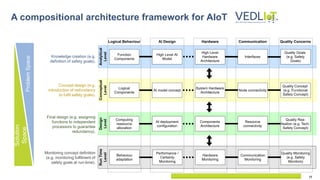
The document describes the Vedliot hardware platform, a heterogeneous computing system designed for various IoT applications ranging from embedded systems to cloud computing, focusing on performance, cost-effectiveness, and energy efficiency. It highlights various microserver architectures and the integration of accelerators such as GPUs and FPGAs for optimal machine learning performance. The platform also emphasizes seamless operation from edge to cloud, enhancing interoperability across different computing environments.







![9
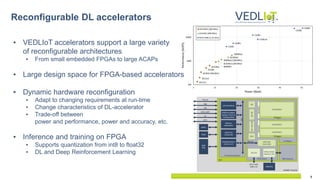
Peak performance values of specialized accelerators, provided by the vendors
(precisions varying from INT8 to FP32)
Peak Performance of DL Accelerators
Average efficiency at 1000 GOPS /W
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
1
10
100
1,000
10,000
100,000
1,000,000
10,000,000
0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000
Performance
[GOPS]
Power [Watt]
ASIC
GPU
FPGA
Ultra Low Power
High Performance
Low Power](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rp1paper2rgriesslvedliotoverviewv5-renegriessl-230915082705-f6e6adbf/85/VEDLIoT-at-FPL-23_Accelerators-for-Heterogenous-Computing-in-AIoT-9-320.jpg)