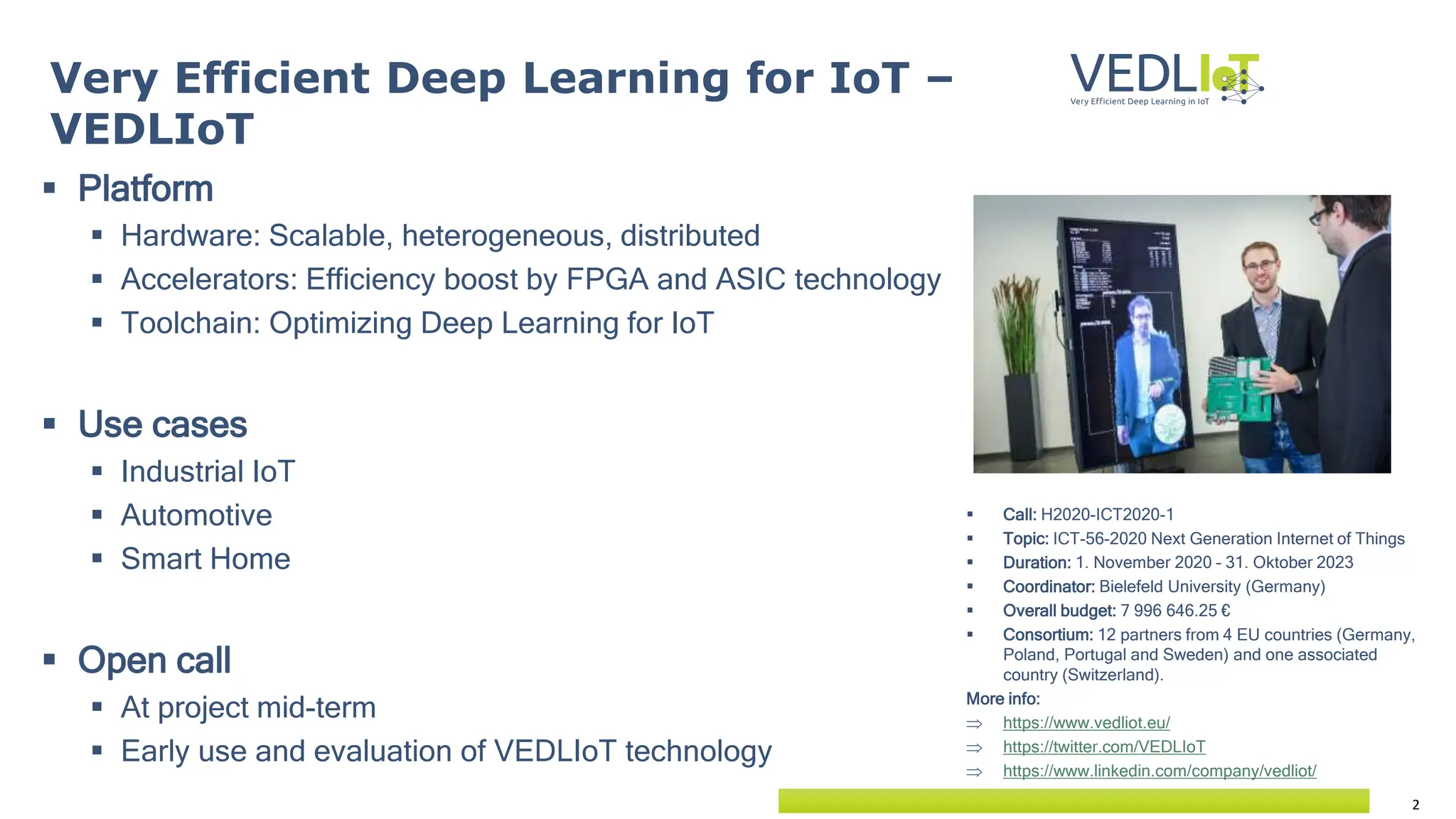
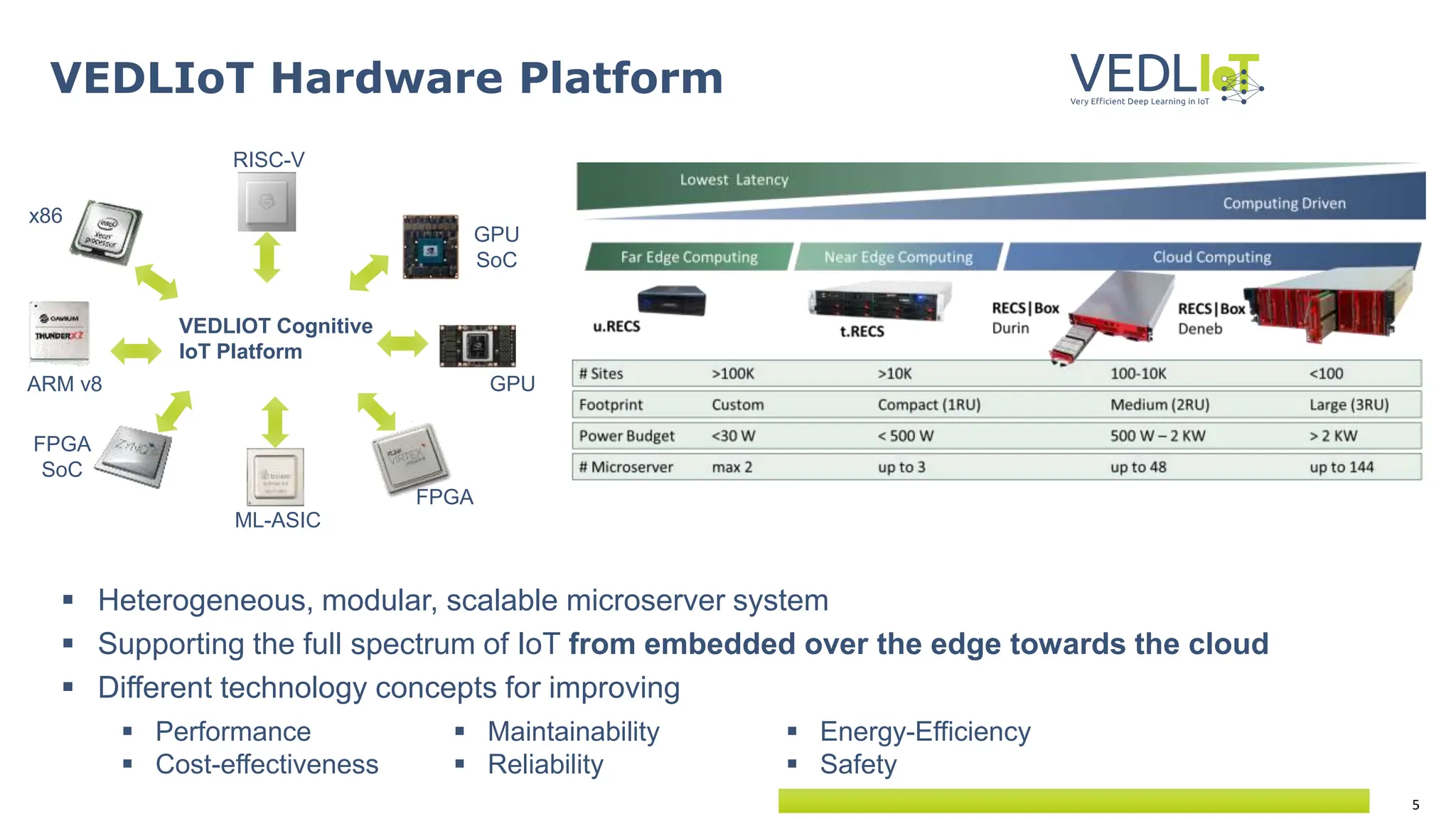
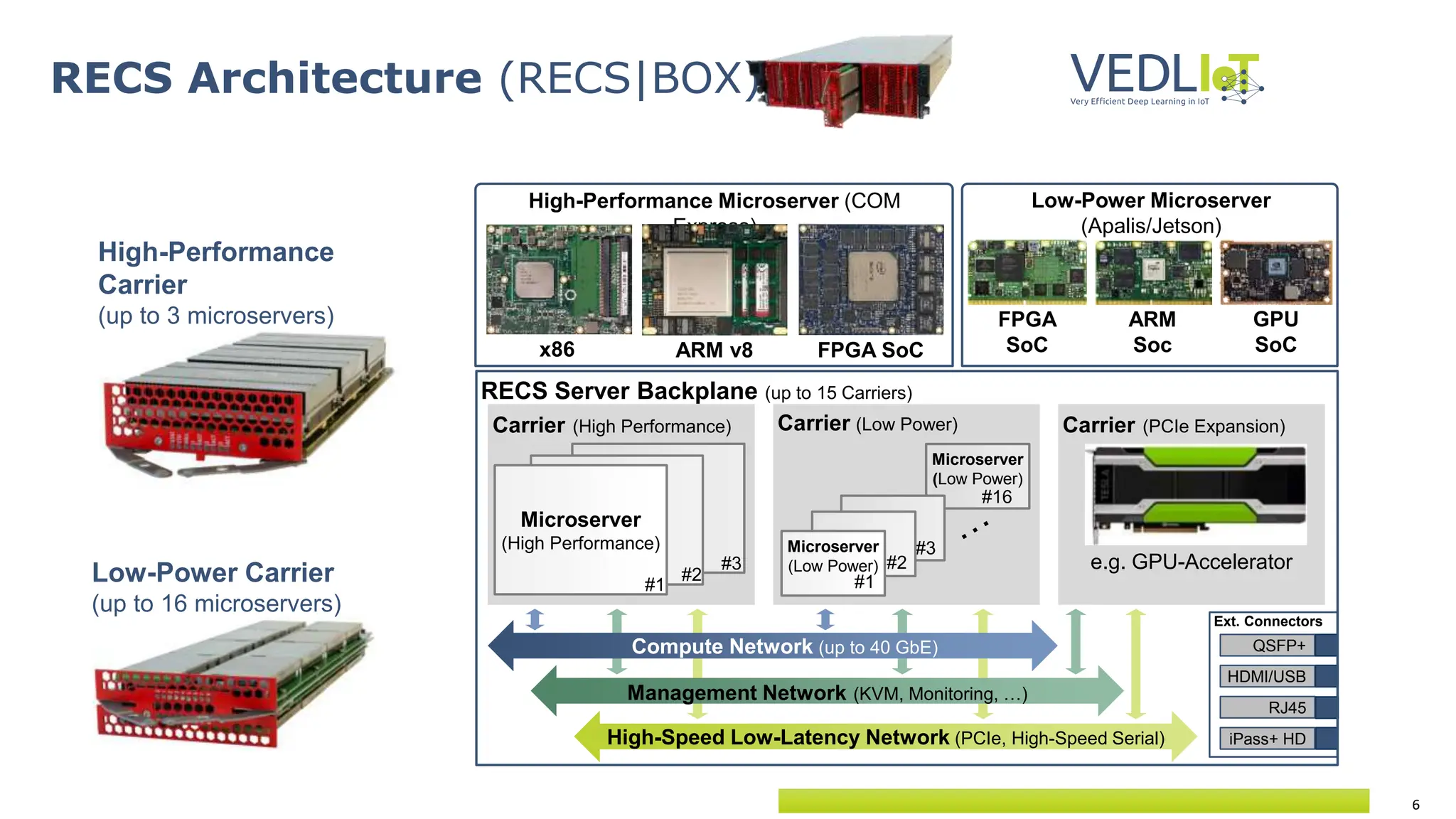
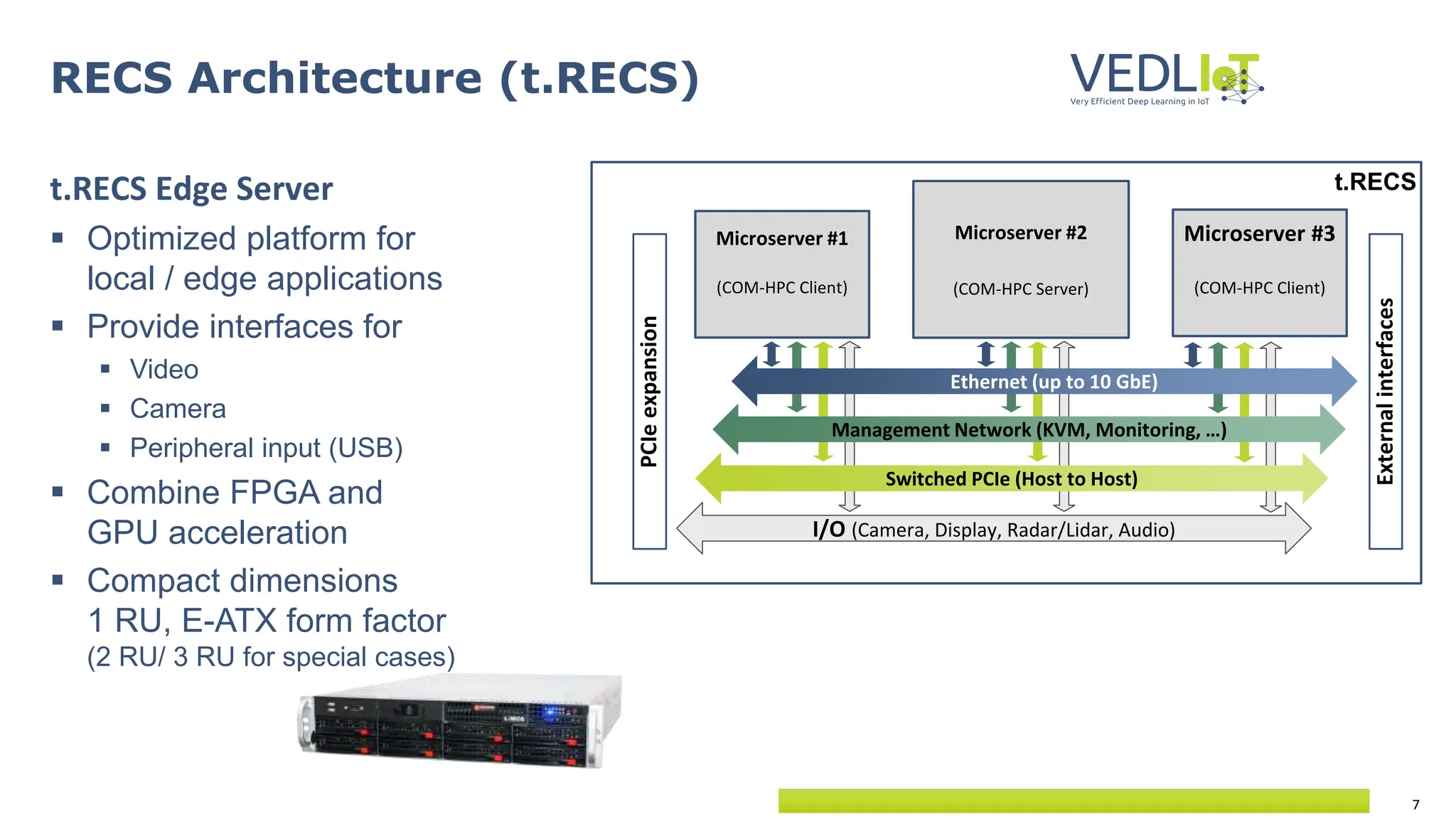
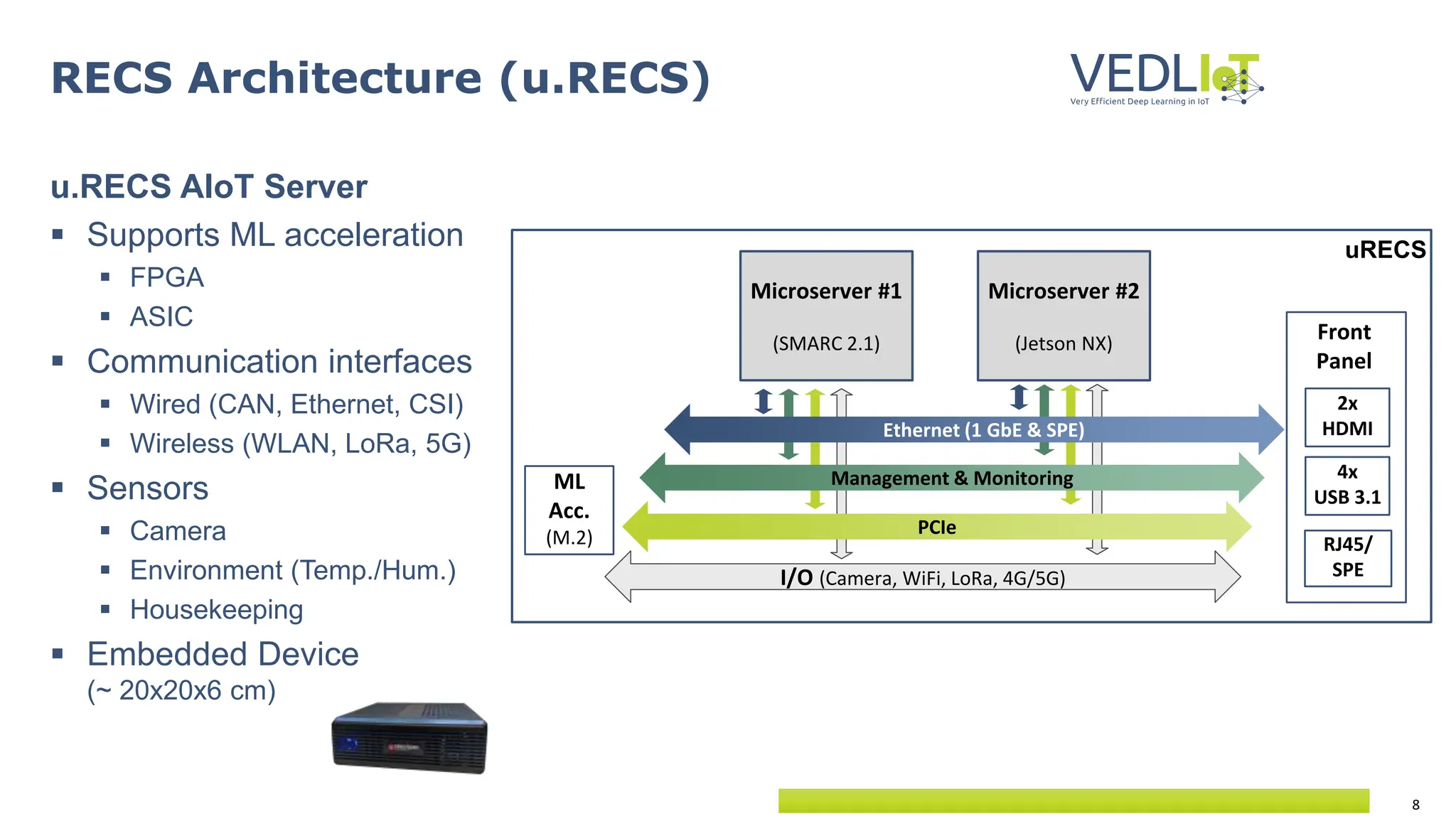
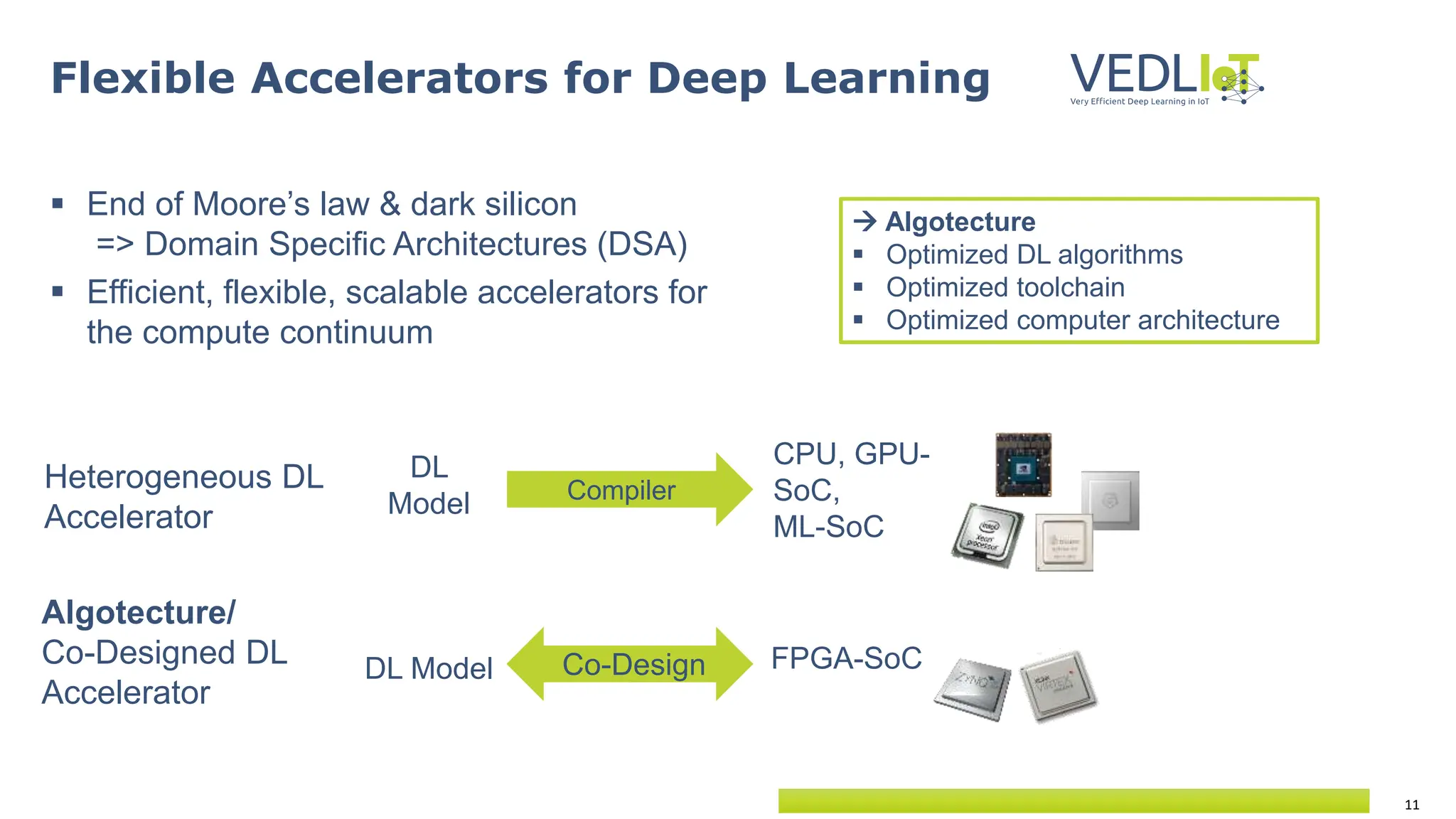
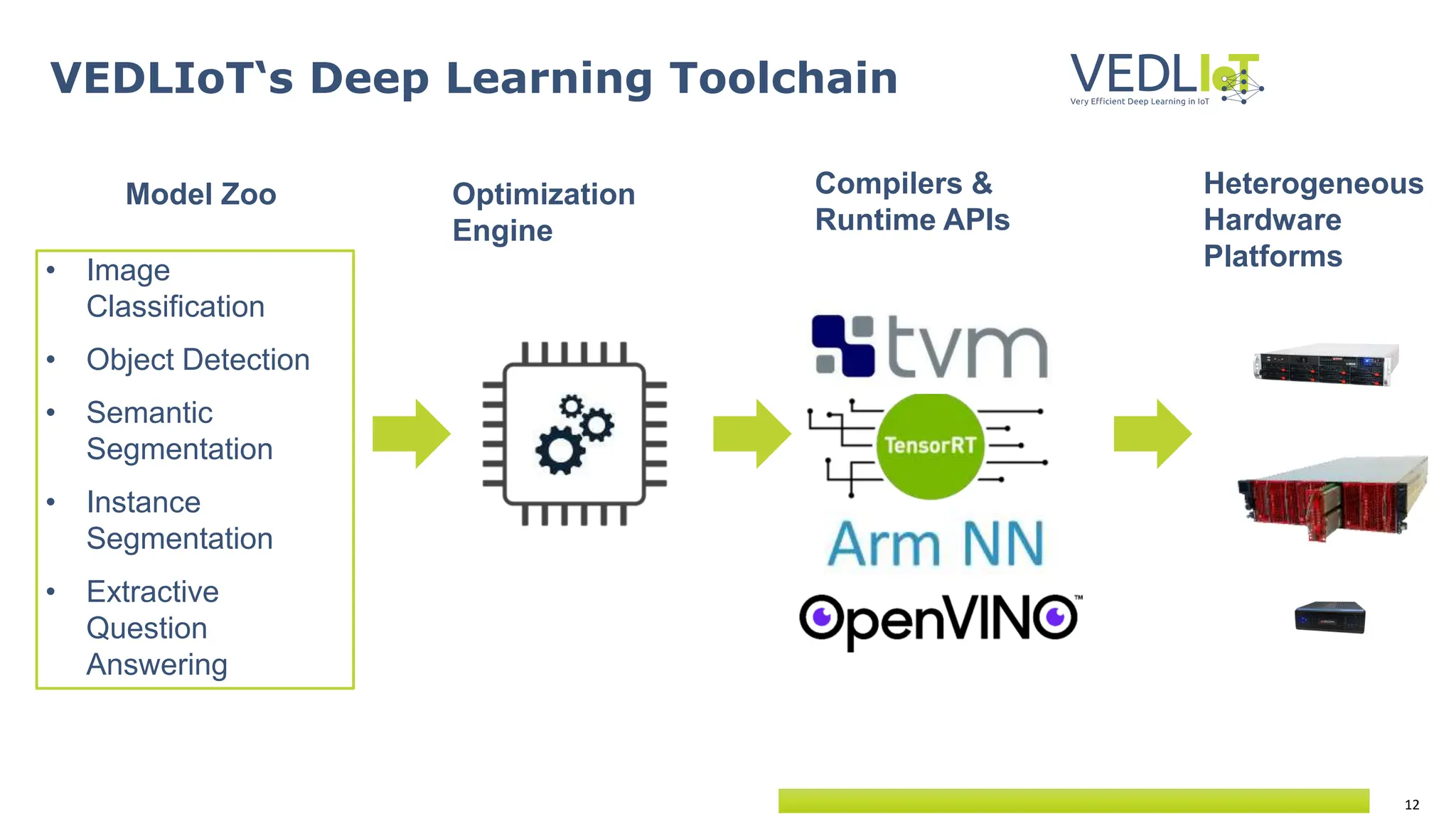
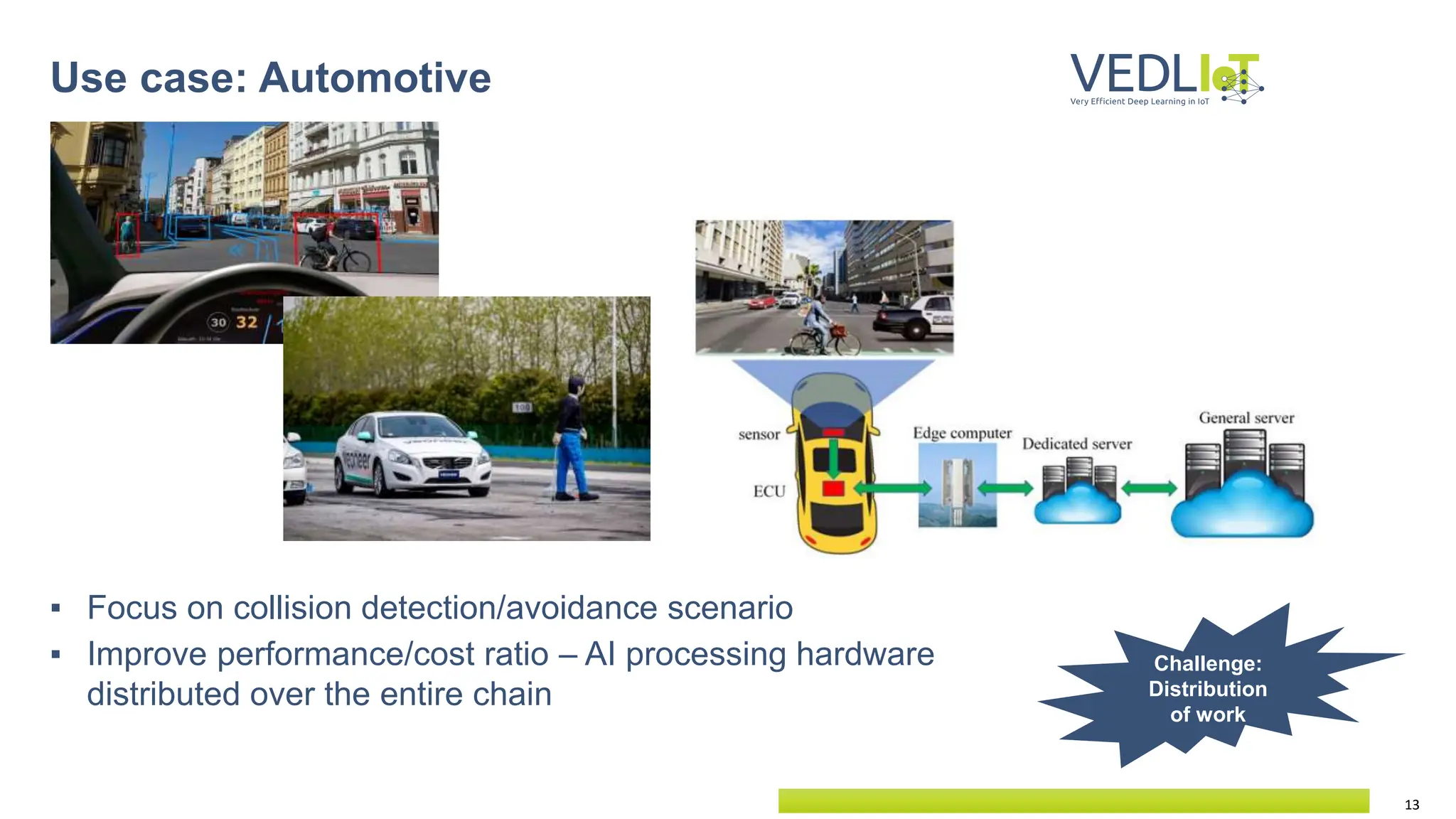
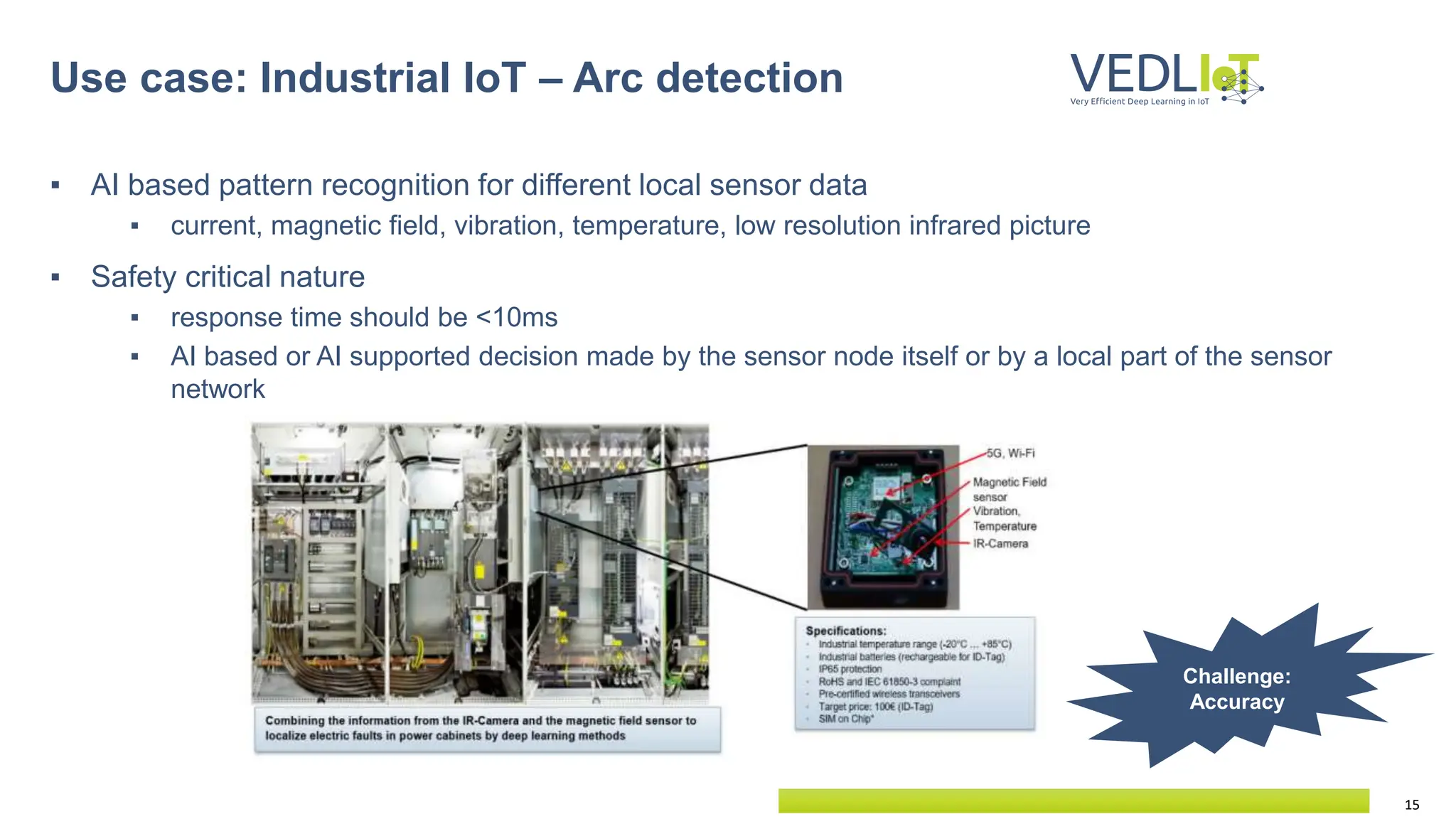
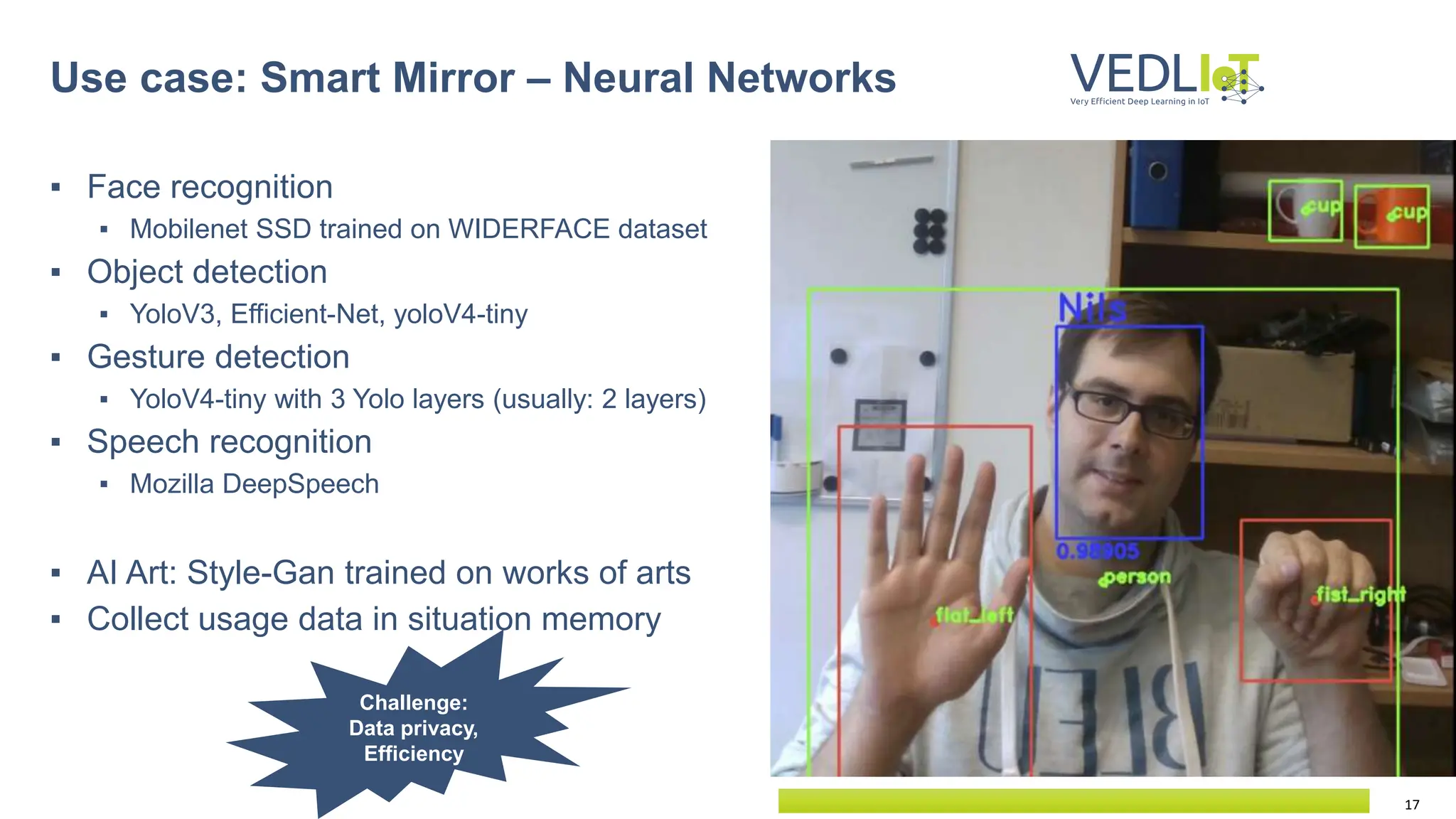
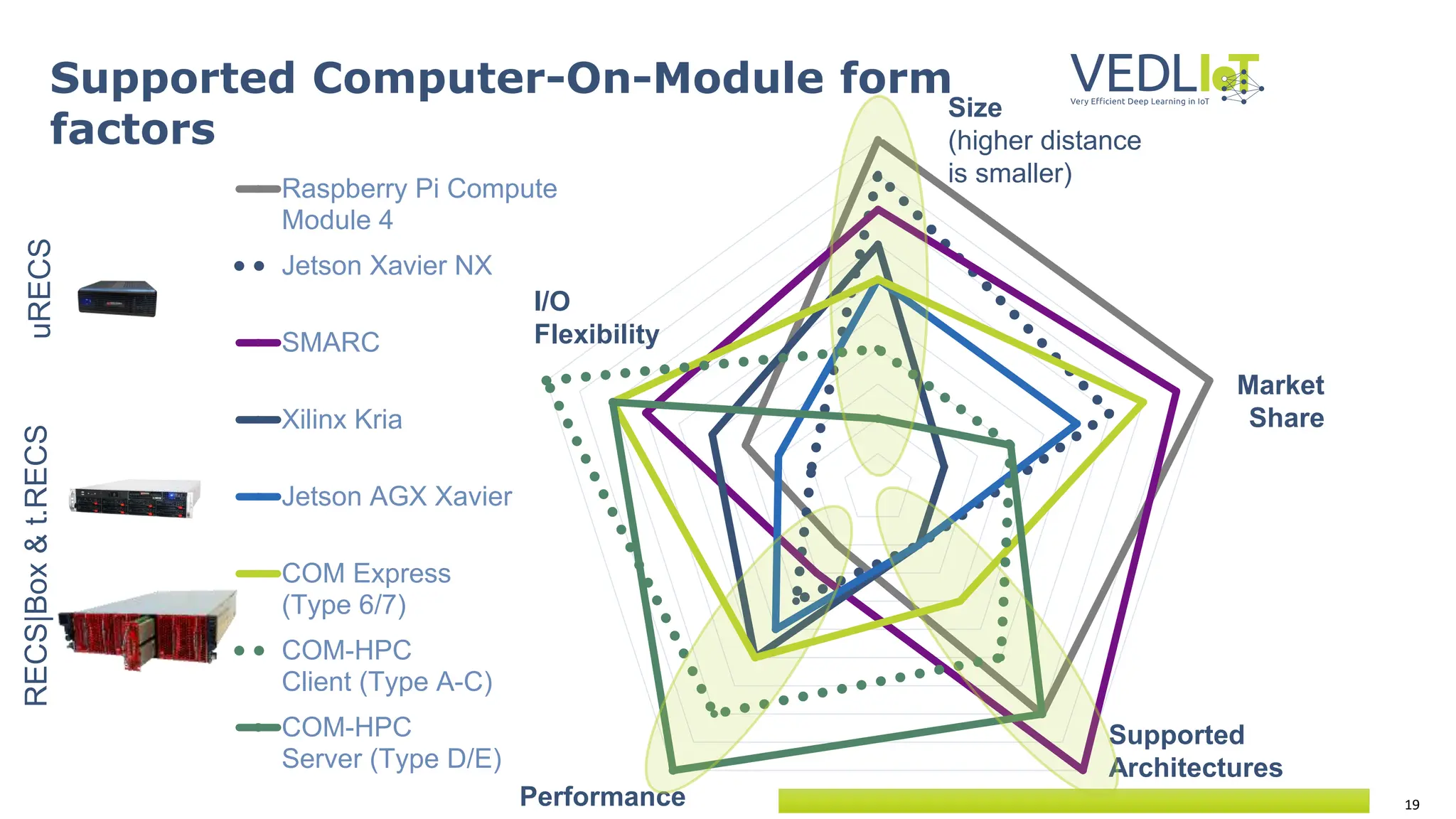
The document provides an overview of the Very Efficient Deep Learning in IoT (VEdLIoT) project, coordinated by Bielefeld University, aimed at optimizing deep learning for various IoT applications with a focus on performance, cost-effectiveness, and energy efficiency. The project, funded under the Horizon 2020 program, spans from November 2020 to October 2023 and includes a consortium of 12 partners across four EU countries. Use cases highlight advancements in industrial IoT, automotive, and smart home technologies, utilizing a modular, scalable hardware platform with specialized accelerators.



![10
Peak performance values of specialized accelerators, provided
by the vendors (precisions varying from INT8 to FP32)
Peak Performance of DL Accelerators
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
Kendryte K210
[CELLRANGE]
[CELL…
[CELLRA…
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRA…
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
1
10
100
1000
10000
100000
1000000
0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000
Performance
[GOPS]
Power [Watt]
Devices
IP Cores
Average efficiency at 1000 GOPS /W](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conasense2022vedliotoverview-240206111918-9307947a/75/CONASENSE-2022_Jens-Hagemeyer-presentation-10-2048.jpg)



![20
Benchmark performance of DL accelerators
Comparison based on currently available architectures
VEDLIoT will include new specialized accelerators
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
Coral (M.2) Coral (Dev.) Xavier AGX
(LP)
Xavier AGX
(HP)
Xavier NX TX2 Nano GTX1660 ZU15 ZU3 Xeon-D1577 Epyc3451 Myriad GAP8
Energy Efficiency [GOPS/W]
ResNet50 Int 8 ResNet50 FP16 ResNet50 FP32
YoloV4 Int 8 YoloV4 FP16 YoloV4 FP32
MobileNet Int 8 MobileNet FP16 MobileNet FP32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conasense2022vedliotoverview-240206111918-9307947a/75/CONASENSE-2022_Jens-Hagemeyer-presentation-20-2048.jpg)
![21
Benchmark performance of DL accelerators
YoloV4
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLR…
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRA…
[CELLRANGE]
10
100
1000
10000
2 4 8 16 32 64 128
Performance
[GOPS]
Power [Watt]
INT8 FP16 FP32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conasense2022vedliotoverview-240206111918-9307947a/75/CONASENSE-2022_Jens-Hagemeyer-presentation-21-2048.jpg)
![22
Benchmark performance of DL accelerators
ResNet50
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELL…
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
10
100
1000
10000
2 4 8 16 32 64 128
Performance
[GOPS]
Power [Watt]
INT8 FP16 FP32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conasense2022vedliotoverview-240206111918-9307947a/75/CONASENSE-2022_Jens-Hagemeyer-presentation-22-2048.jpg)
![23
[CELLRANGE] [CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CEL…
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
[CELLRANGE]
10
100
1000
10000
2 4 8 16 32 64 128
Performance
[GOPS]
Power [Watt]
INT8 FP16 FP32
Benchmark performance of DL accelerators
MobileNetV3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conasense2022vedliotoverview-240206111918-9307947a/75/CONASENSE-2022_Jens-Hagemeyer-presentation-23-2048.jpg)