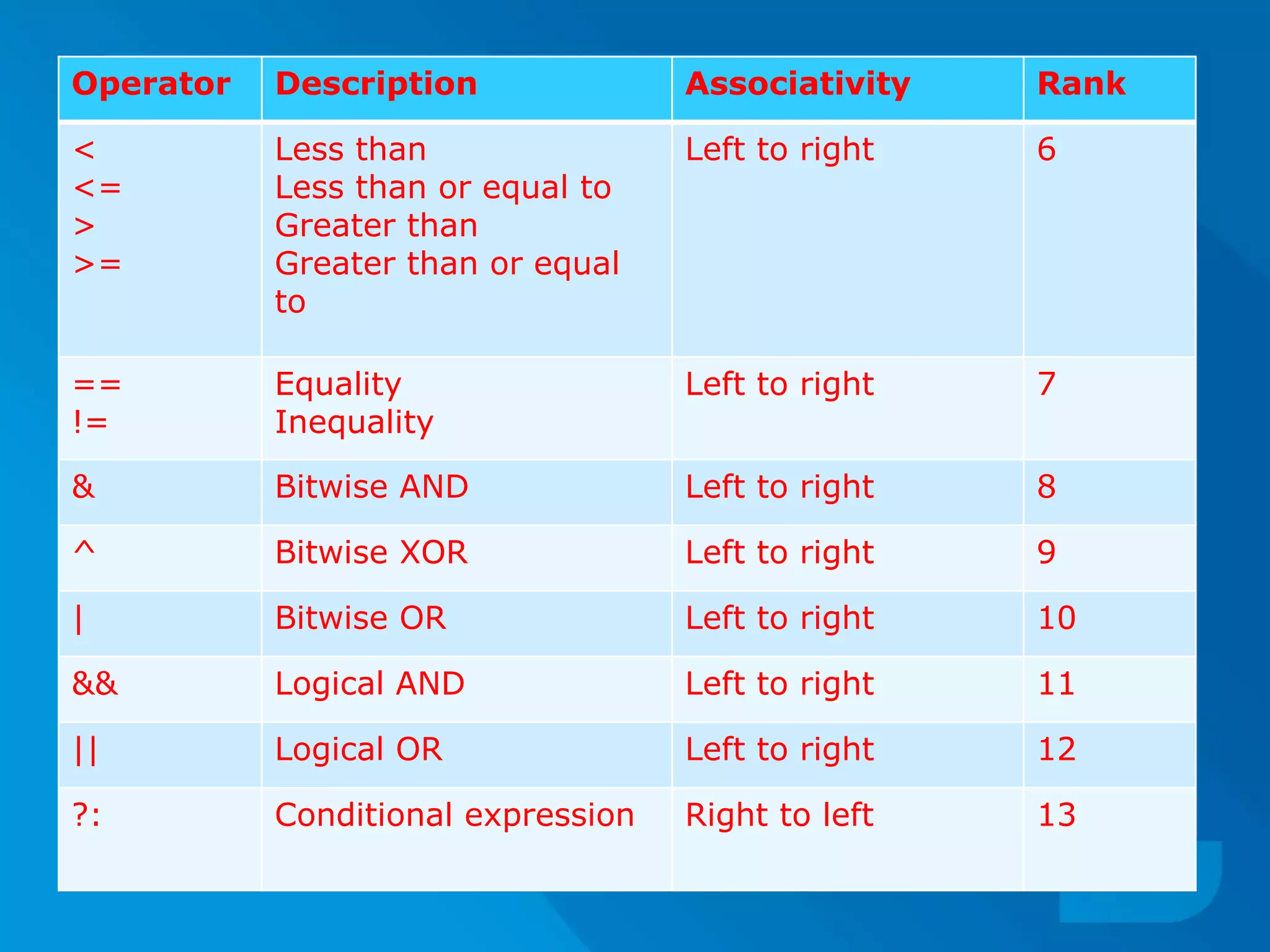
![Summary of operator precedence
17
‘Comma’ operator has lowest precedence.
‘Unary Operators’ are operators having highest
precedence.
Operators sharing common block in the above
table have equal priority or precedence.
While solving expression, equal priority operators
are handled on the basis of FIFO [First in First Out]
i.e., Operator Coming First is handled First.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cpuseminar-151116115630-lva1-app6892/75/Type-Conversion-Precedence-and-Associativity-17-2048.jpg)


