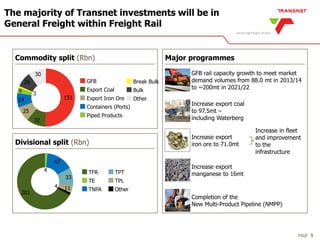
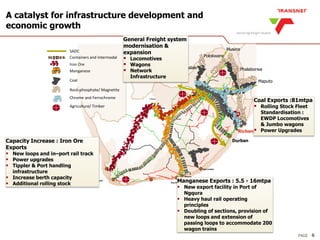
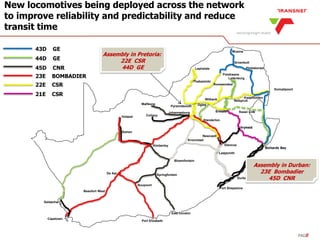
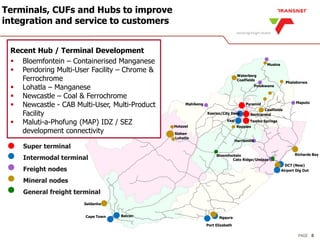
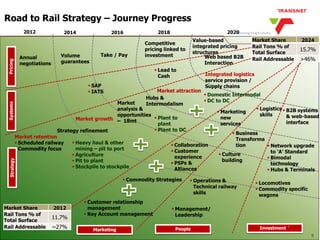
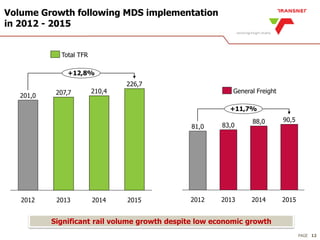
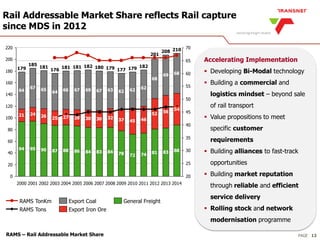
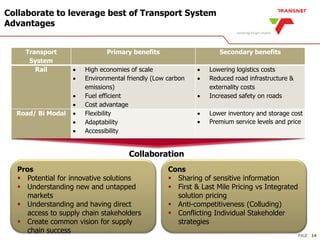
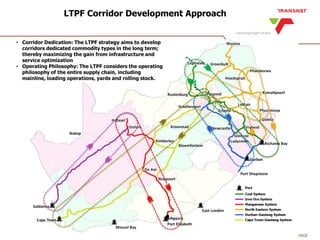
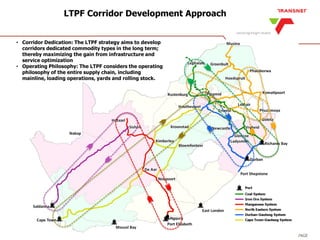
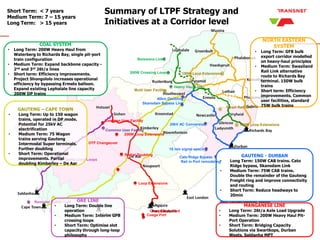
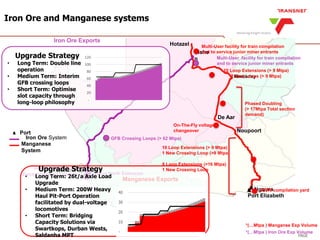
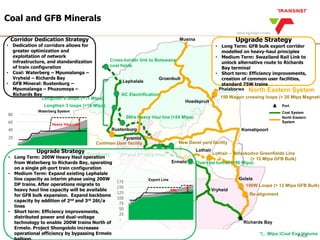
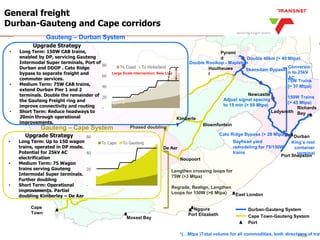
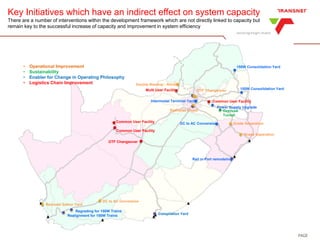
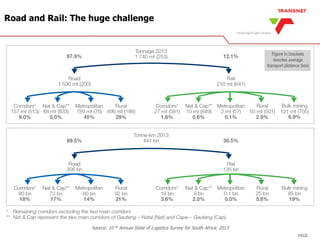
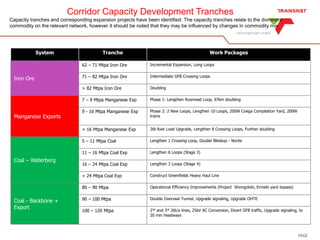
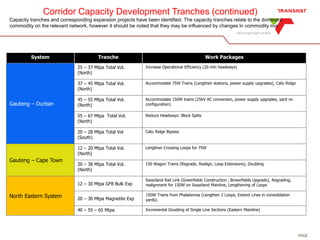
The document outlines Transnet's strategies and investments in the freight rail sector aimed at increasing rail market share, improving infrastructure, and enhancing logistics efficiency. Key focus areas include integrating rail systems, modernizing rolling stock and network infrastructure, and developing multi-user facilities for various commodities. The ultimate goal is to facilitate economic growth through enhanced service delivery, job creation, and reduced logistics costs in the road-rail freight industry.