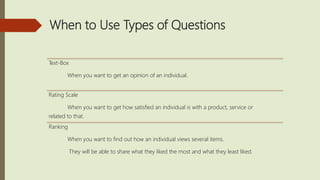
This document provides guidance on creating effective surveys. It discusses survey goals, examples of common survey types, different question types including their uses, question sequencing, feedback, designing your own survey, and processing results. Survey goals and types include customer service, employee engagement, and quizzes. Question types range from true/false, multiple choice, fill-in-the-blank, and rating scales. Sequencing questions from easy to difficult and allowing navigation control is advised. Feedback should be provided when possible. Instructions guide the reader through designing their own survey on a topic of choice and distributing/collecting responses from peers. The document concludes with discussing providing an overview and summary of survey results.