Metabolic Fate of Pyruvate and Cori cycle and Alanine cycle Cori & Alanine cycle and Lactate Dehydrogenase Deficiency (LDHA) and Malate aspartate shuttle (cycle) and Glycerol phosphate shuttle and Mitochondrial shuttle
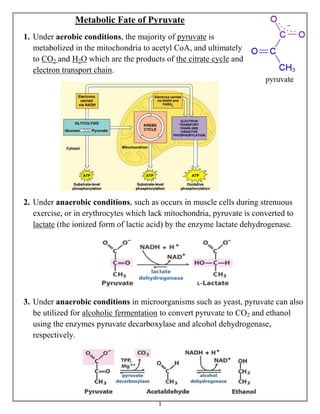
- 1. 1 Metabolic Fate of Pyruvate 1. Under aerobic conditions, the majority of pyruvate is metabolized in the mitochondria to acetyl CoA, and ultimately to CO2 and H2O which are the products of the citrate cycle and electron transport chain. 2. Under anaerobic conditions, such as occurs in muscle cells during strenuous exercise, or in erythrocytes which lack mitochondria, pyruvate is converted to lactate (the ionized form of lactic acid) by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase. 3. Under anaerobic conditions in microorganisms such as yeast, pyruvate can also be utilized for alcoholic fermentation to convert pyruvate to CO2 and ethanol using the enzymes pyruvate decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase, respectively.
- 2. 2 The Cori Cycle is important for peak performance in athletic competition • Athletes "warm down" after exercise to enhance circulation so that lactate will be cleared from the muscle and be used in the liver for glucose synthesis via the Cori cycle. • Pyruvate can also be converted anaerobically to ethanol and CO2 by fermentation in some microorganisms, or converted to lactate. Cori cycle • The Cori cycle, named after its discoverers, Carl Cori and Gerty Cori, refers to the metabolic pathway in which lactate produced by anaerobic glycolysis in the muscles moves to the liver and is converted to glucose, which then returns to the muscles and is converted back to lactate.
- 3. 3 Watch on YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ORIx2WYNWqs&list=PLTF9h- T1TcJhcNo9M1VFXz6rMKT6CM_wd&index=17
- 4. 4 • Cori cycle have two pathway: - in the muscle called glycolysis - In the liver called gluconeogenesis ○ The two pathway are continuous during muscle extensive work • Muscular activity requires energy, which is provided by the breakdown of glycogen in the skeletal muscles. • The breakdown of glycogen, a process known as glycogenolysis, releases glucose in the form of glucose-6-phosphate (G-6-P). • G-6-P is readily fed into glycolysis, a process that provides ATP to the muscle cells as an energy source. • During muscular activity, the store of ATP needs to be constantly replenished. • When the supply of oxygen is sufficient, this energy comes from feeding pyruvate, one product of glycolysis, into the Krebs cycle. • When oxygen supply is insufficient, typically during intense muscular activity, energy must be released through anaerobic respiration. • Anaerobic respiration converts pyruvate to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase. • Most important, fermentation regenerates NAD+ , maintaining the NAD+ concentration so that additional glycolysis reactions can occur. • The fermentation step oxidizes the NADH produced by glycolysis back to NAD+ , transferring two electrons from NADH to reduce pyruvate into lactate.
- 5. 5 • Instead of accumulating inside the muscle cells, lactate produced by anaerobic fermentation is taken up by the liver. • This initiates the other half of the Cori cycle. • In the liver, gluconeogenesis occurs. • From an intuitive perspective, gluconeogenesis reverses both glycolysis and fermentation by converting lactate first into pyruvate, and finally back to glucose. • The glucose is then supplied to the muscles through the bloodstream; it is ready to be fed into further glycolysis reactions. • If muscle activity has stopped, the glucose is used to replenish the supplies of glycogen through glycogenesis. • Overall, the glycolysis part of the cycle produces 2 ATP molecules at a cost of 6 ATP molecules consumed in the gluconeogenesis part. • Each iteration of the cycle must be maintained by a net consumption of 4 ATP molecules. • As a result, the cycle cannot be sustained indefinitely. • The intensive consumption of ATP molecules indicates that the Cori cycle shifts the metabolic burden from the muscles to the liver. ♣ Significance The cycle's importance is based on the prevention of lactic acidosis in the muscle under anaerobic conditions. However, normally before this happens the lactic acid is moved out of the muscles and into the liver. The cycle is also important in producing ATP, an energy source, during muscle activity. The Cori cycle functions more efficiently when muscle activity has ceased. This allows the oxygen debt to be repaid such that the Kreb's cycle and electron transport chain can produce energy at peak efficiency.
- 6. 6 Alanine cycle Cori & Alanine cycle • The alanine cycle is quite similar to the Cori cycle. - Alanine is non-essential amino acid therefore it can produced or converted to other forms. • When muscles produce lactate during times of decreased oxygen, they also produce alanine. • This alanine is shuttled to the liver where it is used to make glucose. • The alanine cycle is less productive than the Cori Cycle, which uses lactate, since a byproduct of energy production from alanine is production of urea. • Removal of the urea is energy-dependent, thus the net ATP produced is less than that found in the Cori Cycle. • However, unlike in the Cori Cycle, NADH is conserved because lactate is not formed.
- 7. 7 • This allows for it to be oxidized via the electron transport chain. • This pathway requires the presence of alanine aminotransferase (Transaminases), which is restricted to tissues such as muscle, liver, and the intestine. • Therefore, this pathway is used instead of the Cori Cycle only when an aminotransferase is present and when there is a need to transfer ammonia to the liver. • Get rid of lactate prevent acidosis and reduce glucose but get rid of alanine it reduce ammonia which is very dangerous to brain, and body converted it to urea therefore alanine cycle is not preferable at the body to produce energy (less frequent than Cori cycle). ♣ Alanine cycle also serves other purposes: • Recycles carbon skeletons between muscle and liver • Transports NH4+ to the liver and is converted into urea. ◘ Draw the relation between Cori cycle and alanine cycle. (Question)
- 8. 8 Lactate Dehydrogenase Deficiency (LDHA) • These patients cannot maintain moderate levels of exercise due to an inability to utilize glycolysis to produce ATP needed for muscle contraction under anaerobic conditions. (Suffer from fatigue) • When lactate dehydrogenase levels are insufficient, the level of NAD+ becomes limiting during exercise and flux through the glyceraldehyde-3-P dehydrogenase reaction is inhibited (Step in glycolysis). Malate aspartate shuttle (cycle)
- 9. 9
- 10. 10 Draw Malate oxaloacetate shuttle (Question) • Some ketones body doesn’t have the ability to getting into mitochondria matrix as pyruvate, oxaloacetate, β-hydroxybutyric acid and acetone. • The malate-aspartate shuttle function Is to convert keto acid (oxaloacetate) to non essential amino acid (Aspartate). • The malate-aspartate shuttle (sometimes also the malate shuttle) is a biochemical system for translocating electrons produced during glycolysis across the semipermeable inner membrane of the mitochondrion for oxidative phosphorylation in eukaryotes. • These electrons enter the electron transport chain of the mitochondria via reduction equivalents to generate ATP. • The shuttle system is required because the mitochondrial inner membrane is impermeable to NADH, the primary reducing equivalent of the electron transport chain.
- 11. 11 • To circumvent this, malate carries the reducing equivalents across the membrane. • The primary enzyme in the malate-aspartate shuttle is malate dehydrogenase. • Malate dehydrogenase is present in two forms in the shuttle system: - Mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase and Cytosolic malate dehydrogenase. • The two malate dehydrogenases are differentiated by their location and structure, and catalyze their reactions in opposite directions in this process. • First, in the cytosol, malate dehydrogenase catalyses the reaction of oxaloacetate and NADH to produce malate and NAD+ . • In this process, two electrons generated from NADH, and an accompanying H+ , are attached to oxaloacetate to form malate. Glycerol phosphate shuttle • The glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle is a mechanism that regenerates NAD+ from NADH, a by-product of glycolysis. • Its importance in transporting reducing equivalents is secondary to the malate- aspartate shuttle. • In this shuttle, the enzyme called cytoplasmic glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 (GPDH-C) converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) (2) to glycerol 3-phosphate (G-3-P) (1) by oxidizing one molecule of NADH to NAD+ as in the following reaction:
- 12. 12 • When the cell doesn’t need energy excess of G-3-P converted into DHAP - DHAP is competitive inhibitor of the Aldolase enzyme. • Glycerol-3-phosphate gets converted back to dihydroxyacetone phosphate by an inner membrane-bound mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 2 (GPDH-M), this time reducing one molecule of enzyme-bound flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) to FADH2. • FADH2 then reduces coenzyme Q (ubiquinone to ubiquinol) which enters into oxidative phosphorylation. • This reaction is irreversible. • The glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle allows the NADH synthesized in the cytosol by glycolysis to contribute to the oxidative phosphorylation pathway in the mitochondria to generate ATP. • It has been found in animals, fungi, and plants
- 13. 13 Mitochondrial shuttle • The mitochondrial shuttles are systems used to transport reducing agents across the inner mitochondrial membrane. • NADH cannot cross the membrane, but it can reduce another molecule that can cross the membrane, so that its electrons can reach the electron transport chain. • The two main systems in humans are: • In humans, the glycerol phosphate shuttle is primarily found in brown adipose tissue, as the conversion is less efficient, thus generating heat, which is one of the main purposes of brown fat. • It is primarily found in babies, though it is present in small amounts in adults around the kidneys and on the back of our necks. • The malate-aspartate shuttle is found in much of the rest of the body.
