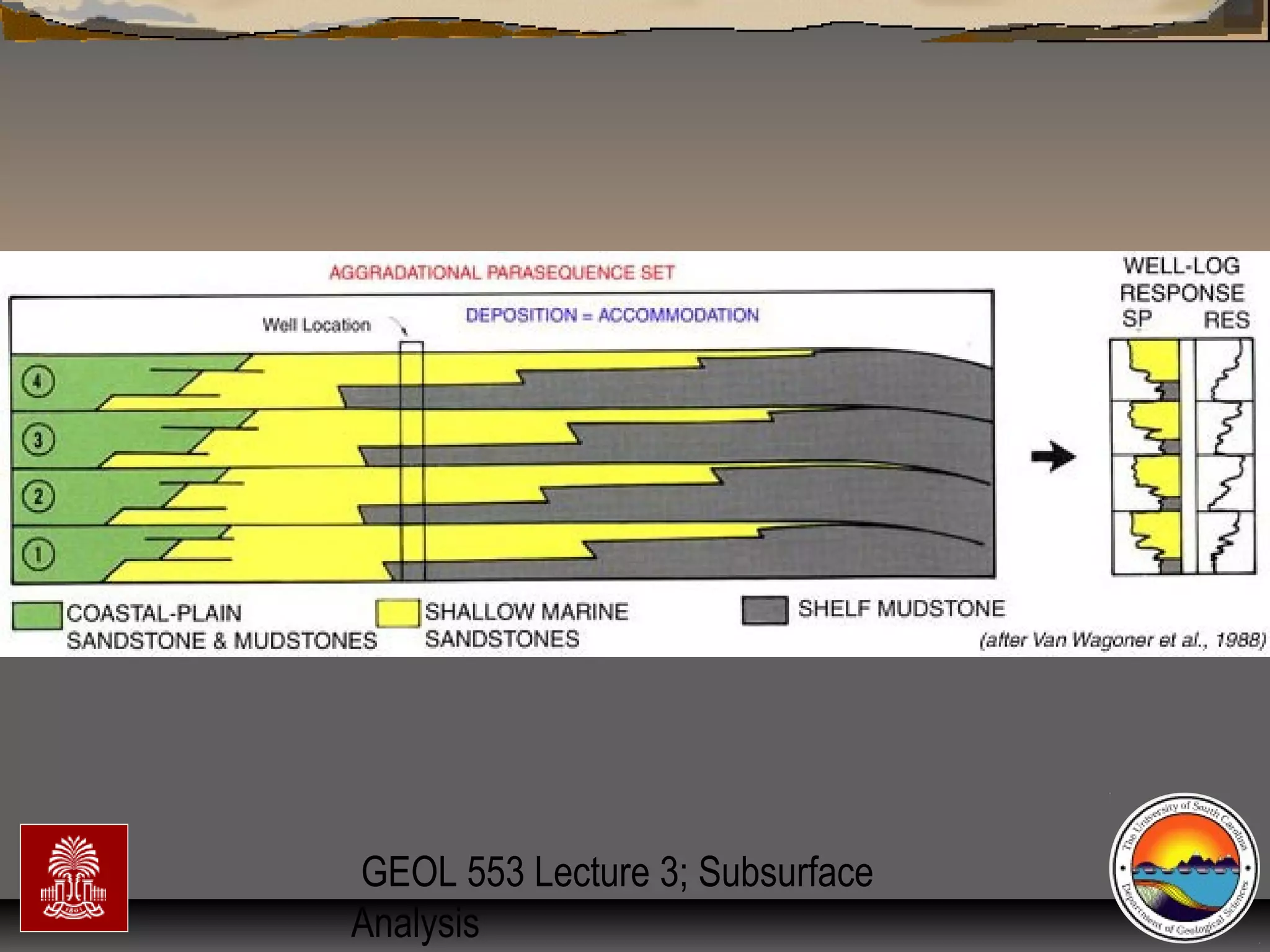
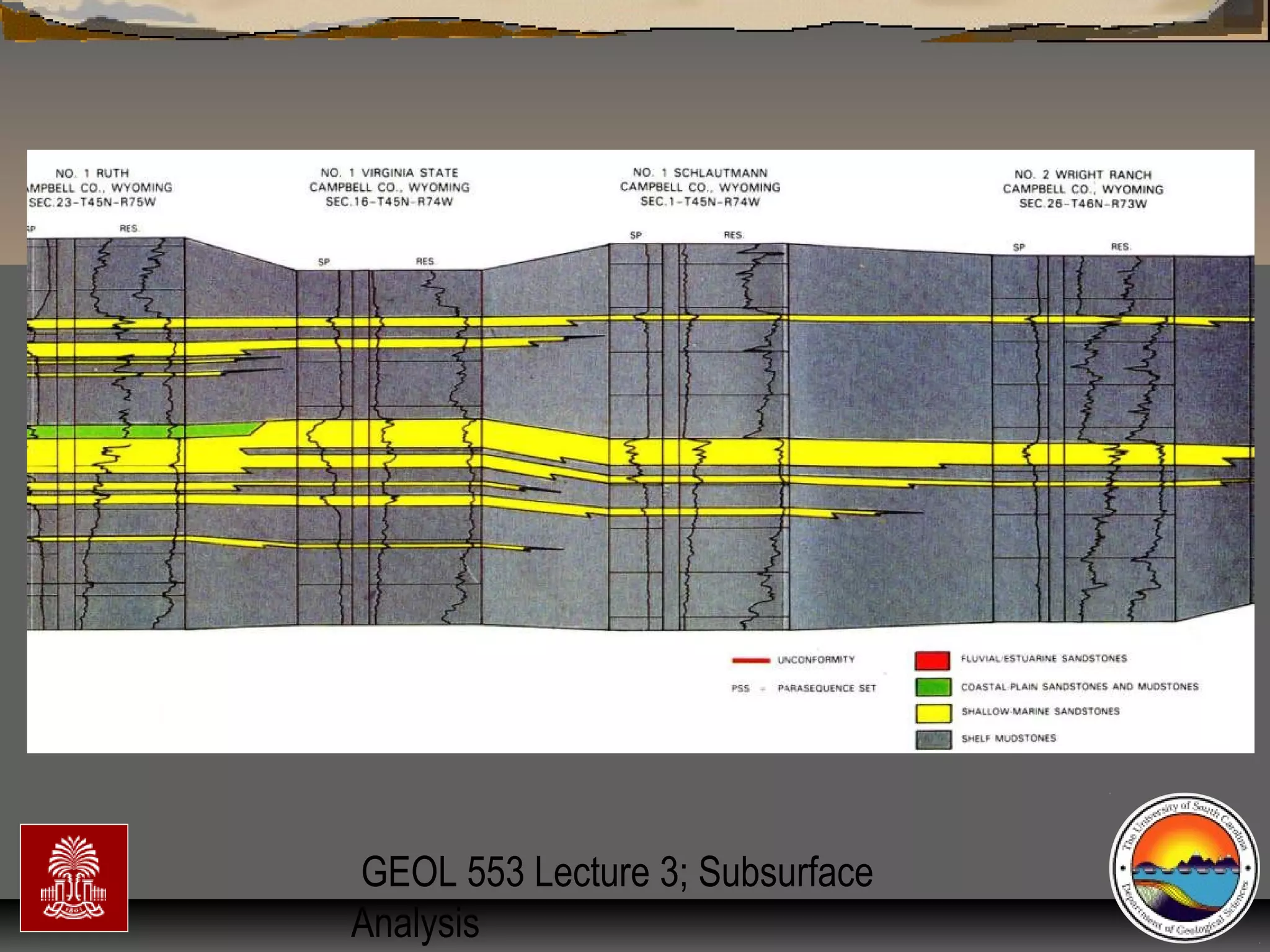
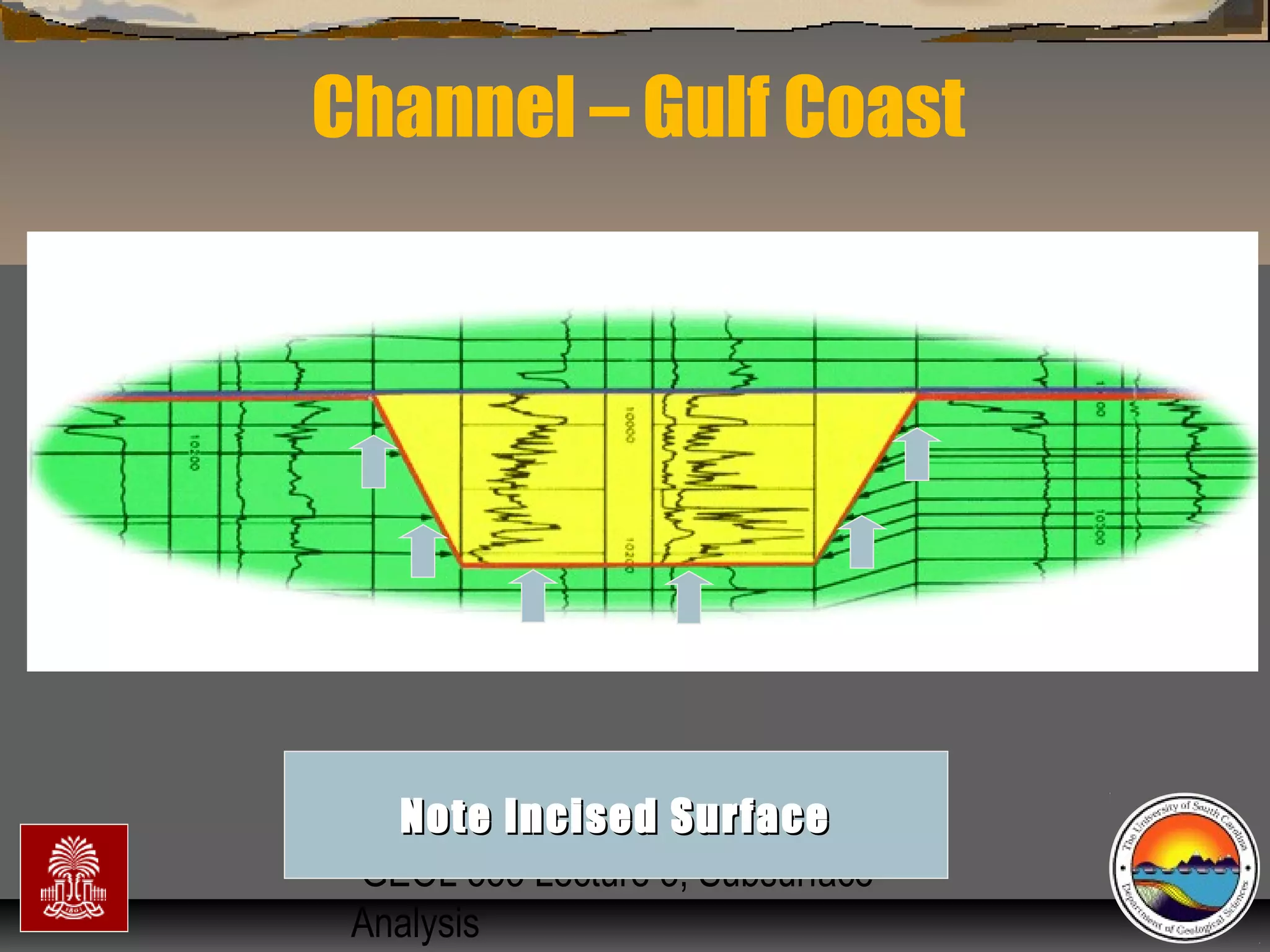
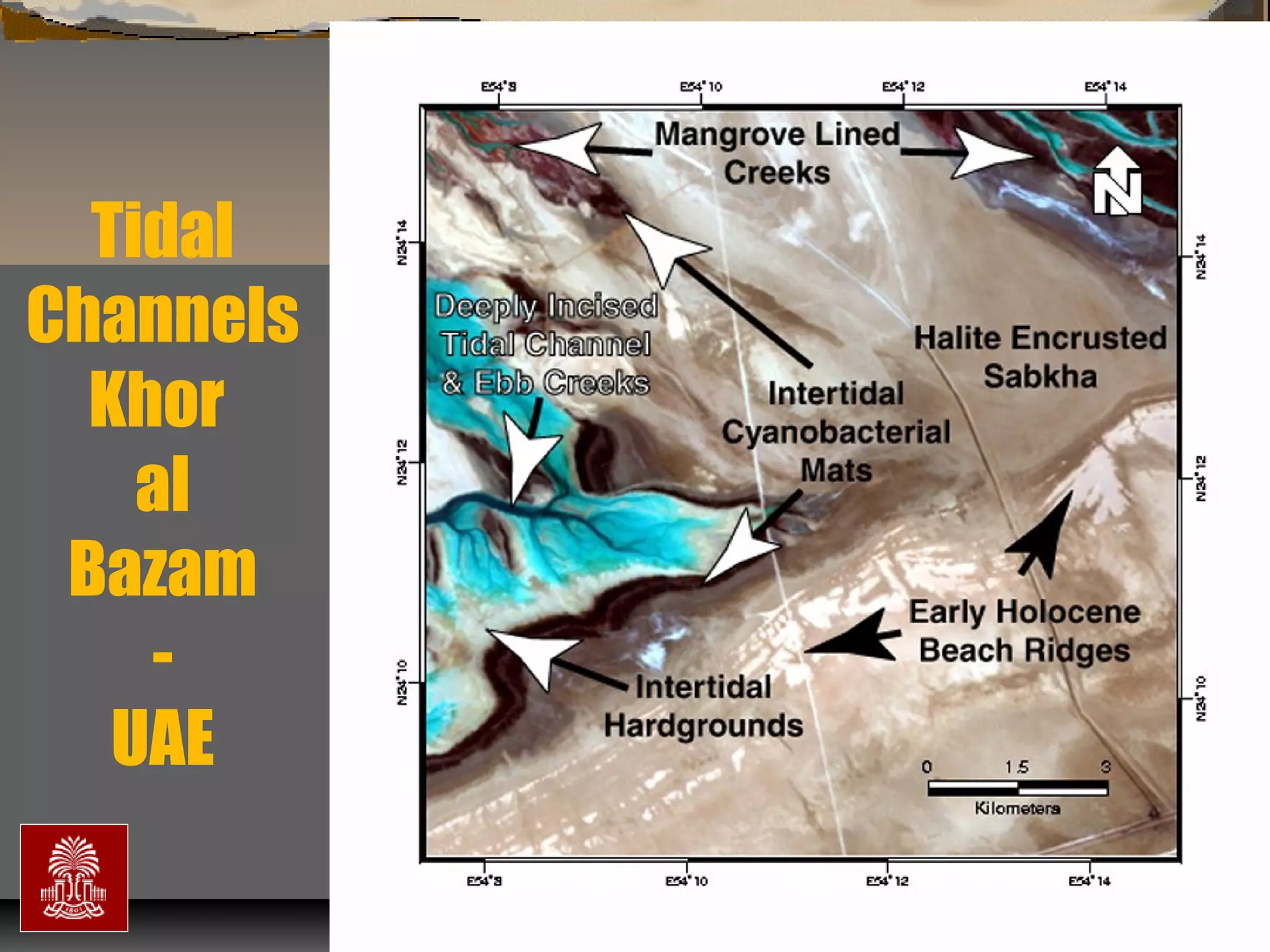
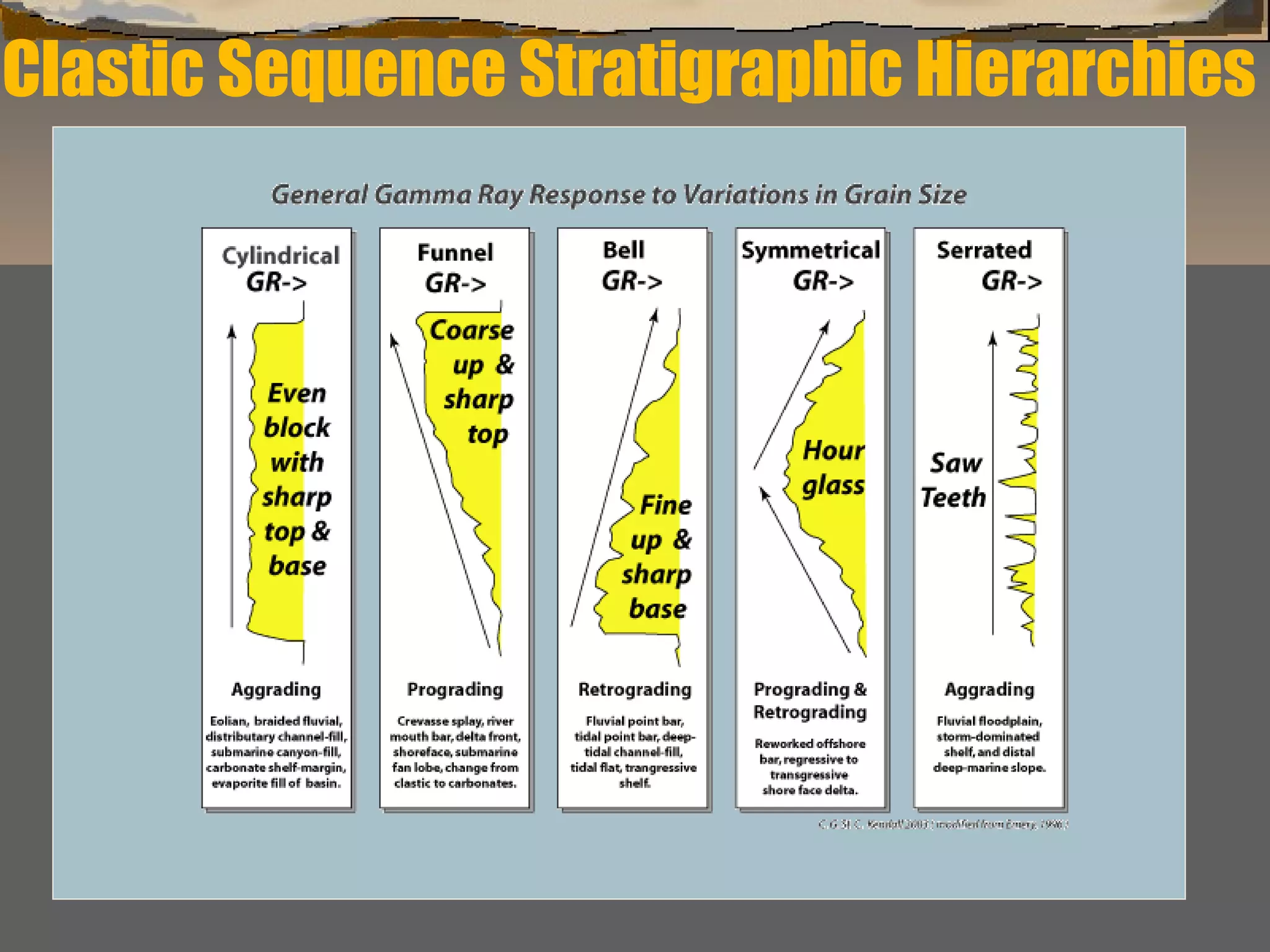
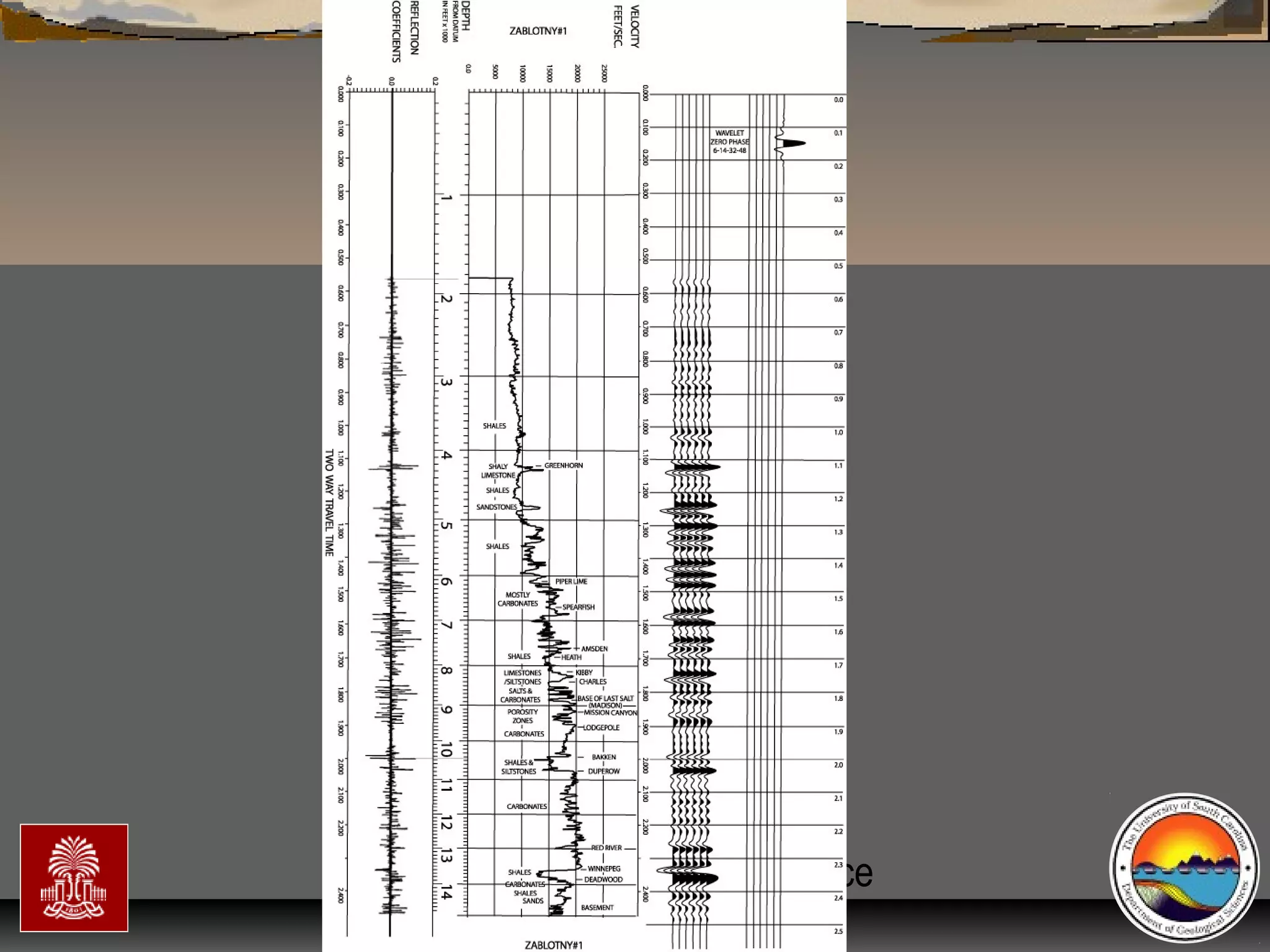
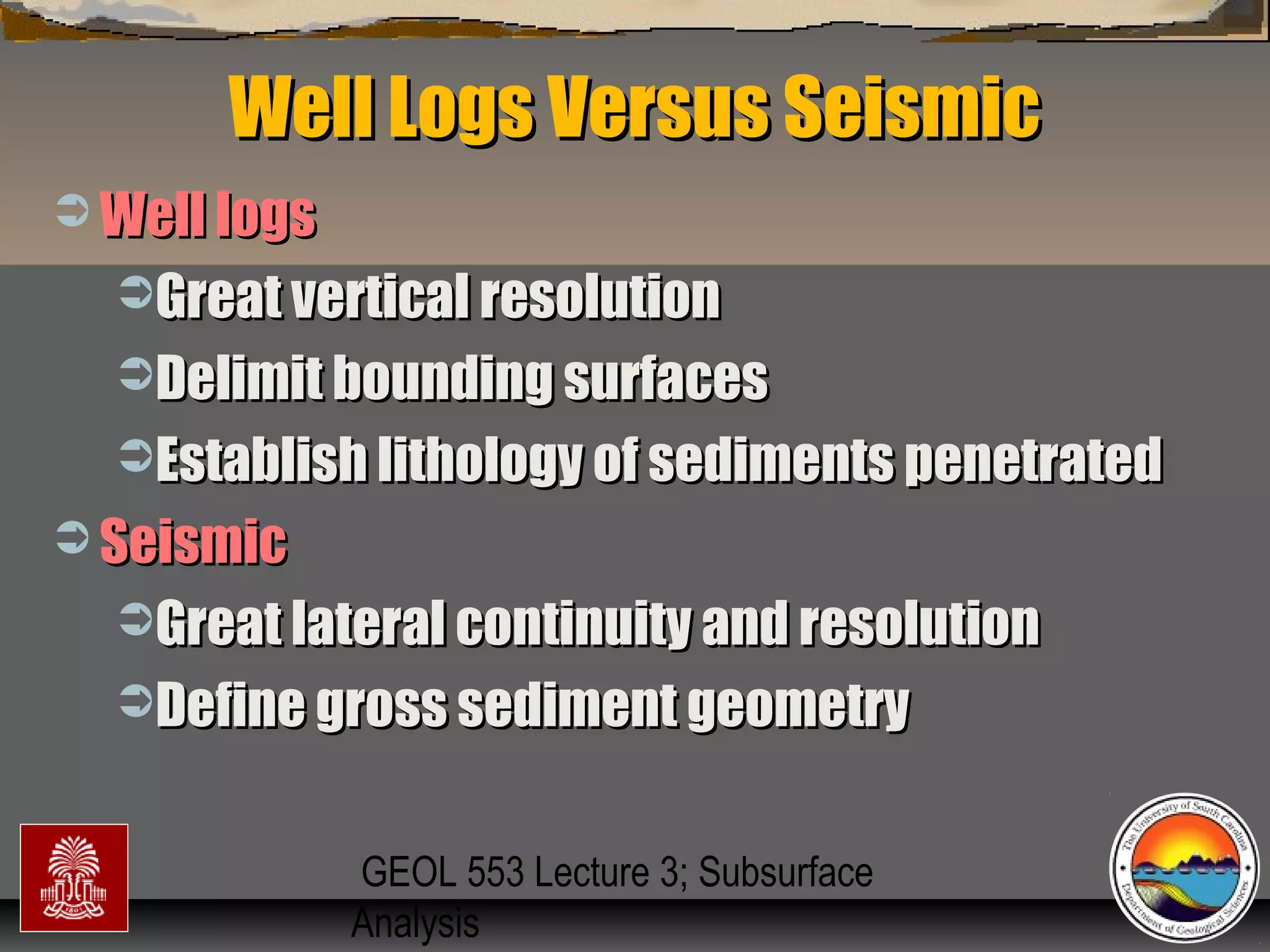
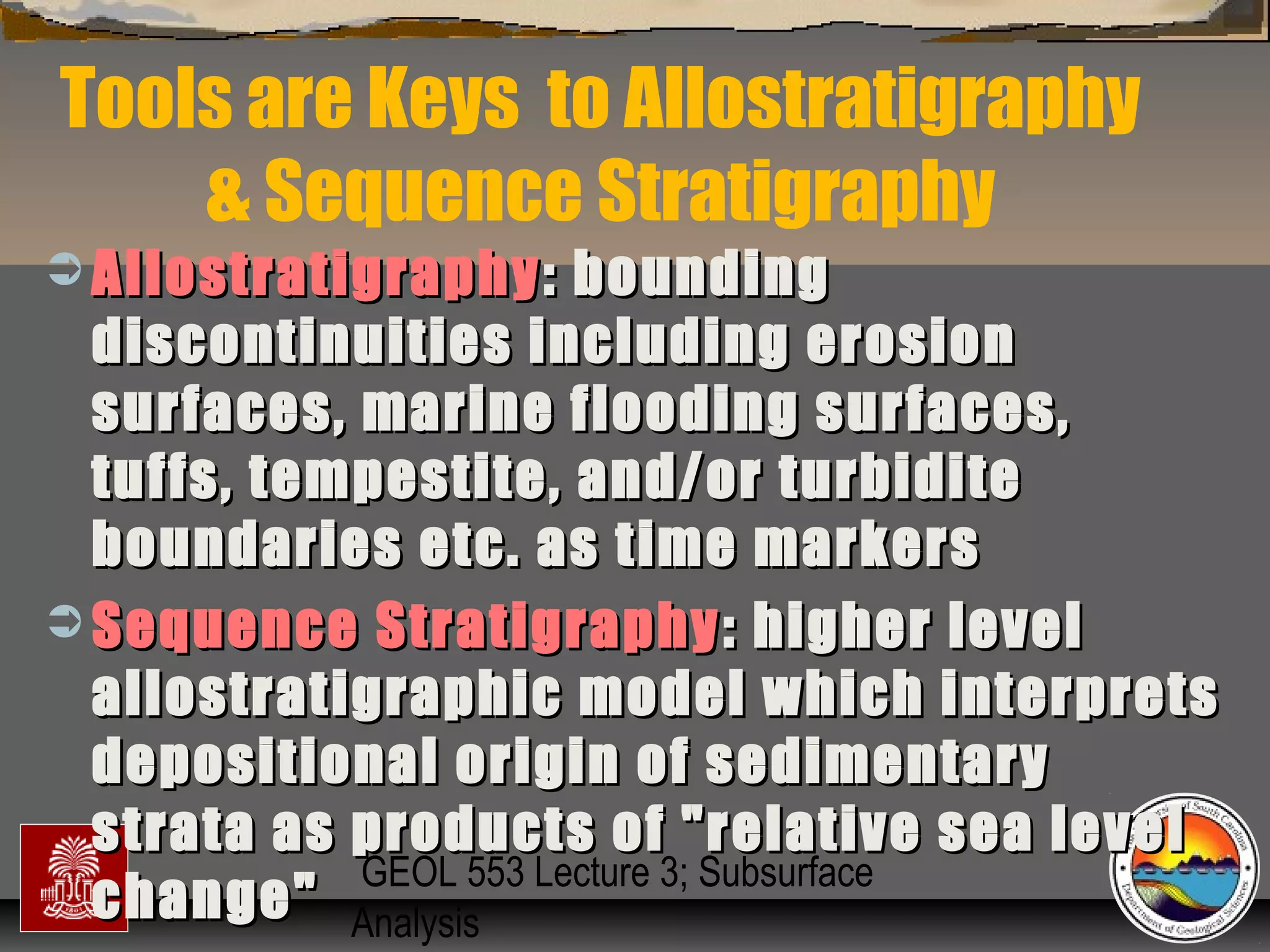
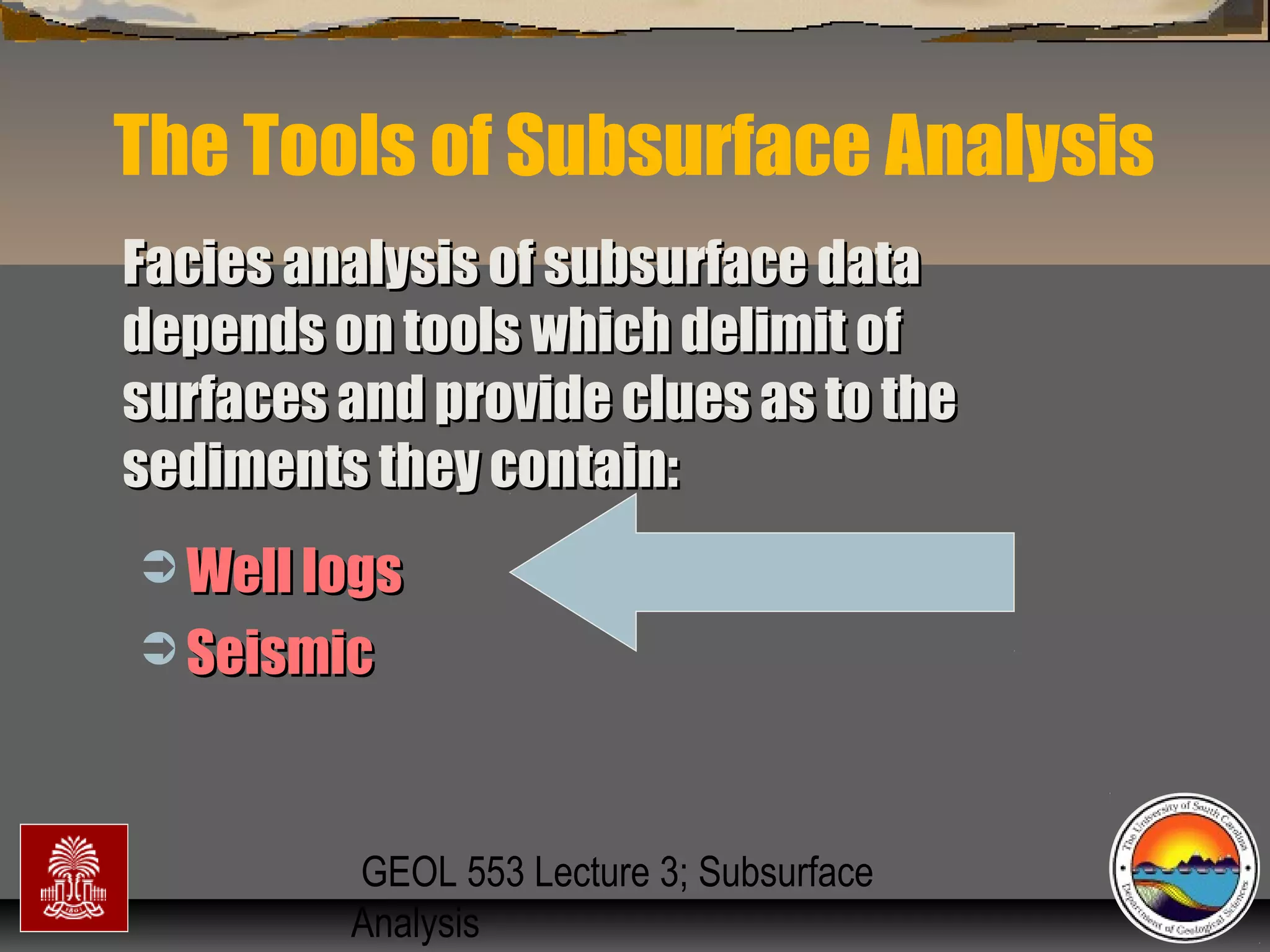
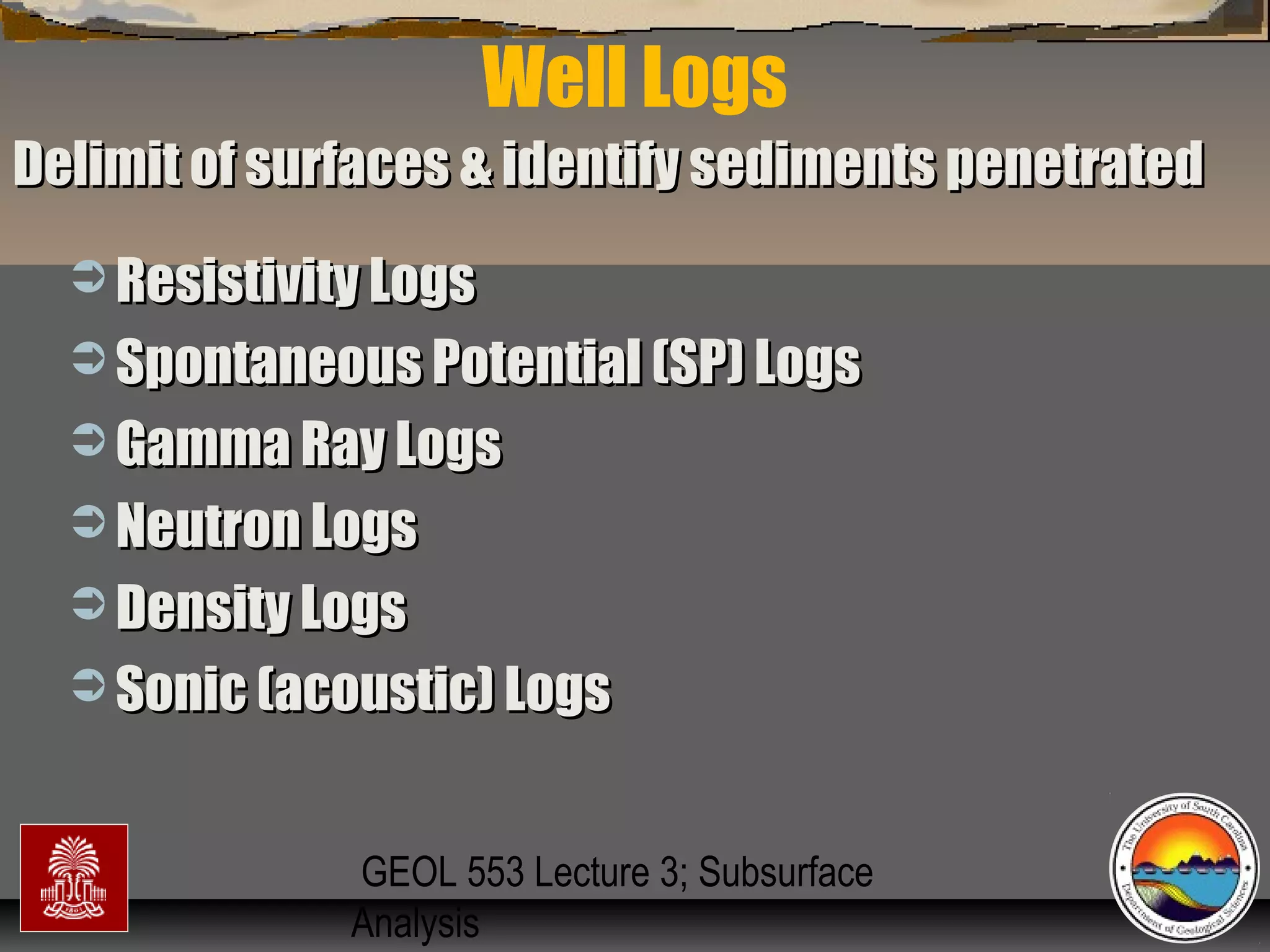
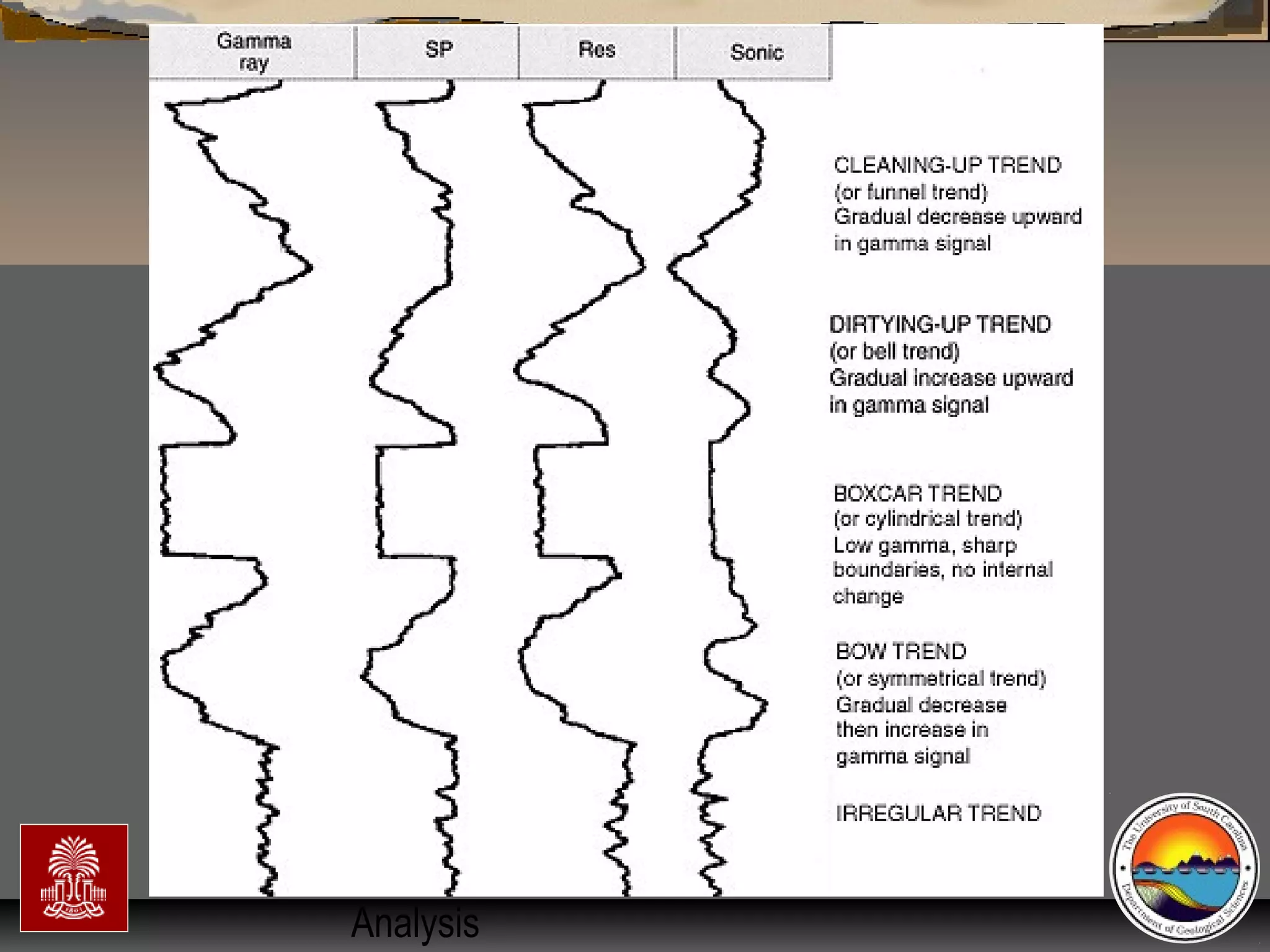
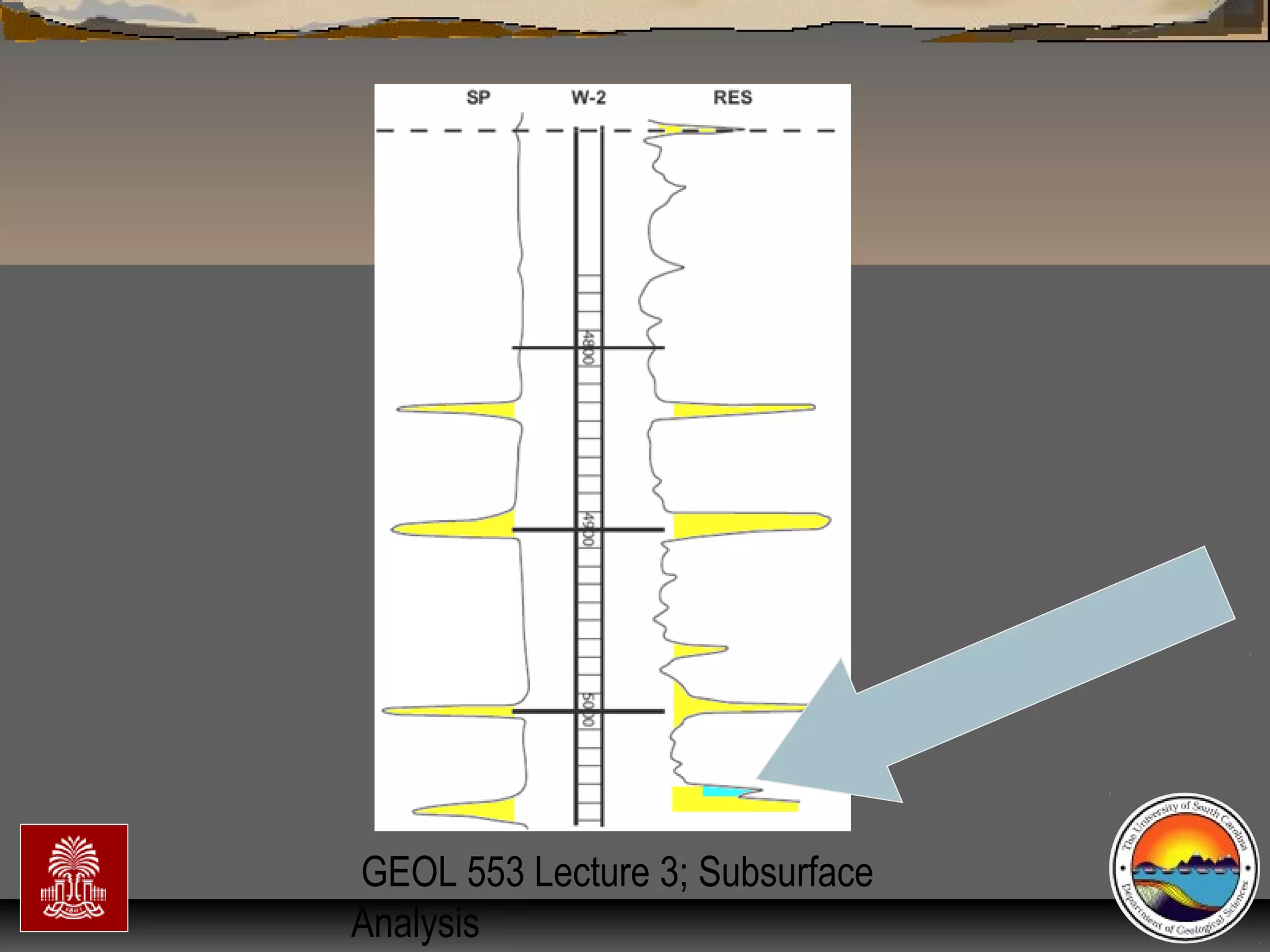
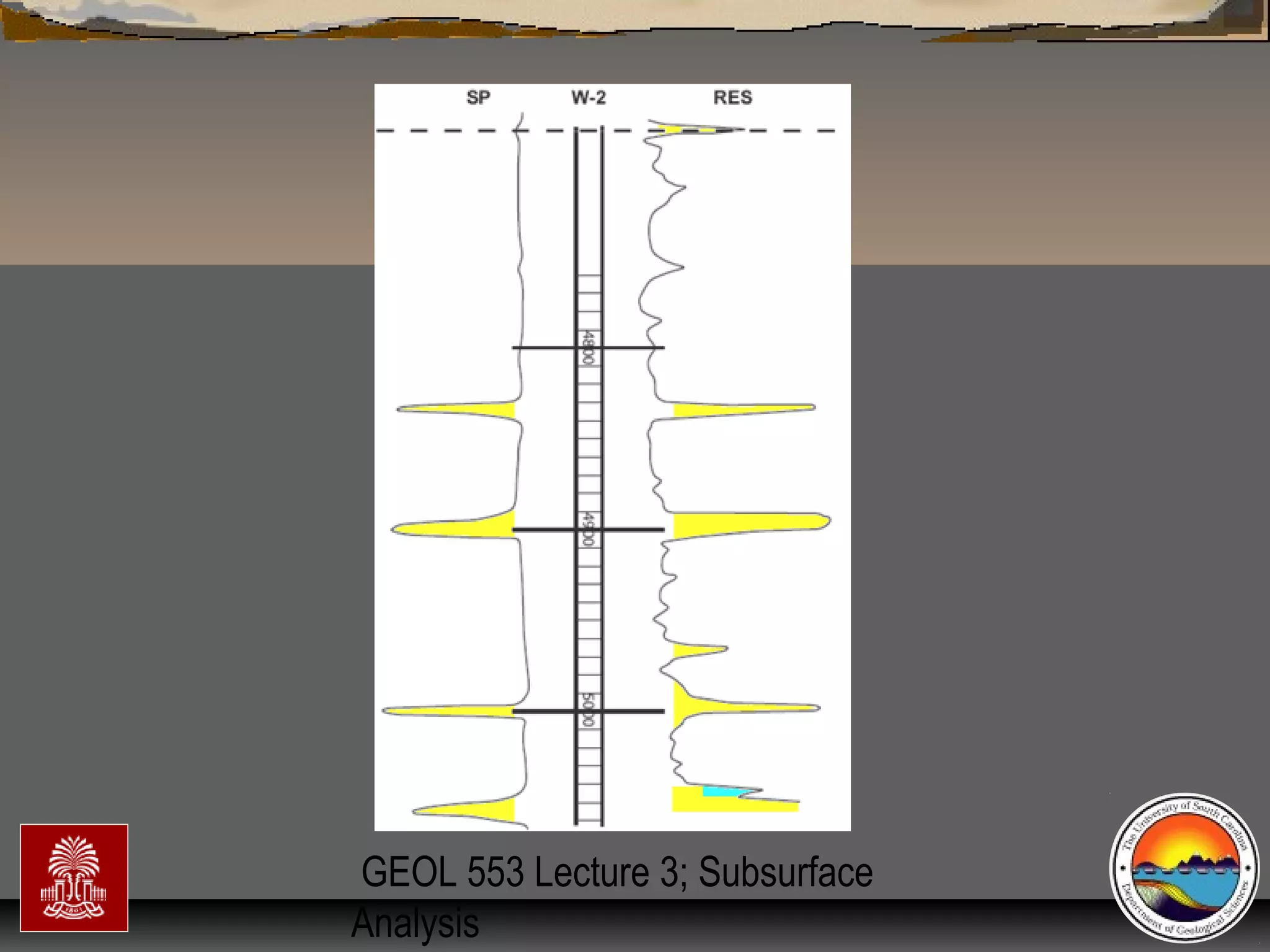
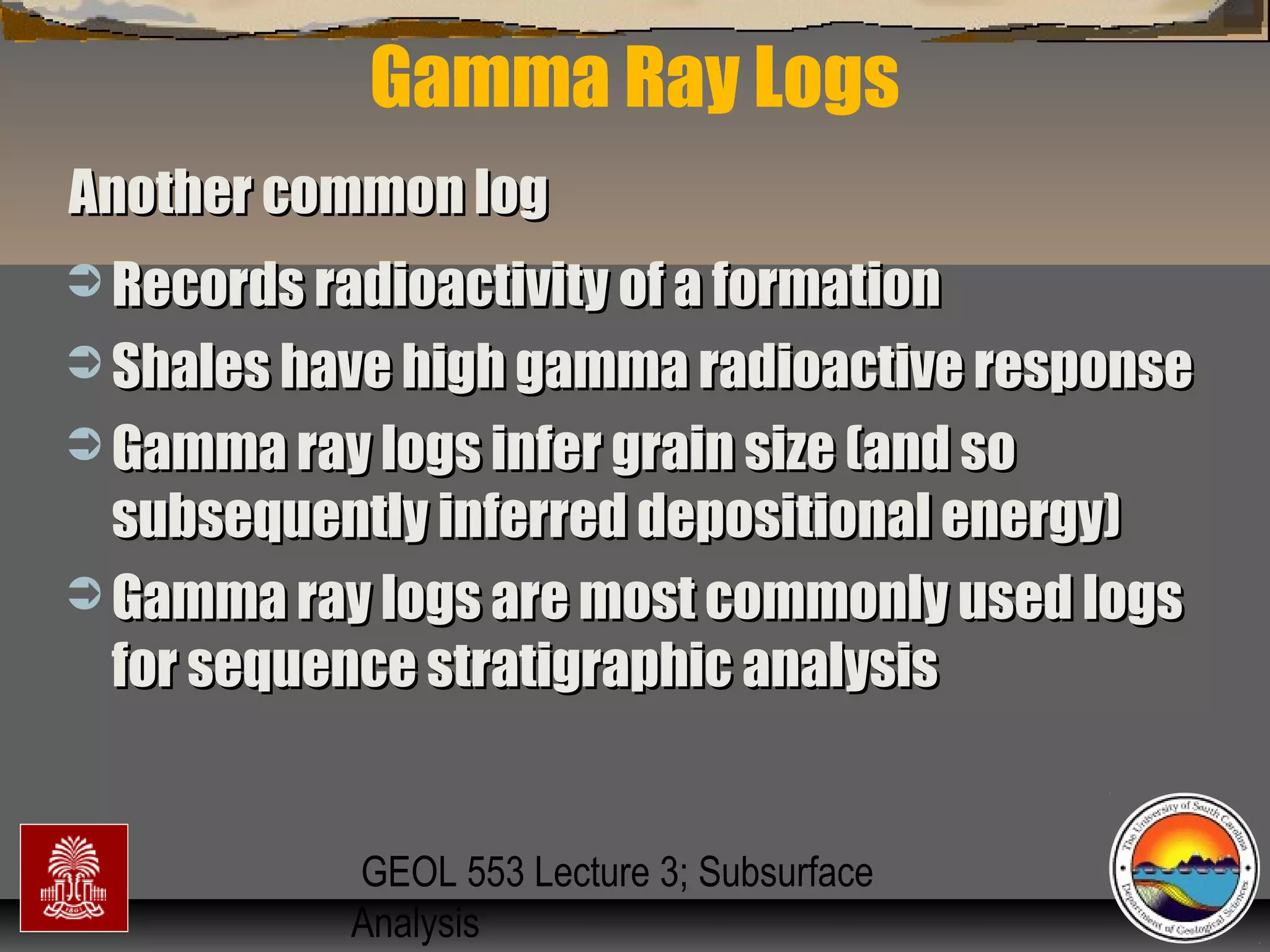
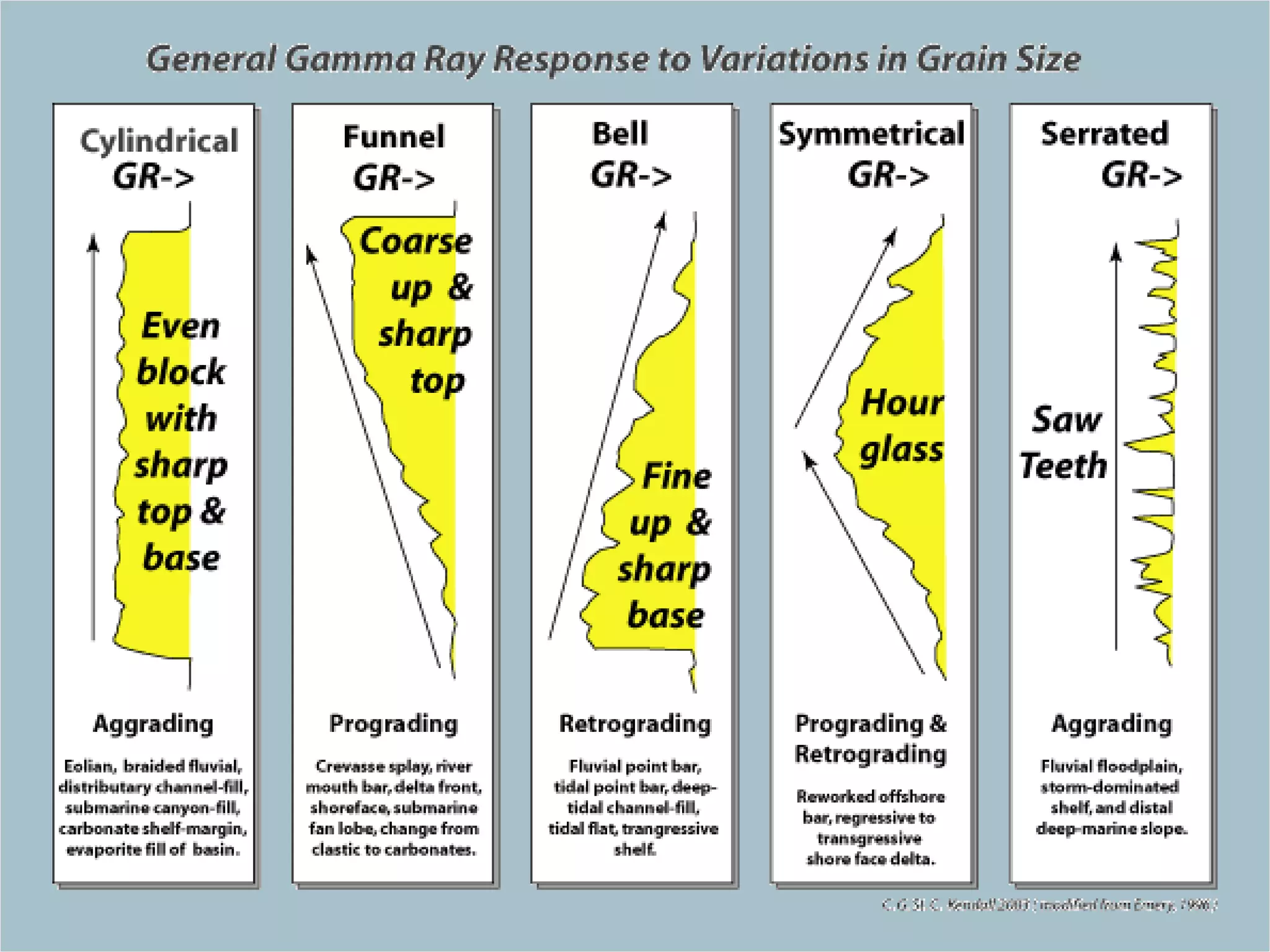
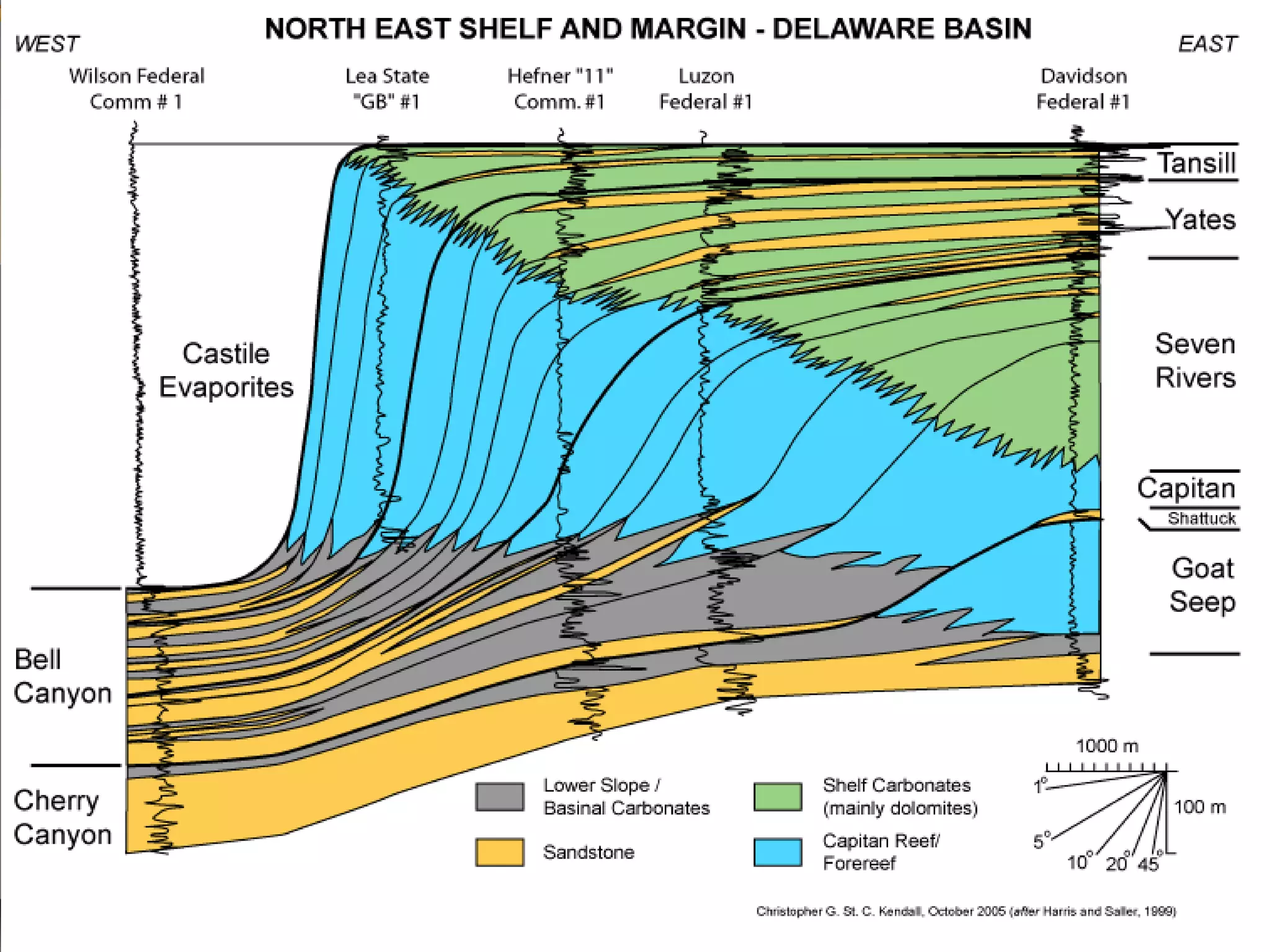
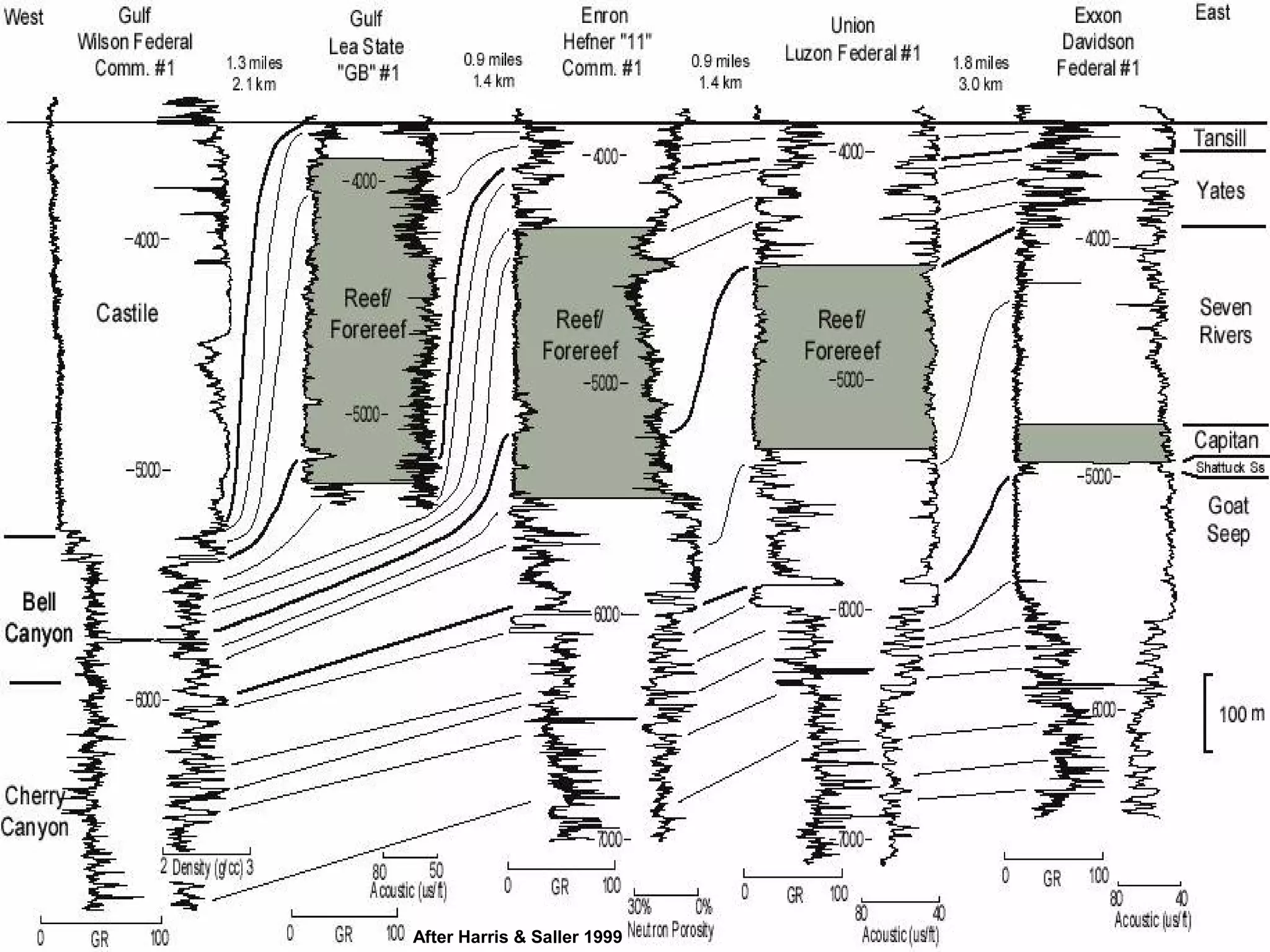
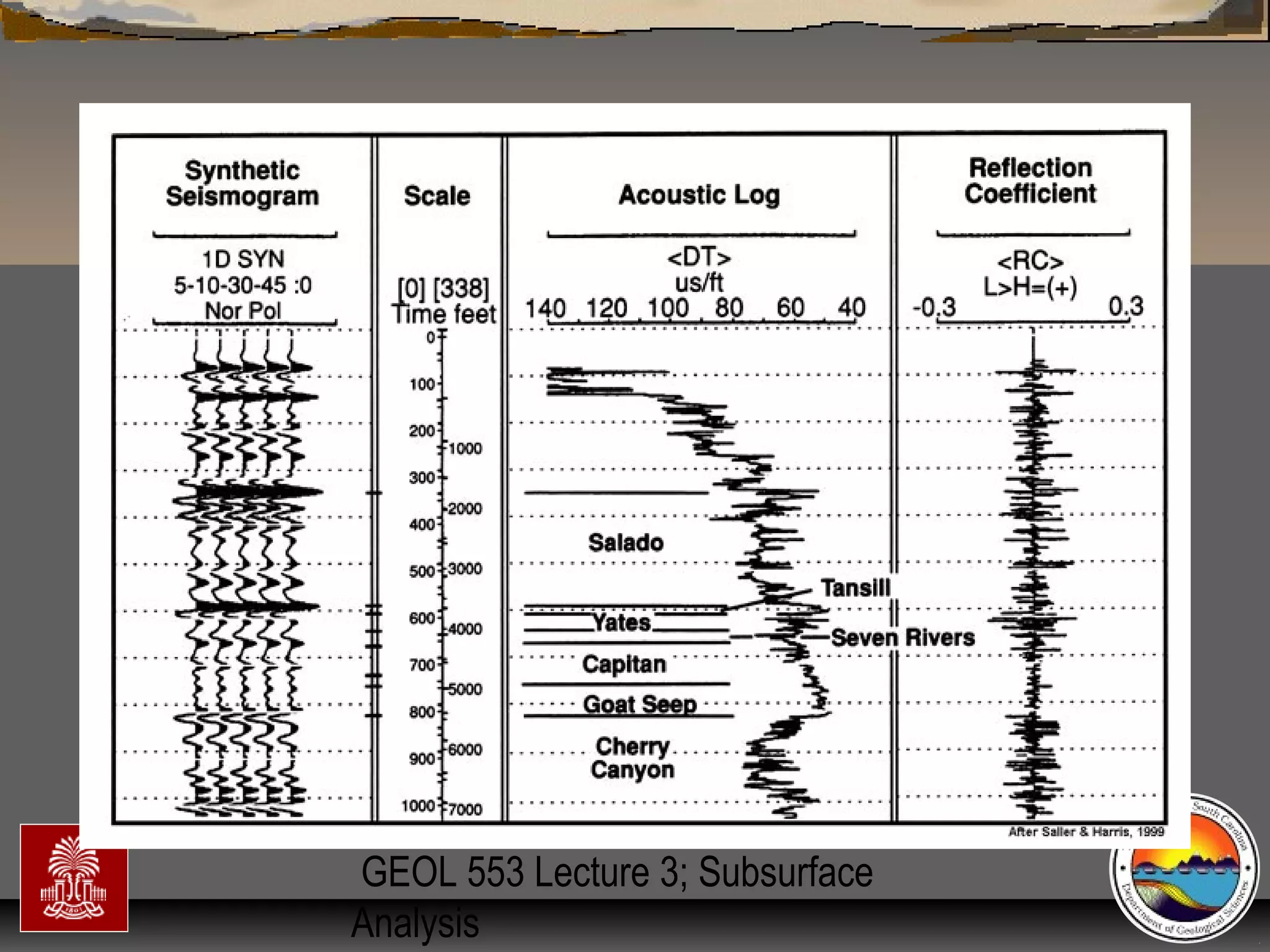
The document discusses the tools used for subsurface analysis in geology, including well logs, cores, seismic data, and gravity and magnetic surveys. It focuses on well logs and seismic data. Well logs provide high vertical resolution and help delimit bounding surfaces and establish lithology. Seismic data provide high lateral continuity and resolution to define sediment geometries. Together these tools are used for allostratigraphy and sequence stratigraphy by identifying bounding discontinuities and sequences reflecting changes in relative sea level.











![GEOL 553 Lecture 3; Subsurface
Analysis
Sequence Stratigraphy
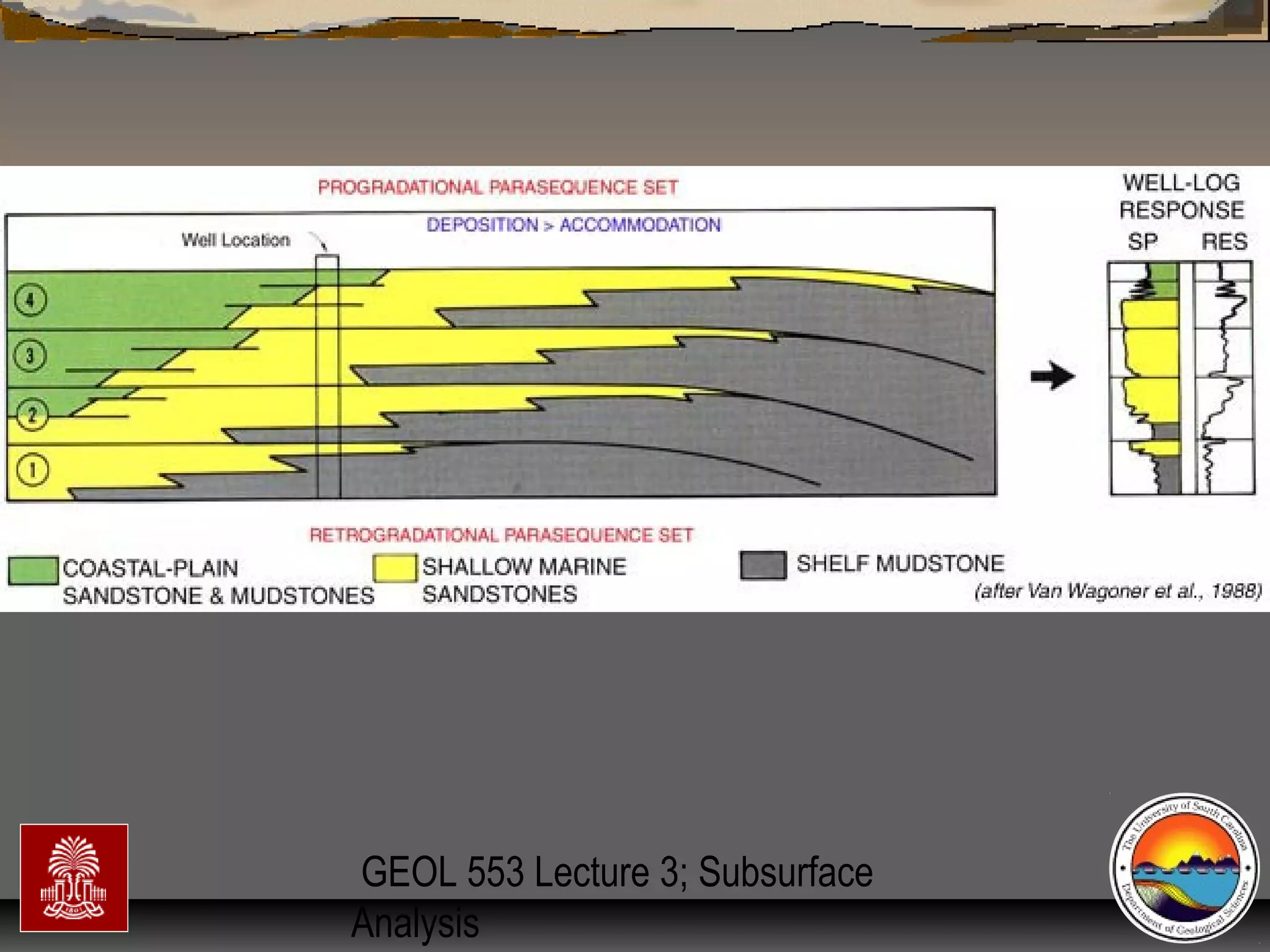
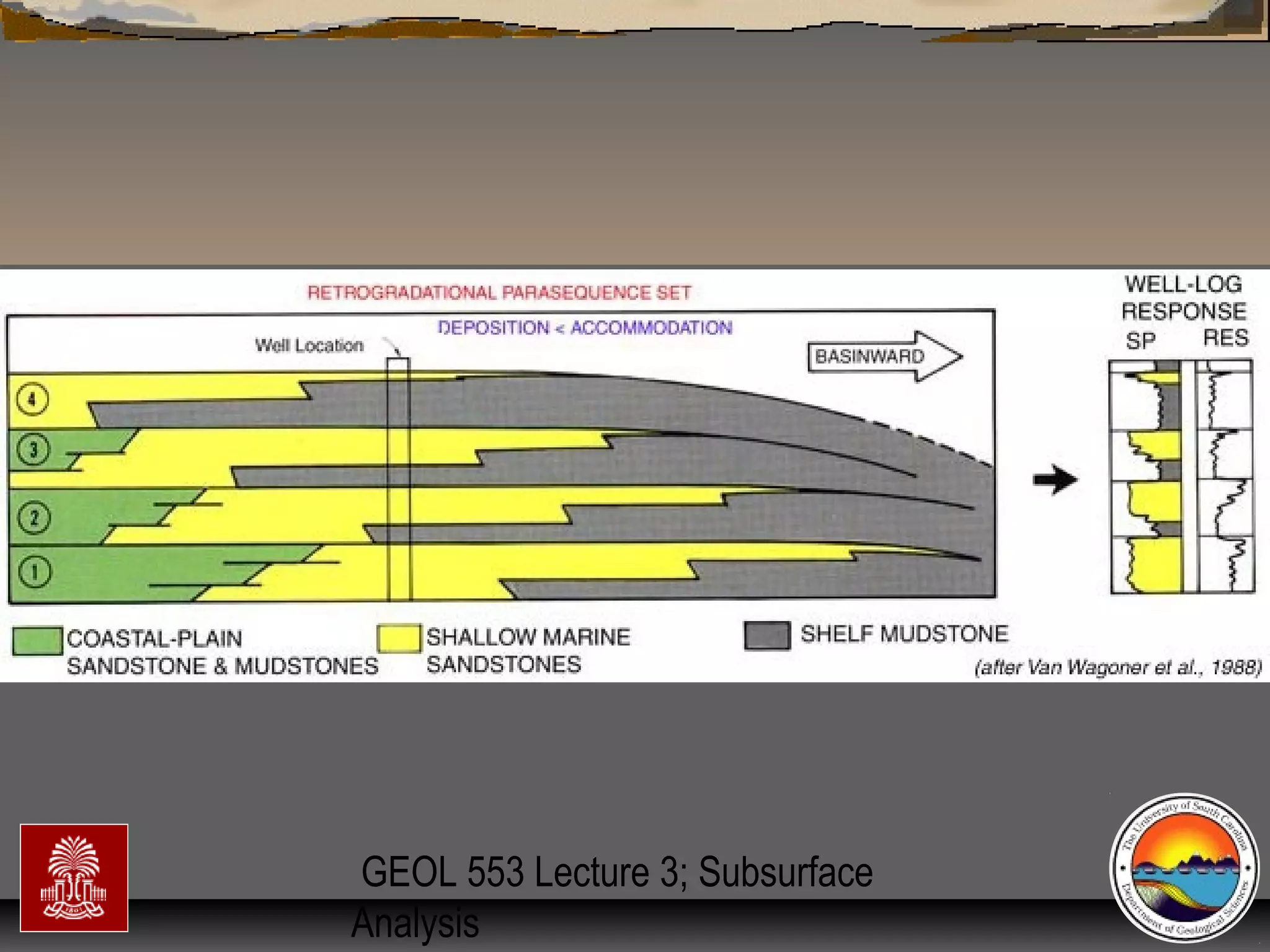
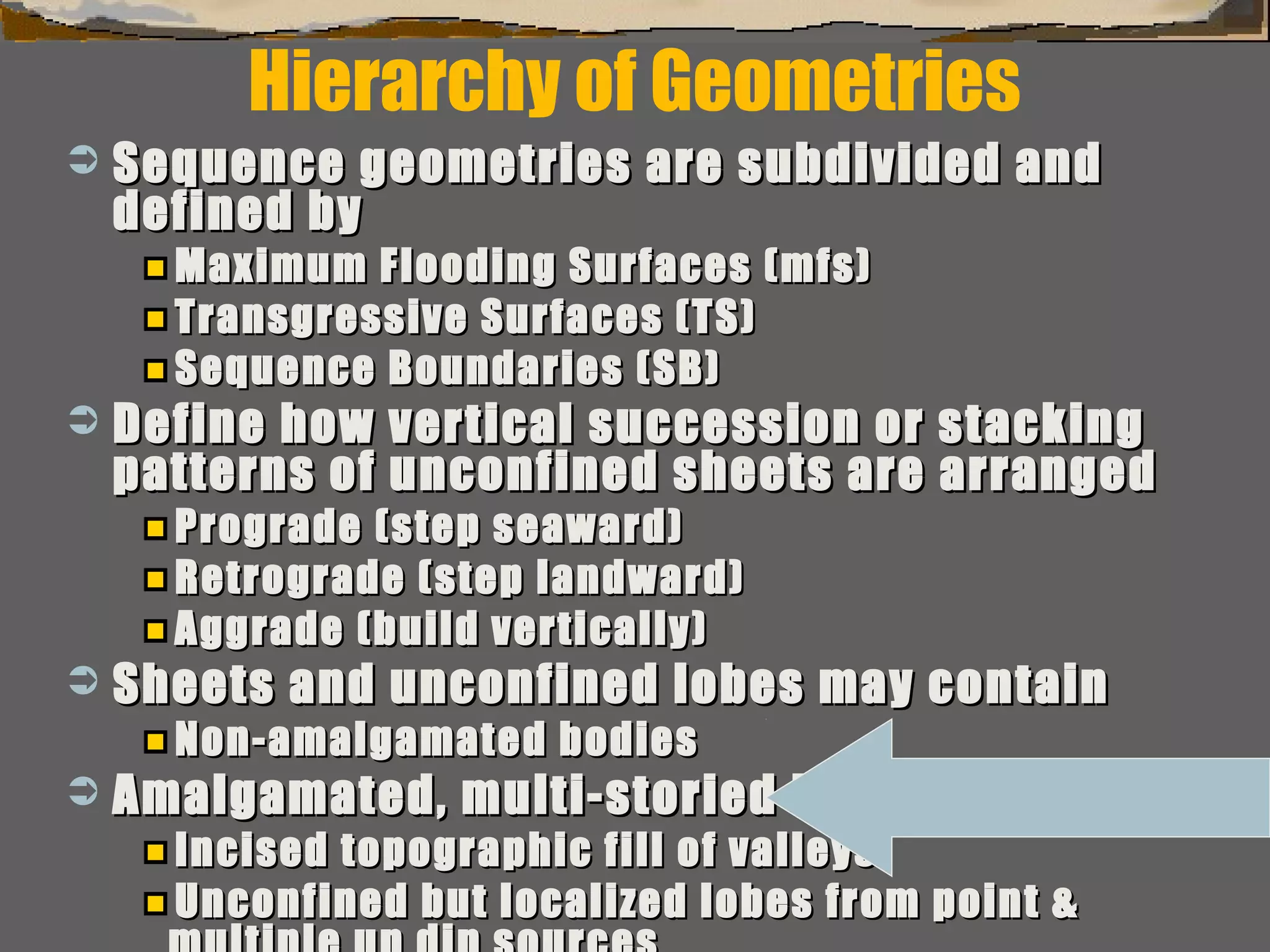
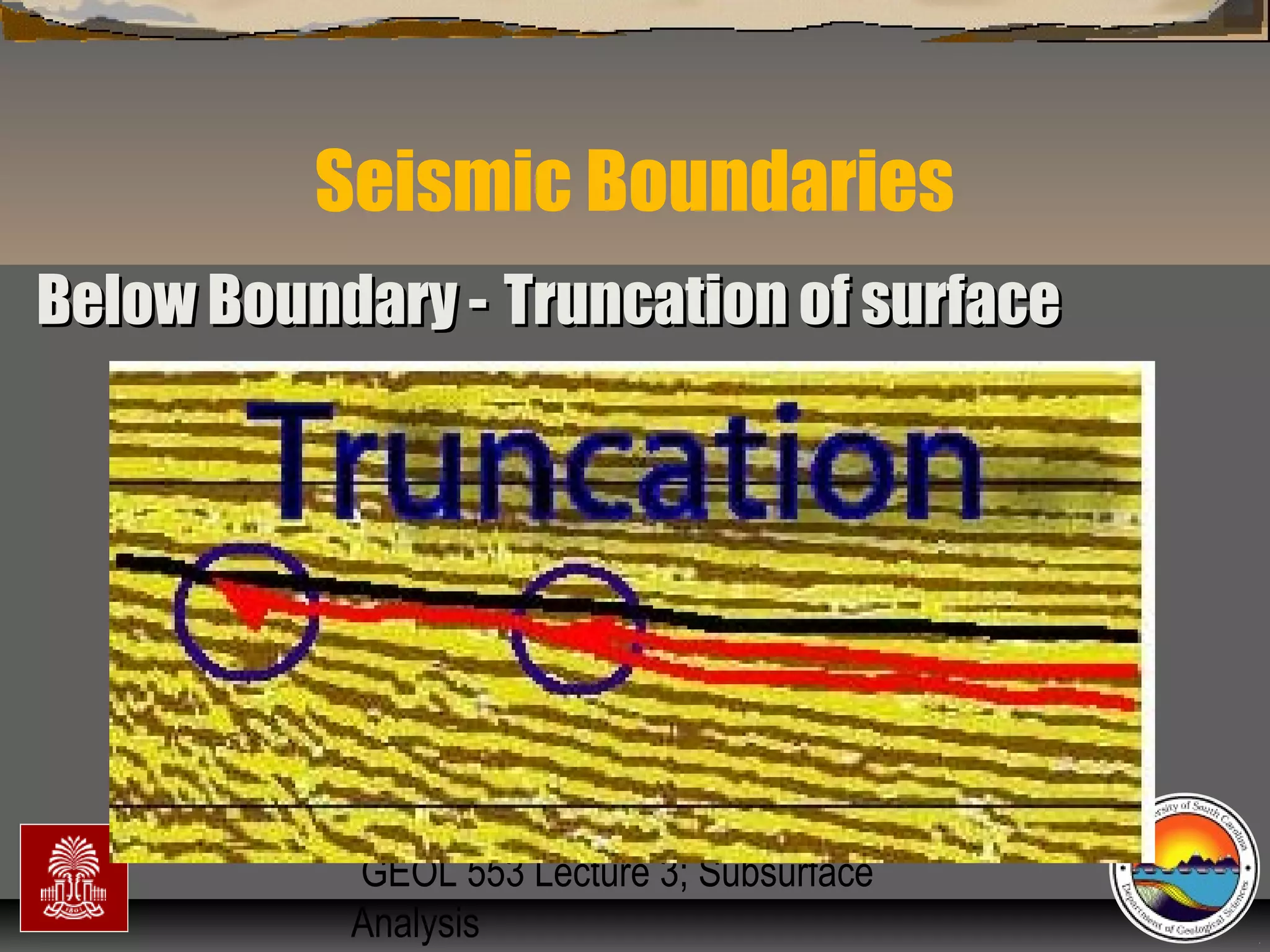
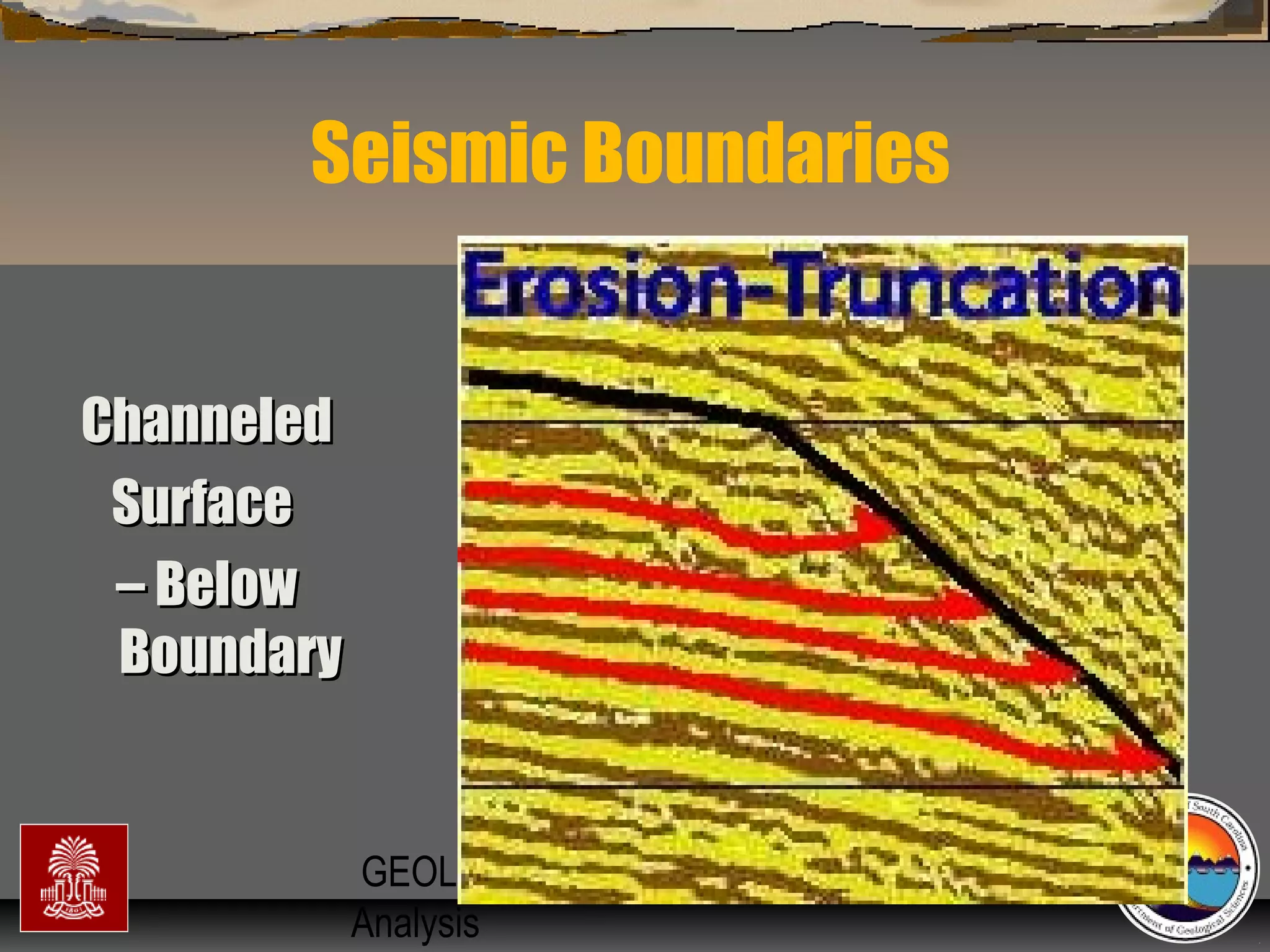
Surfaces of erosion & non-deposition (sequenceSurfaces of erosion & non-deposition (sequence
boundaries)boundaries)
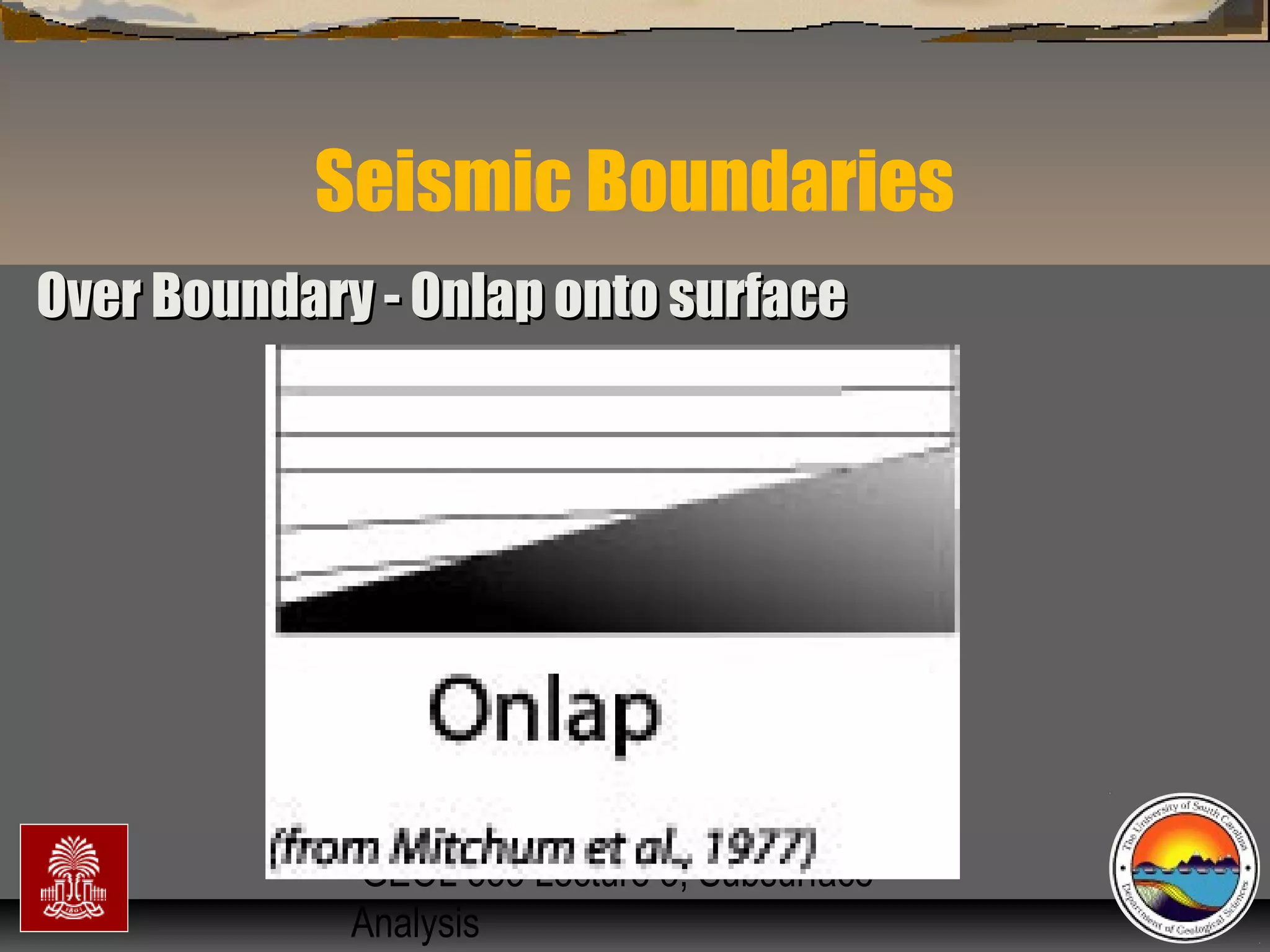
Flooding (trangressive surfaces [TS] &/orFlooding (trangressive surfaces [TS] &/or
maximum flooding surfaces [mfs]) & high standmaximum flooding surfaces [mfs]) & high stand
condensed surfacescondensed surfaces
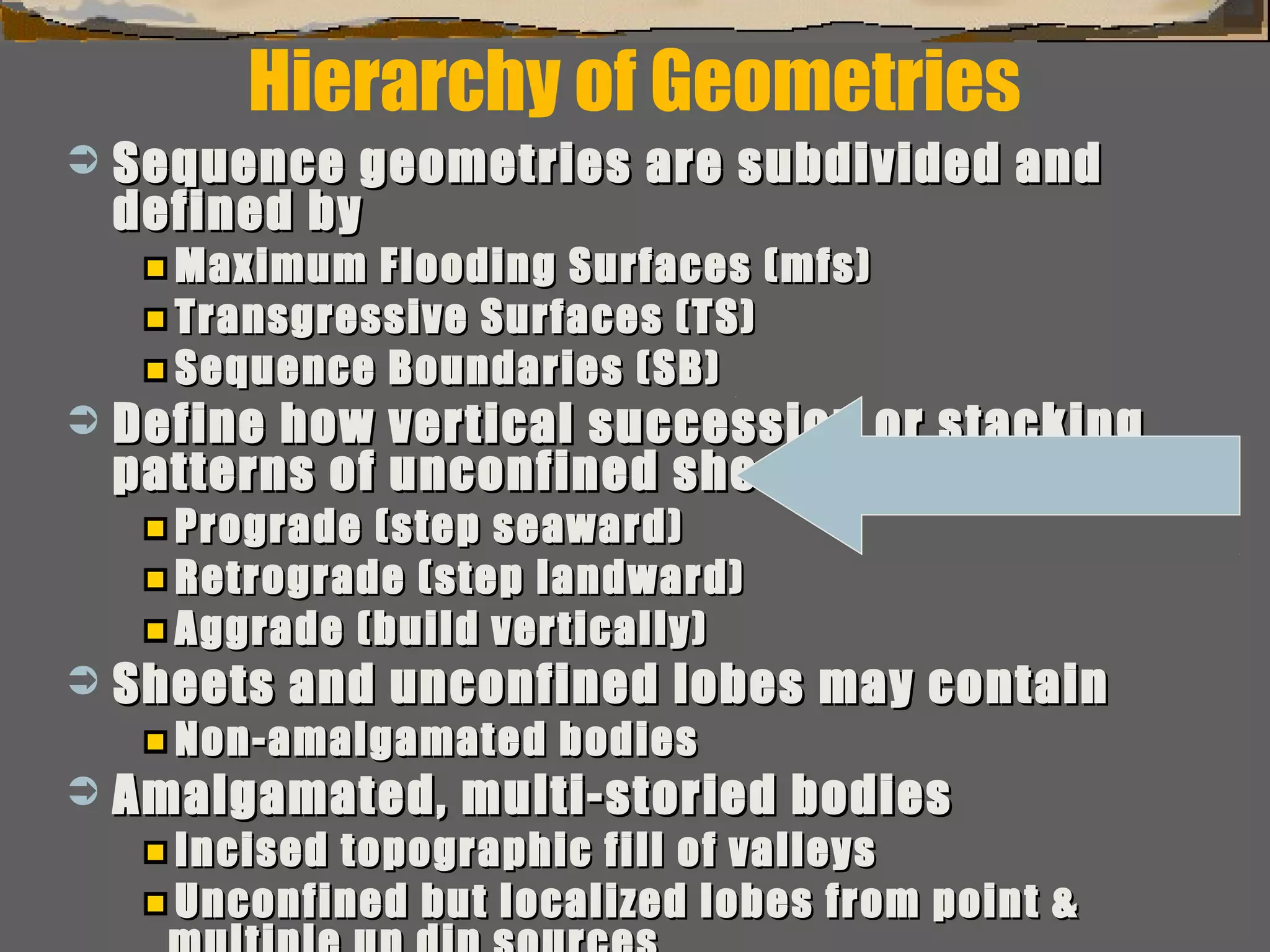
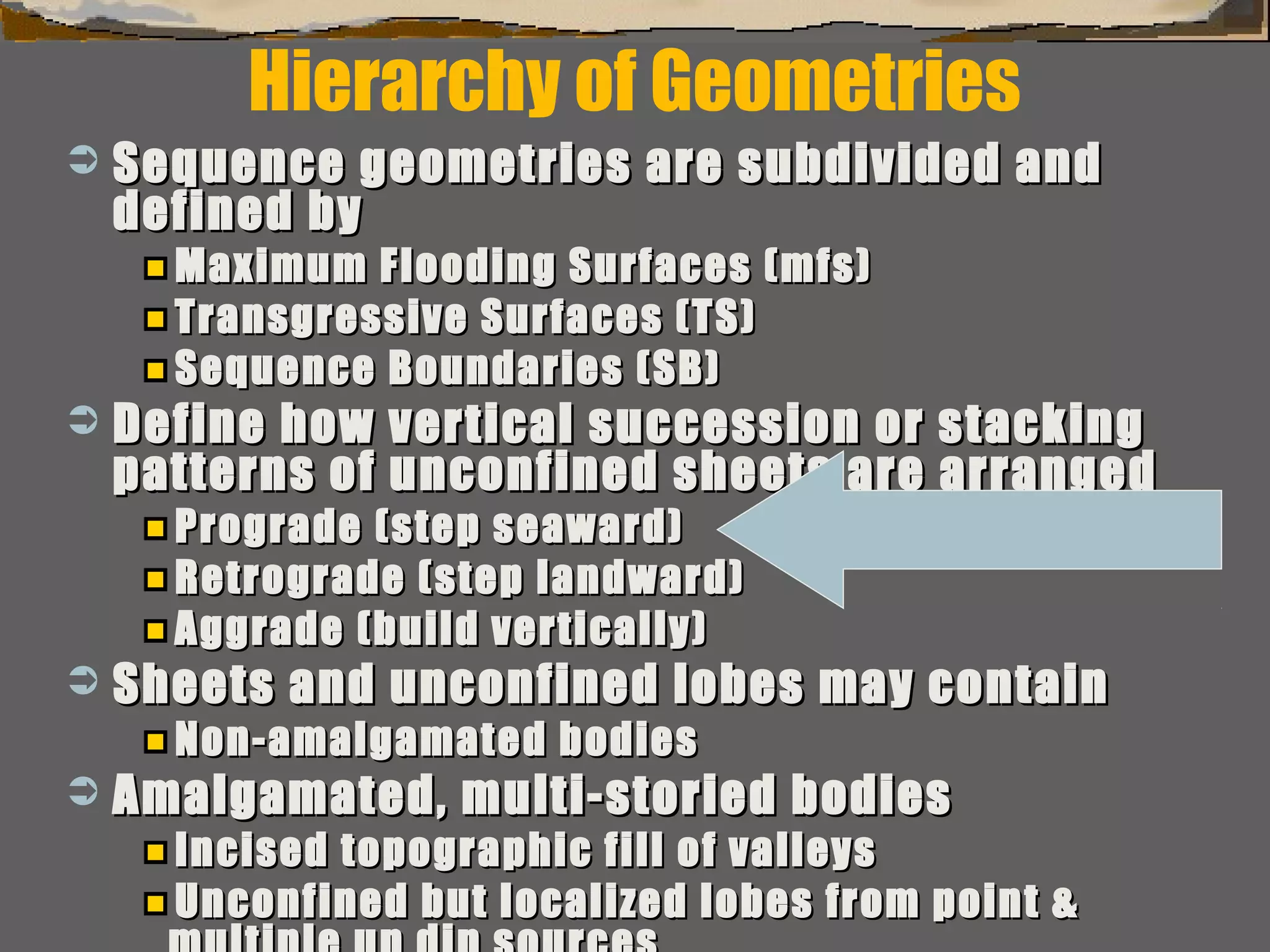
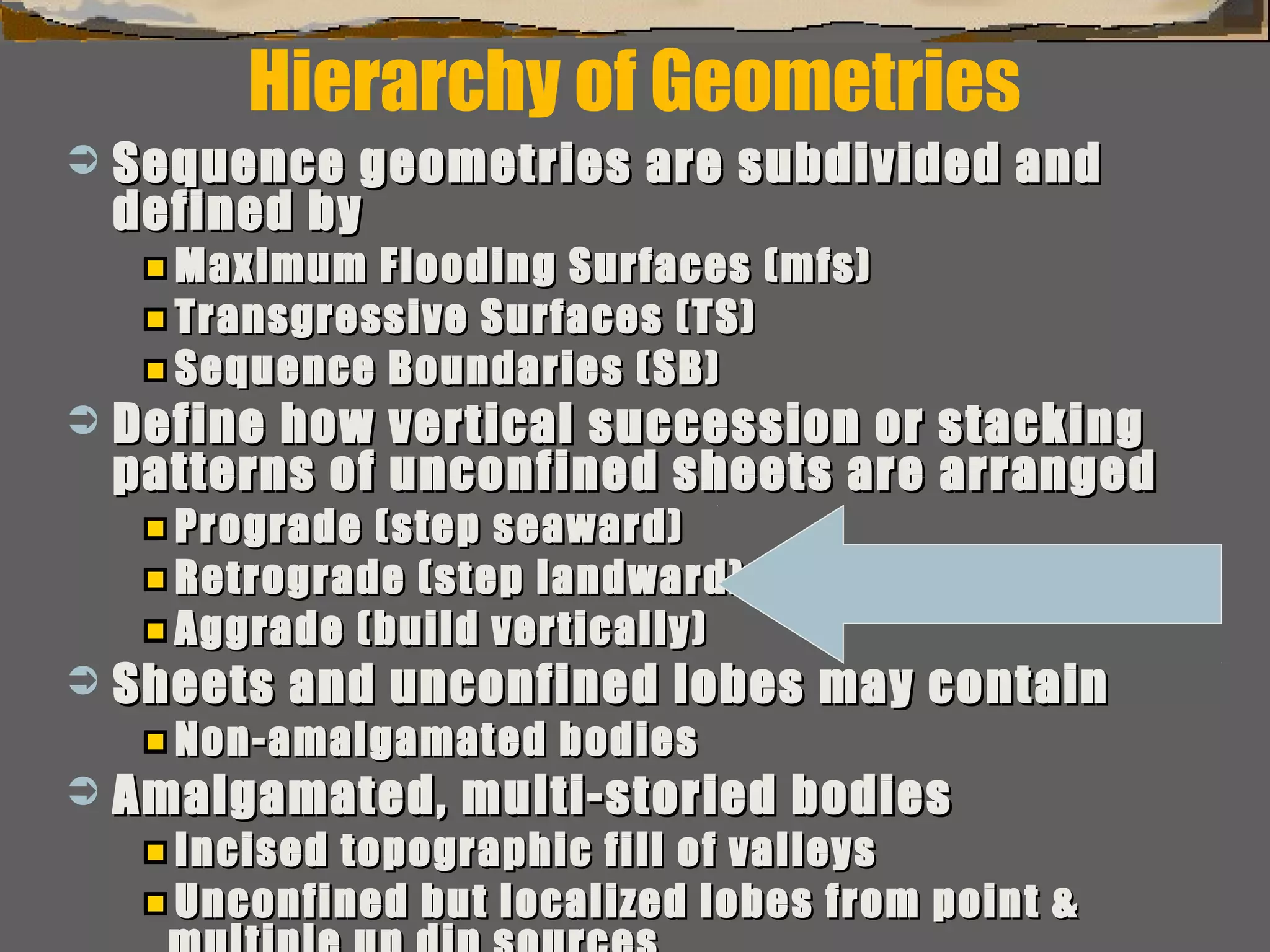
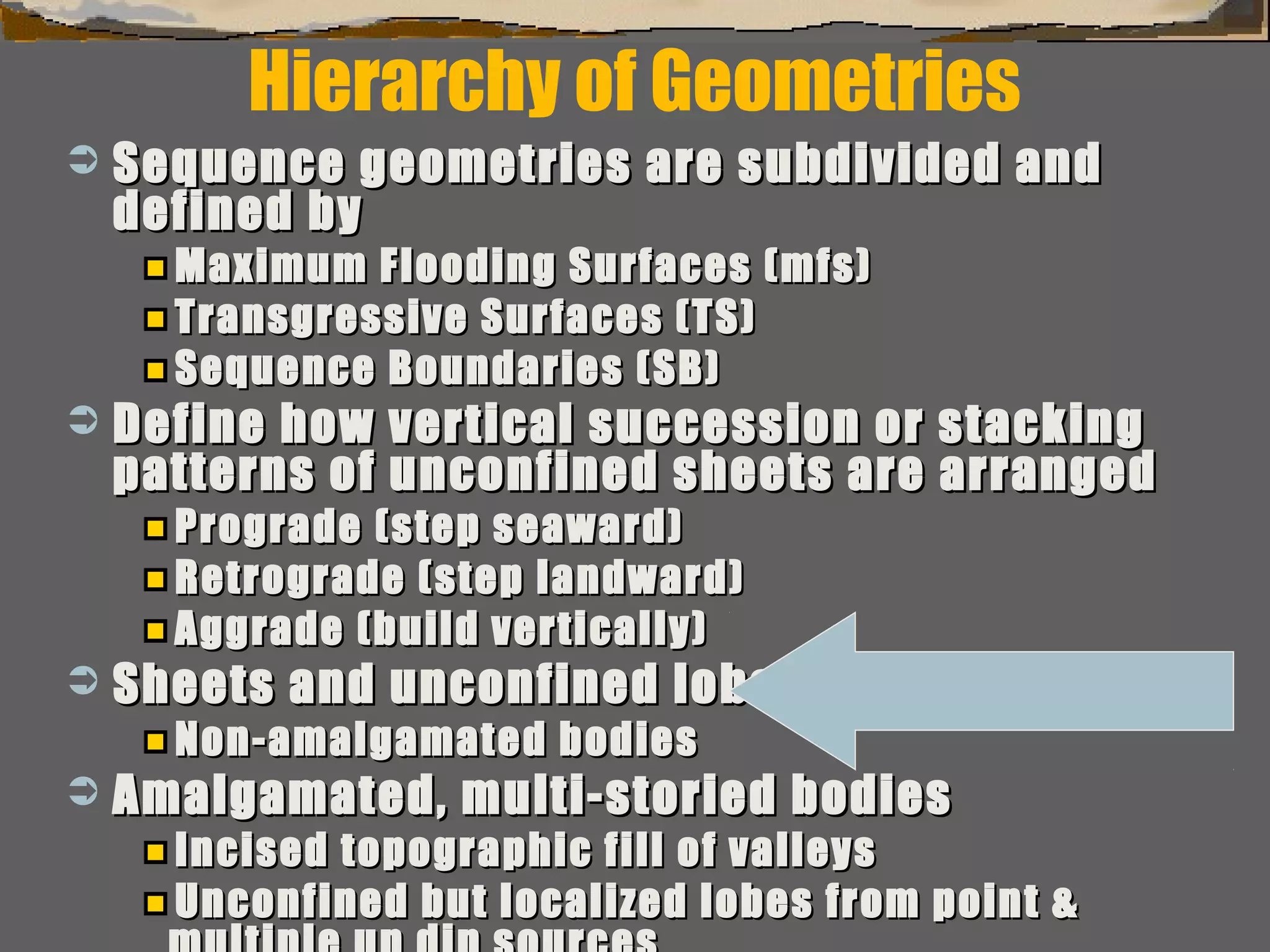
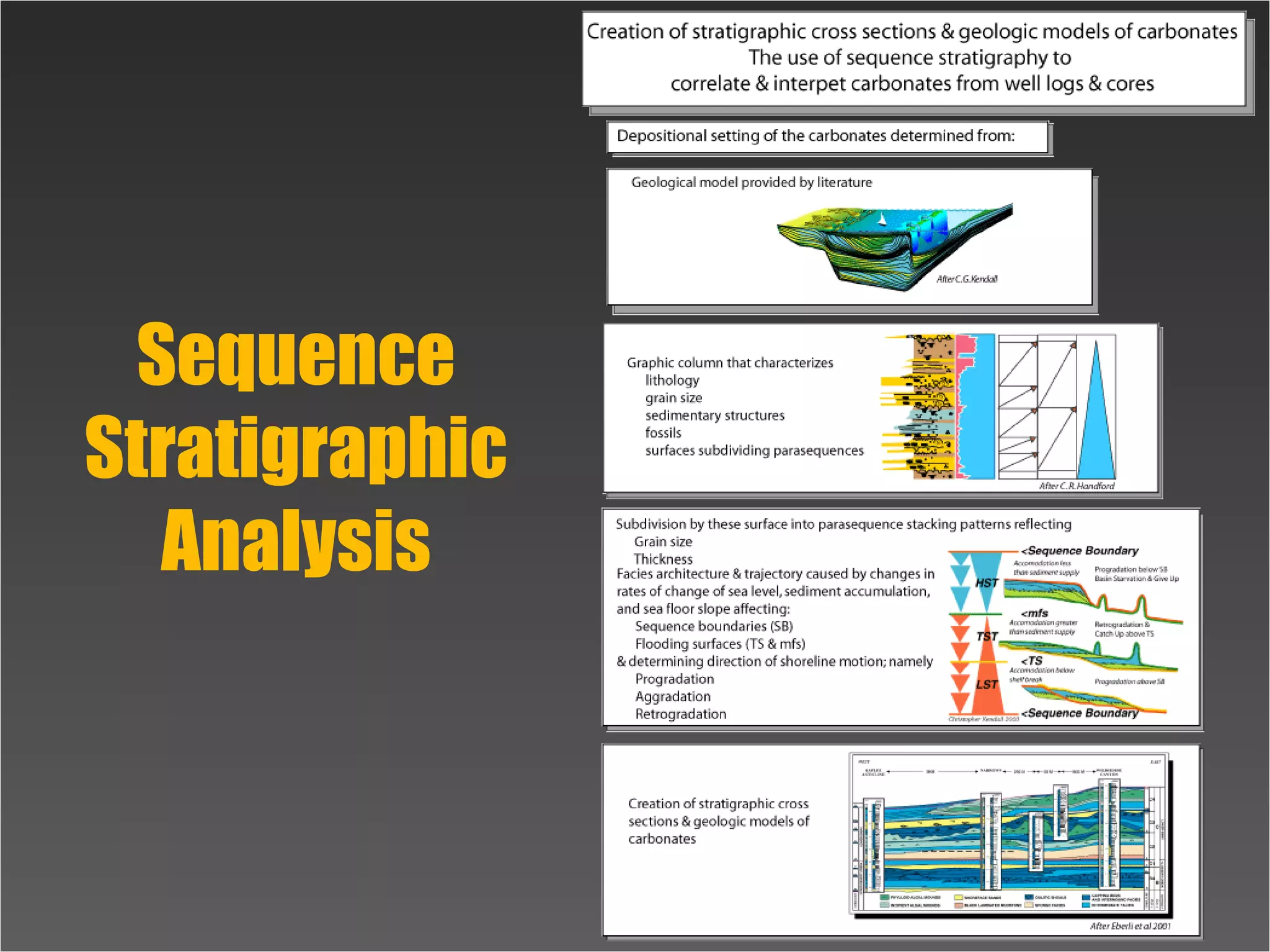
Subdivision & interpretation of sedimentarySubdivision & interpretation of sedimentary
record using a framework surfaces seen inrecord using a framework surfaces seen in
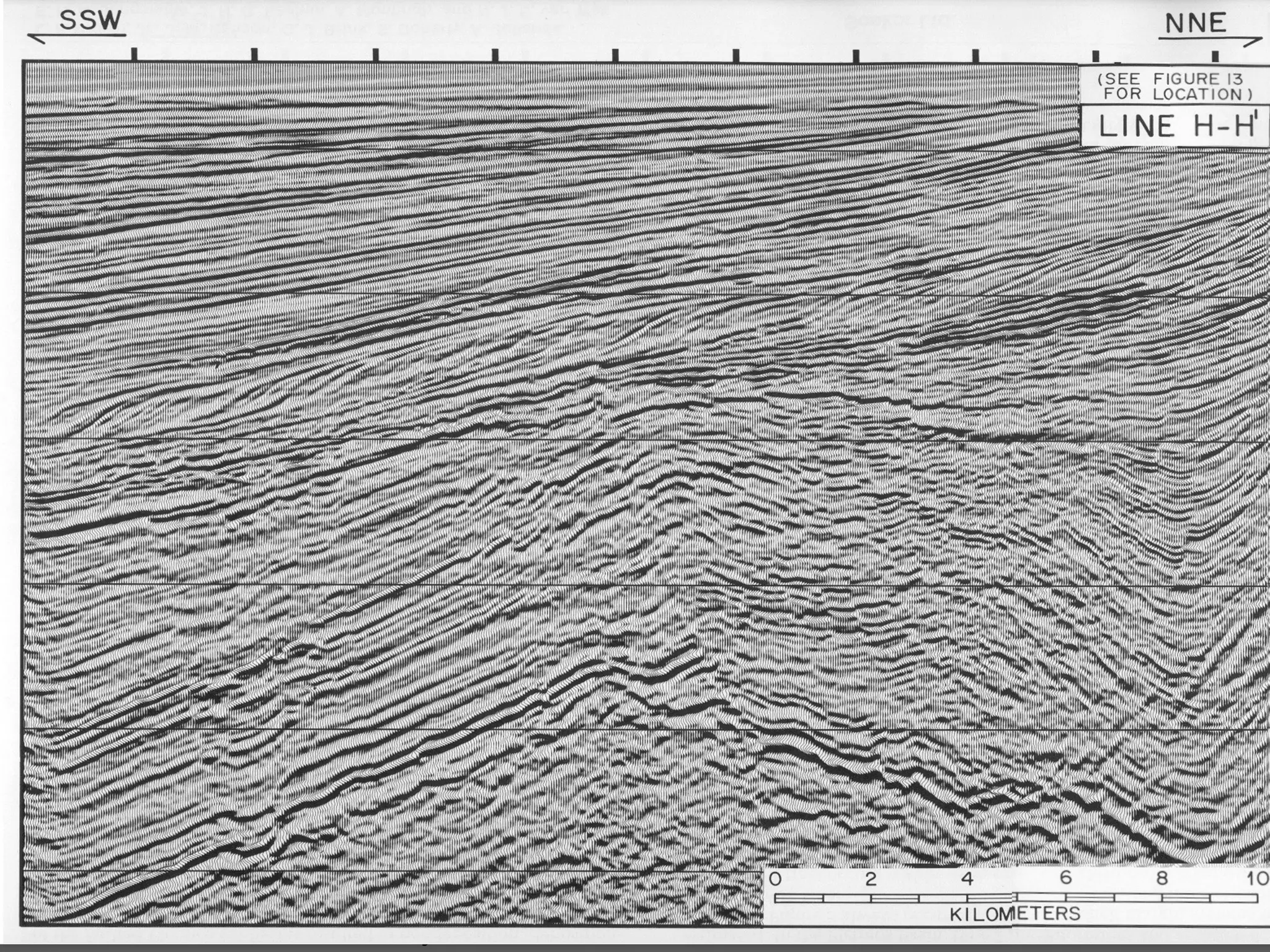
outcrops,outcrops, well logs, & 2-D and 3-D seismicwell logs, & 2-D and 3-D seismic..
Include:Include:
This framework used to predict the extentThis framework used to predict the extent
of sedimentary facies geometry, lithologicof sedimentary facies geometry, lithologic
character, grain size, sorting & reservoircharacter, grain size, sorting & reservoir
qualityquality](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tools4subsurfaceanalysis-181130084917/75/Tools-for-subsurface-analysis-34-2048.jpg)