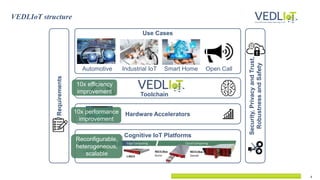
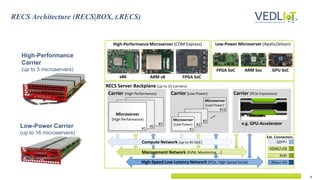
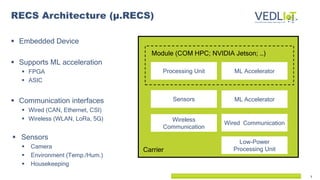
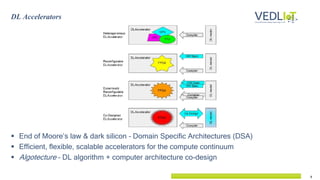
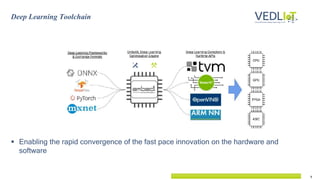
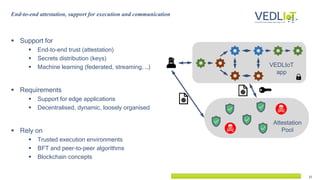
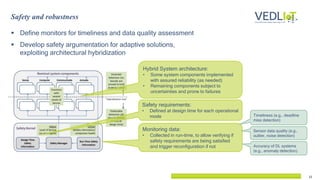
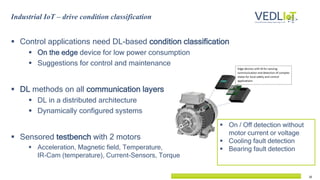
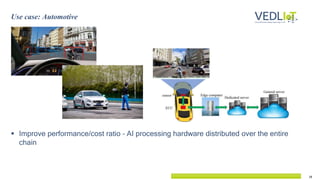
The document presents the Vedliot project focused on advancing efficient deep learning in the Internet of Things (IoT), coordinated by Bielefeld University and involving 12 partners across four EU countries. It outlines the project's goals, budget of approximately 8 million euros, and its applications in industrial IoT, automotive, and smart home environments. The initiative aims to enhance computing power, efficiency, and safety while addressing the need for decentralized and trustworthy AI solutions.