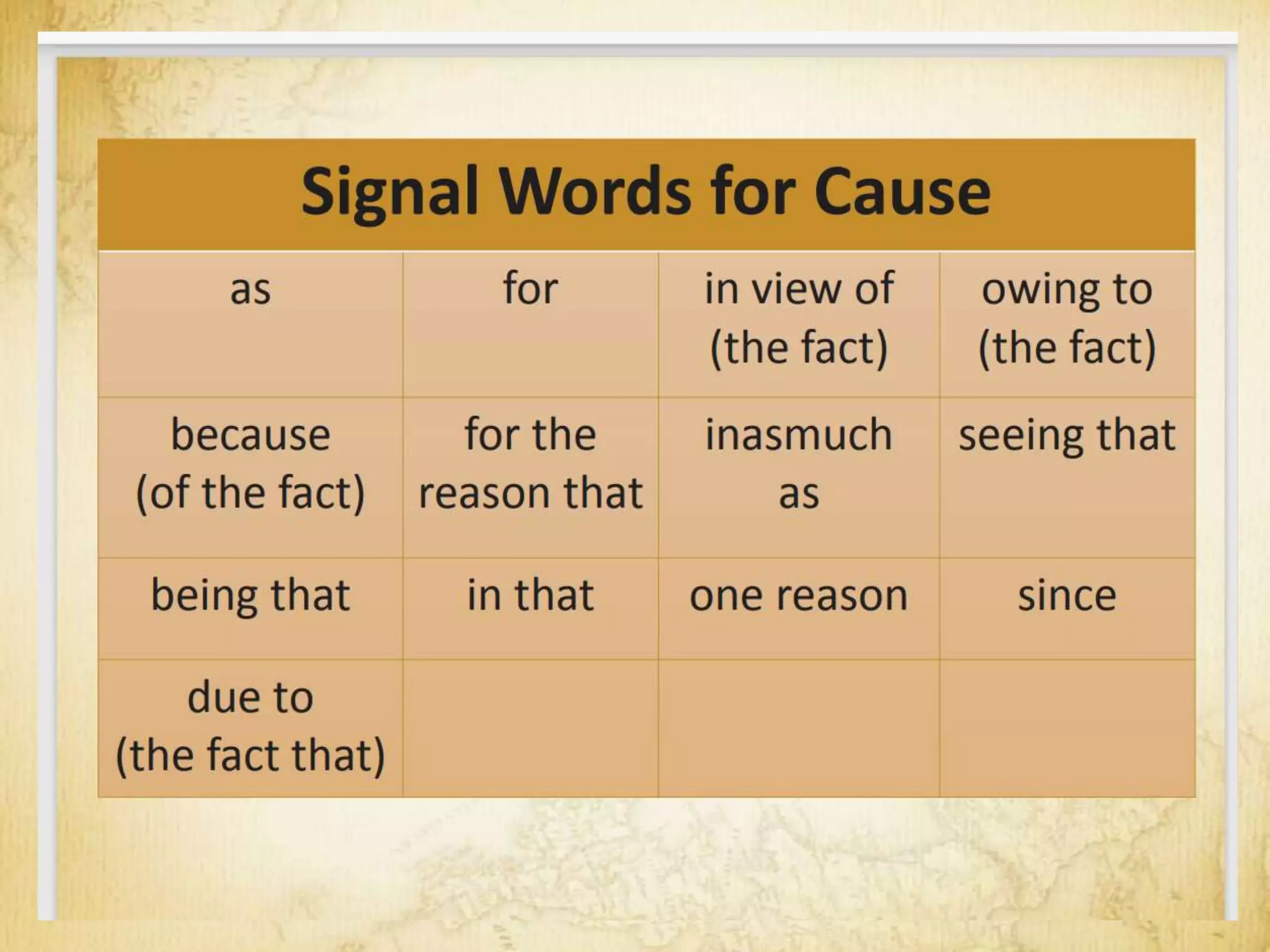
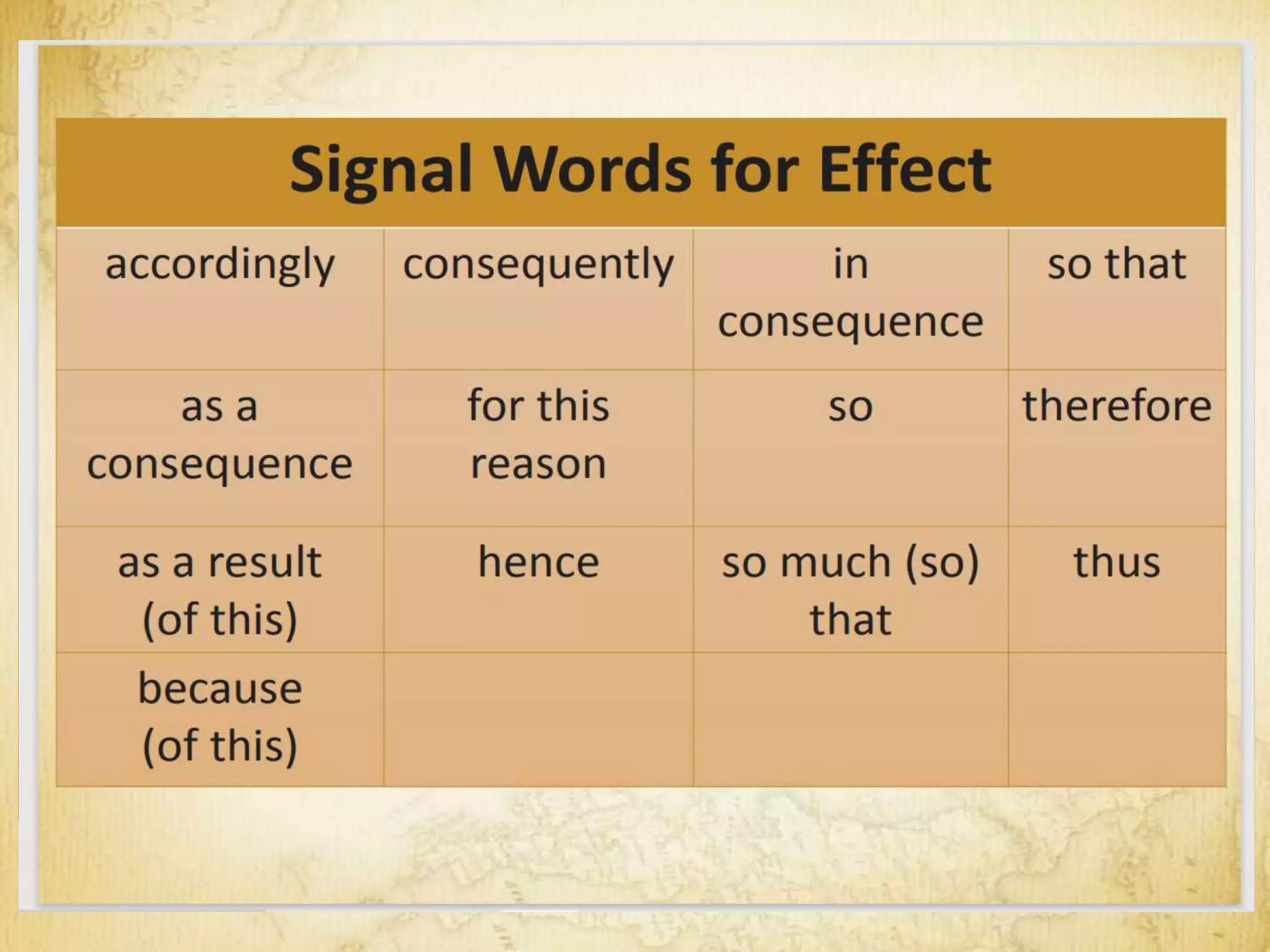
The document outlines eight patterns of development used in writing: narration, description, definition, classification and exemplification, comparison and contrast, cause and effect, problem-solution, and persuasion. It provides examples and characteristics of each pattern, including signal words commonly used to indicate each pattern. For narration, description, and definition, it discusses different varieties within each pattern such as objective vs. subjective description.