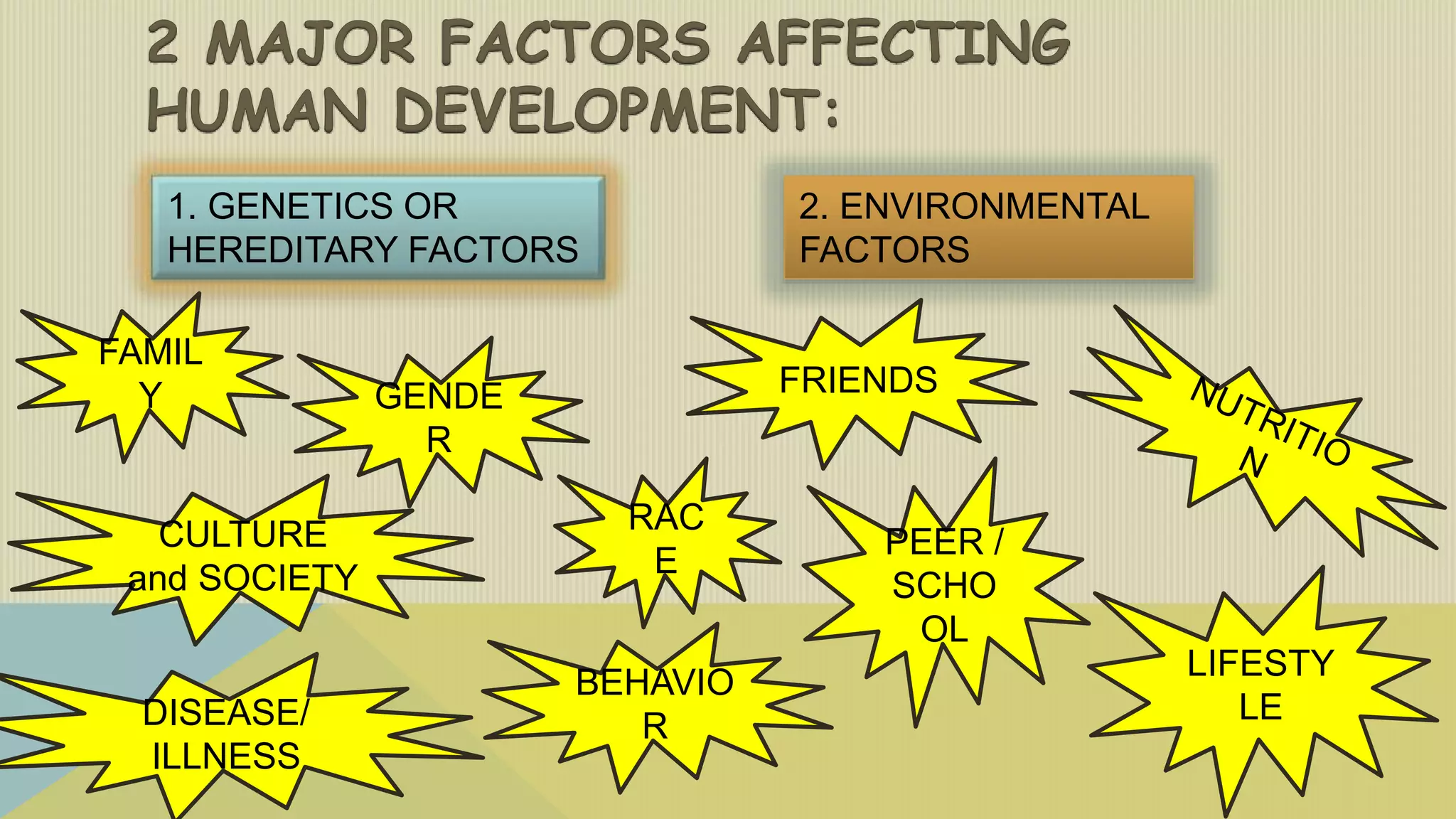
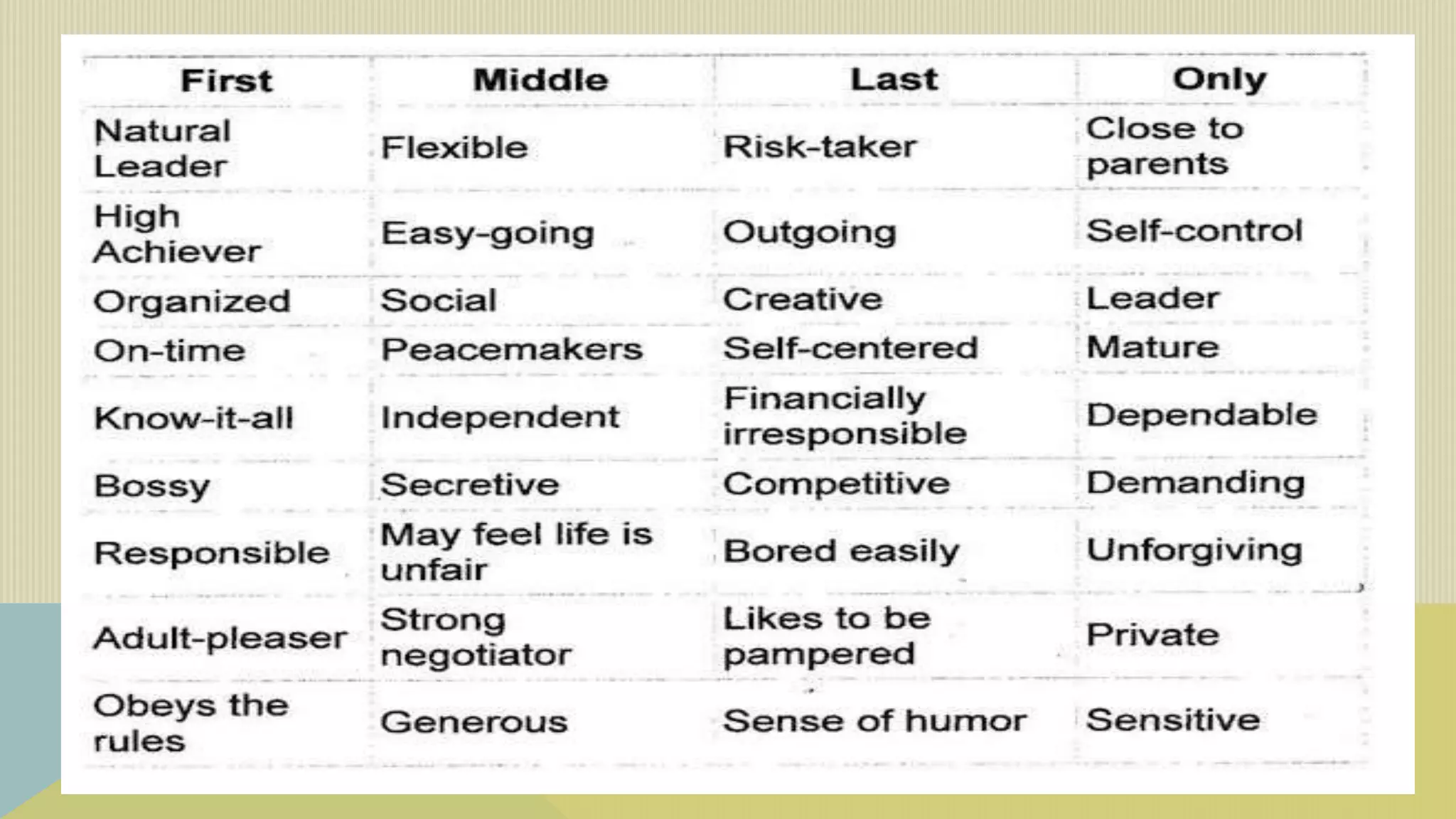
Growth and development depends on both genetic and environmental factors. Genetics influence characteristics like appearance and susceptibility to diseases, while the prenatal environment, family/culture, school, peer groups, nutrition, climate, and trauma can also impact development. Both nature and nurture work together to shape human growth.