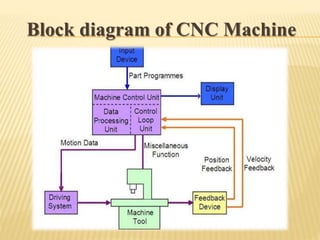
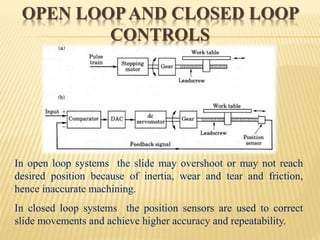
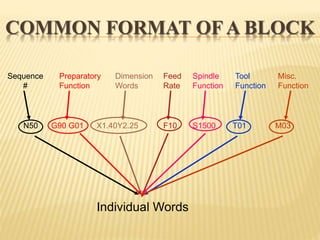
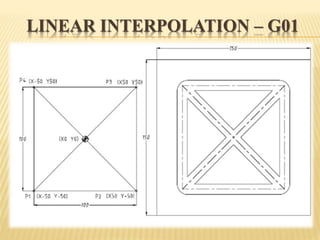
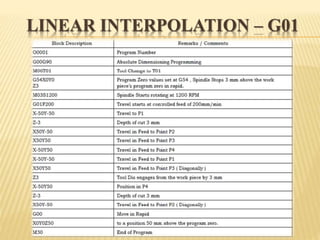
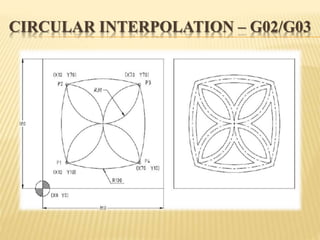
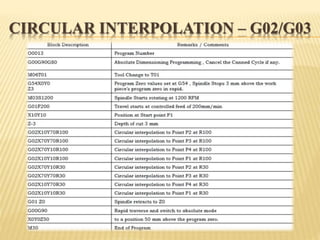
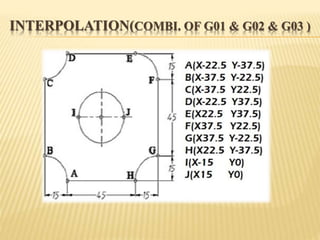
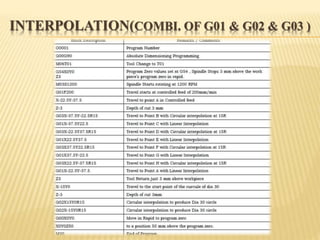
This document provides an overview of computer numerical control (CNC) machines. It discusses the history and evolution of CNC, describes the typical components and functions of a CNC machine including the controller, motors, tool changer and display. The document explains how CNC machines work through programming with G and M codes. It also covers CNC programming basics, common code formats, programming techniques like linear and circular interpolation, advantages and challenges of CNC machines.