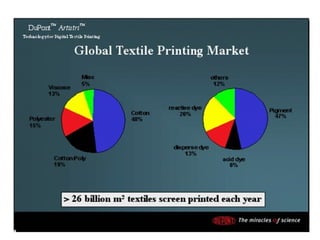
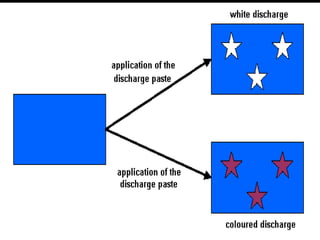
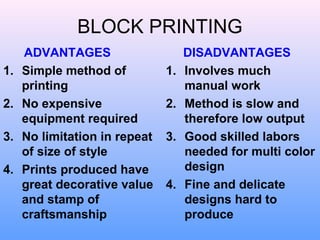
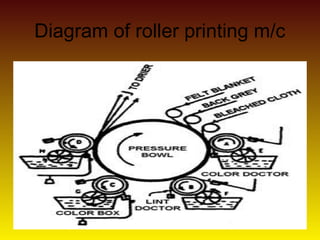
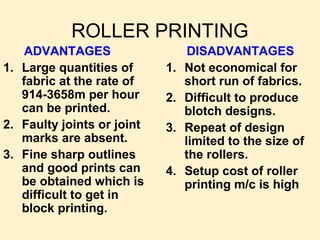
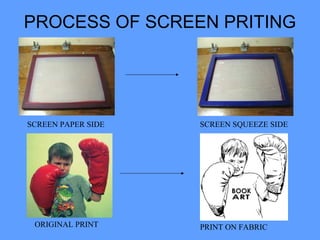
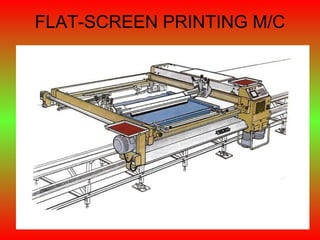
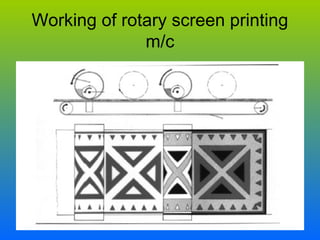
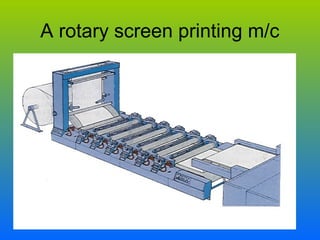
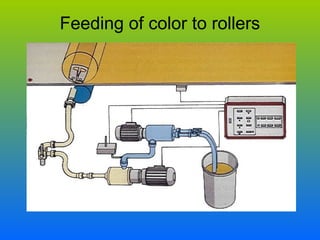
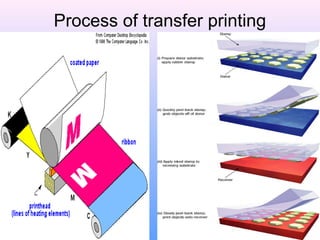
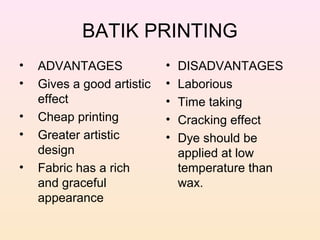
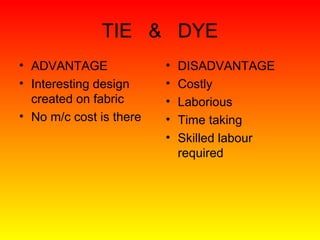
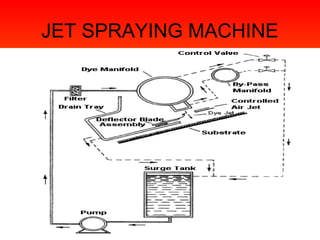
The document discusses various types and styles of printing fabrics. It describes three main approaches to printing color on fabric: direct printing, discharge printing, and resist printing. It then provides details on different printing techniques like block printing, roller printing, screen printing, and others; explaining their process, advantages, and disadvantages. The document also covers various pattern styles used in printing like stripes, checks, dots, geometrical prints, and others.