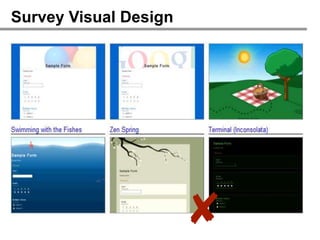
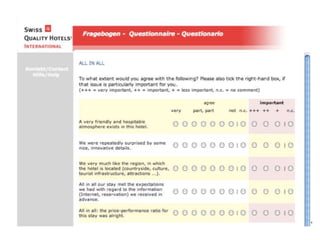
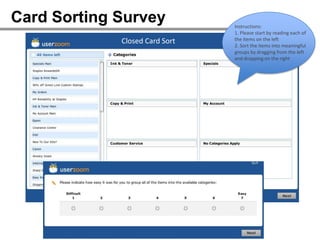
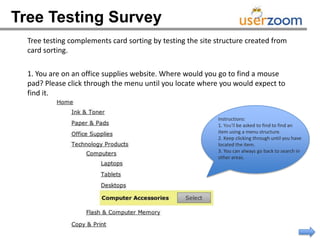
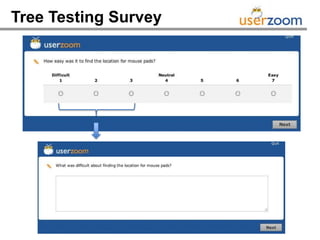
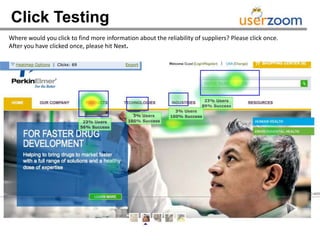
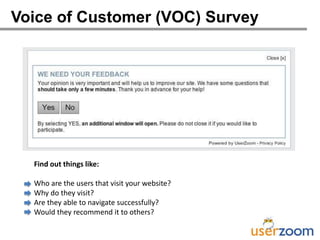
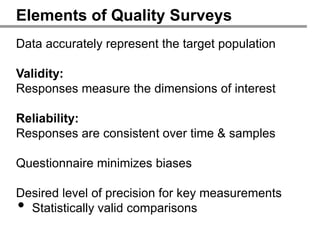
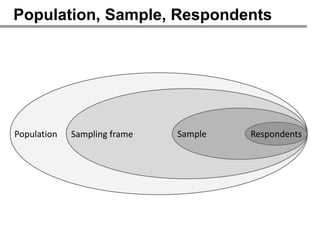
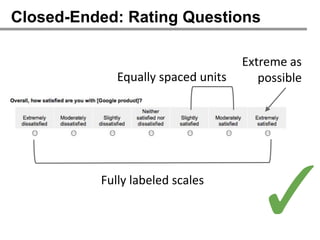
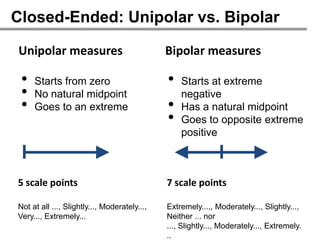
The webinar on designing effective online surveys, led by Elizabeth Ferrall-Nunge and Alfonso de la Nuez, covers key topics such as when to use surveys, attributes of a good survey, question types, and potential biases. It highlights the importance of proper sampling and question design to ensure valid and reliable data while minimizing biases. UserZoom, the hosting company, offers a suite of tools for testing and improving customer experience across websites and mobile apps.




























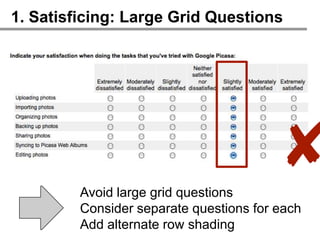


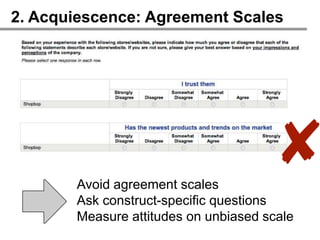
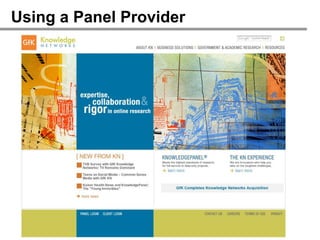
![2. Acquiescence: Agreement Scales
Avoid agreement scales
✘
Ask construct-specific questions
Measure attitudes on unbiased scale
Indicate your level of trust with Shopbop?
[Extremely distrust,...,Extremely trust] ✓](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtodesigneffectiveonlinesurveys10261-121102132559-phpapp01/85/How-to-design-effective-online-surveys-39-320.jpg)






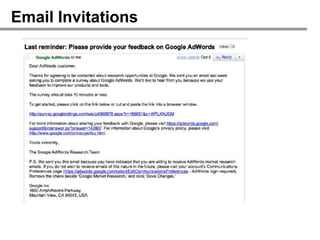
![4. Question Order Bias: Example
1. Which of the following features
would you like to see improved?
✘
[Battery life, weight, screen size, ...]
2. What do you find most
frustrating about your
smartphone?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtodesigneffectiveonlinesurveys10261-121102132559-phpapp01/85/How-to-design-effective-online-surveys-47-320.jpg)