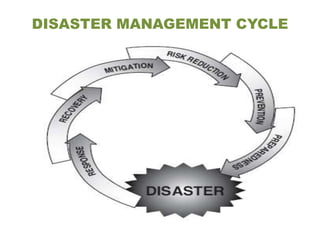
The document discusses various types of disasters including natural disasters like floods, cyclones, earthquakes, landslides and man-made disasters. It describes the disaster management cycle which involves disaster preparedness, disaster response, disaster relief and disaster recovery. Key aspects of disaster management include disaster warning systems, mapping of vulnerable areas, and mitigation measures to reduce damage from disasters like enforcing land use controls and building disaster resilient infrastructure.