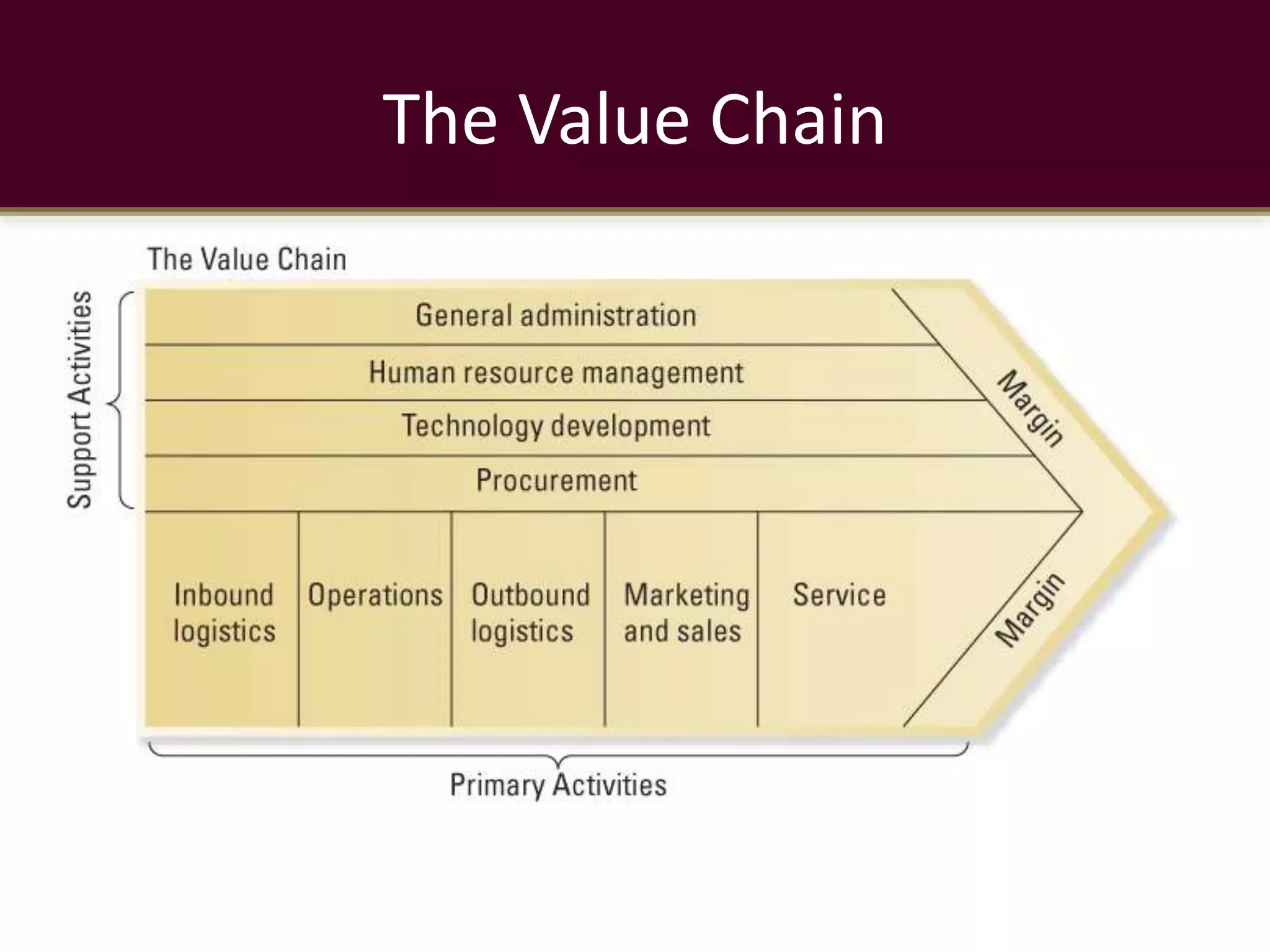
Value chain analysis examines the internal activities a firm engages in to deliver a product or service. It identifies primary activities like inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service, as well as support activities including procurement, technology development, human resources, and general administration. Google relies on over 70 offices globally for operations and uses marketing through online and offline channels, though sales are predominantly online. Customer service at Google is provided through online forums rather than phone support due to the large customer base.