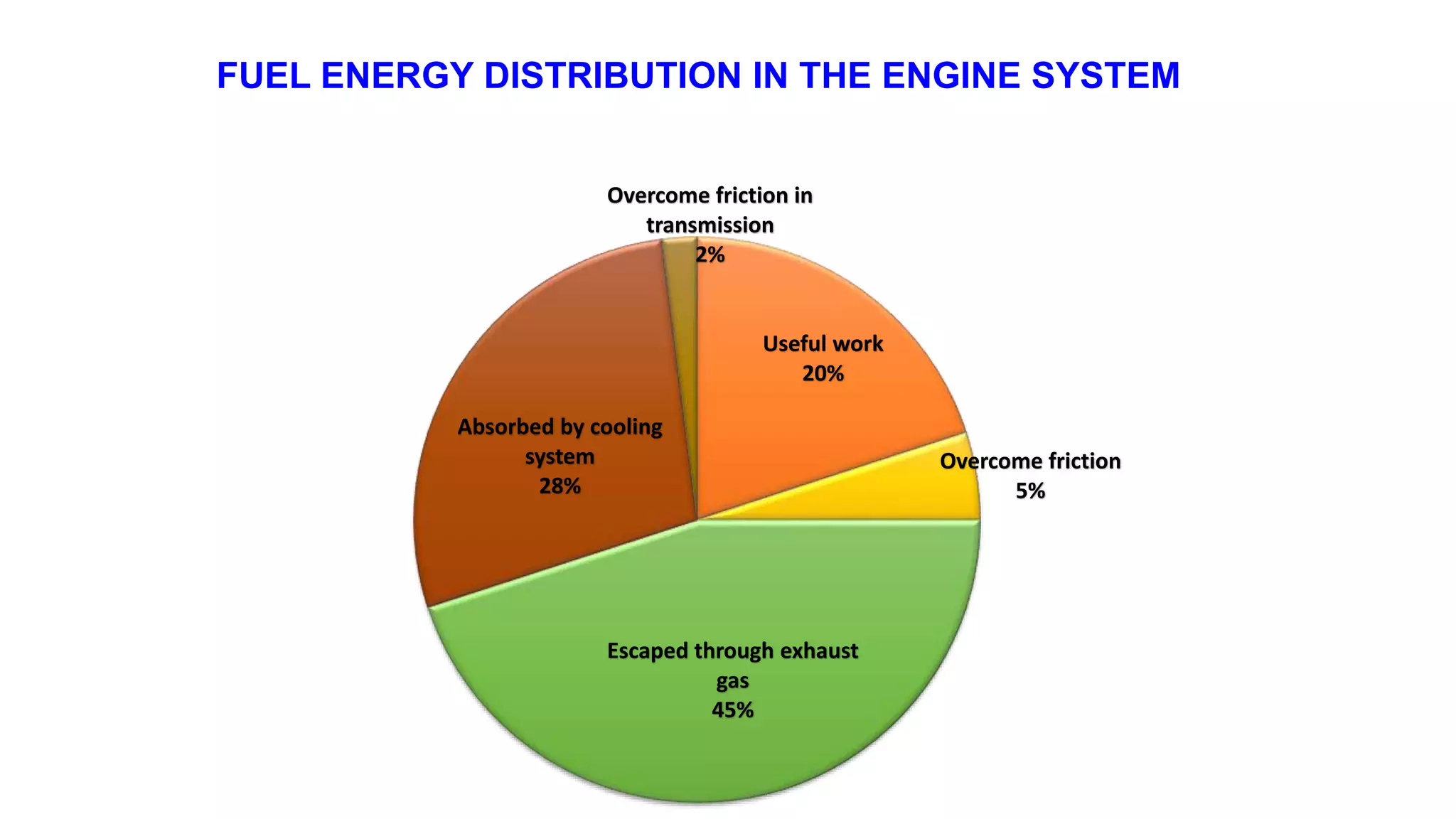
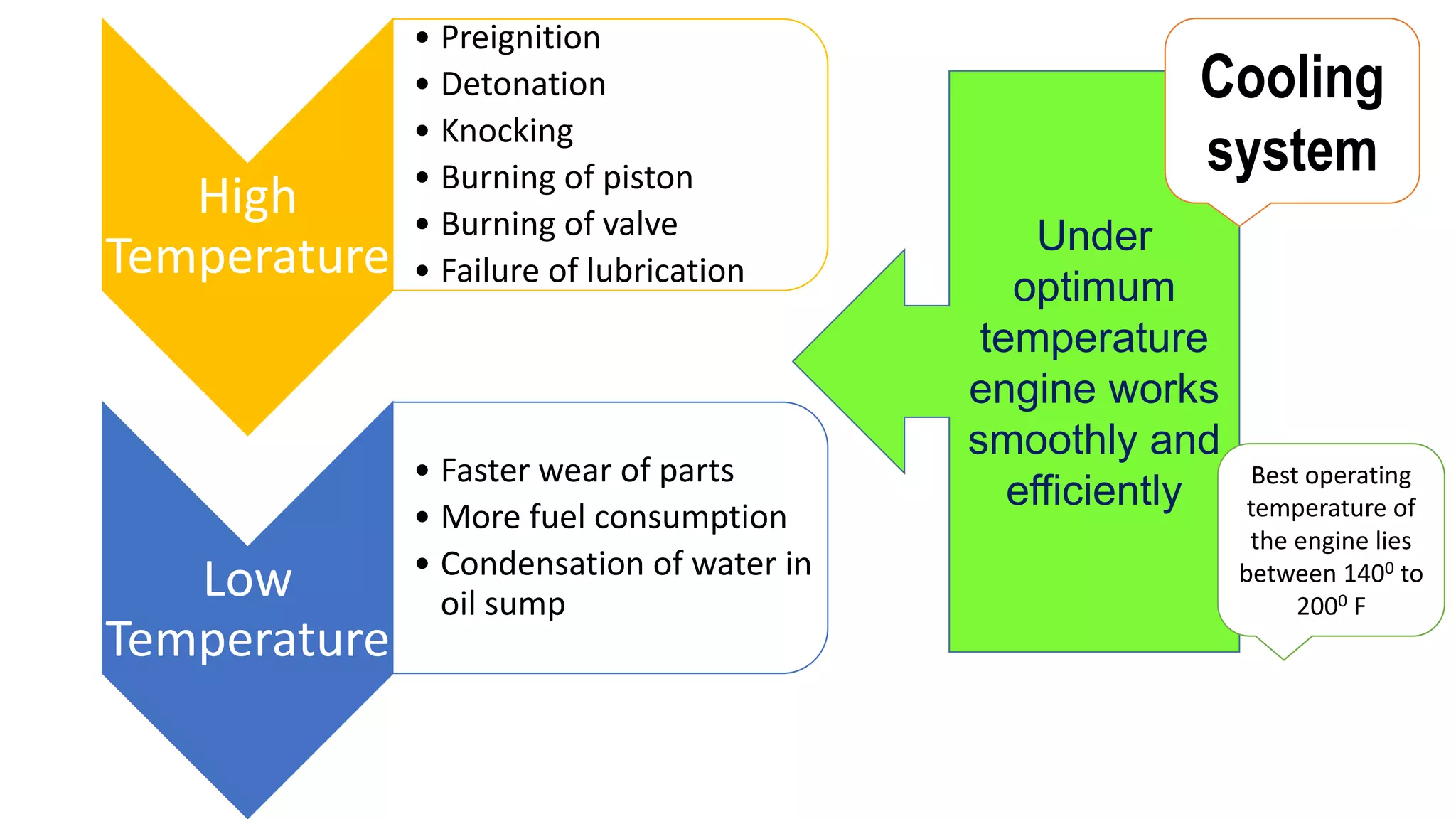
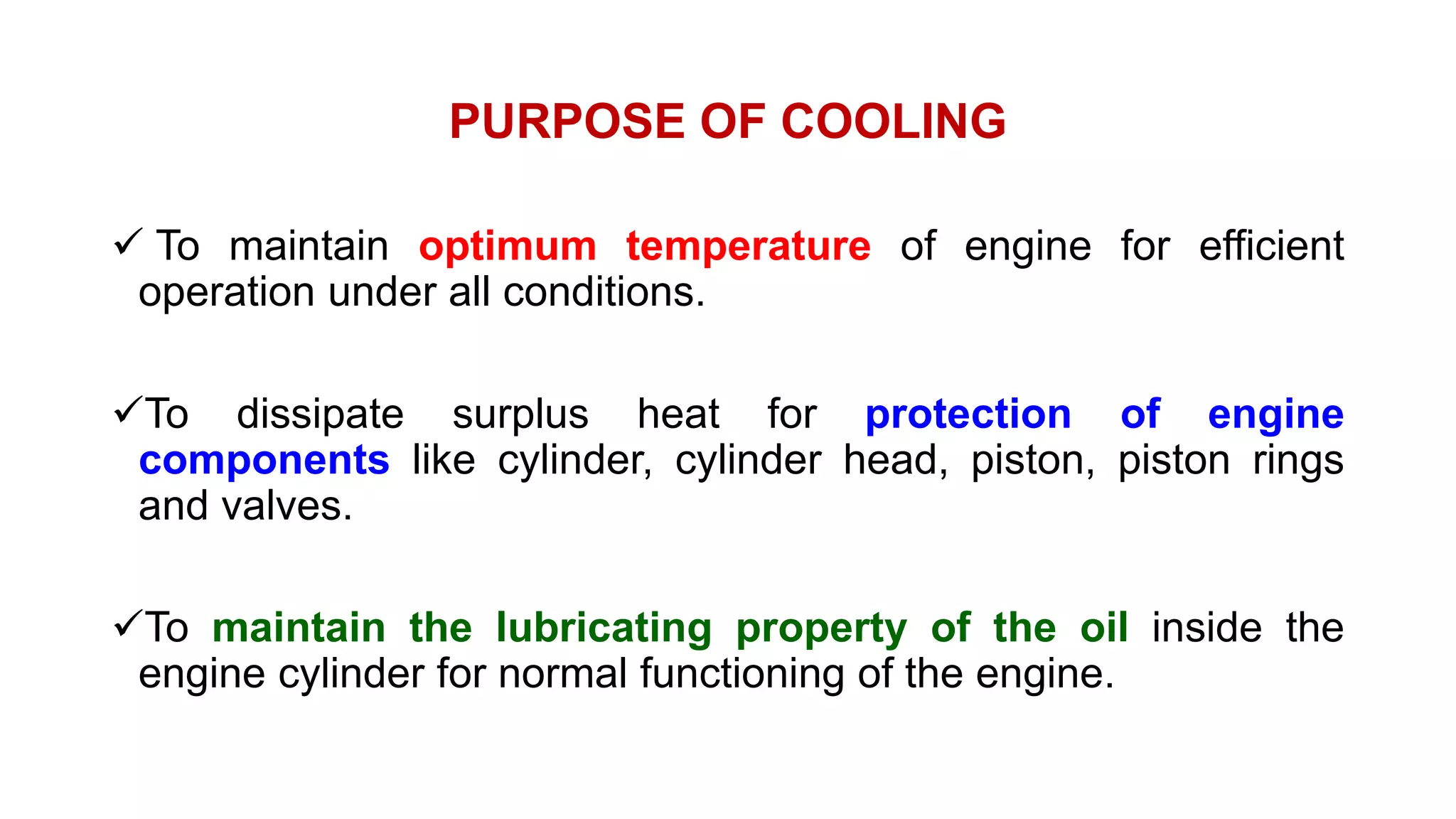
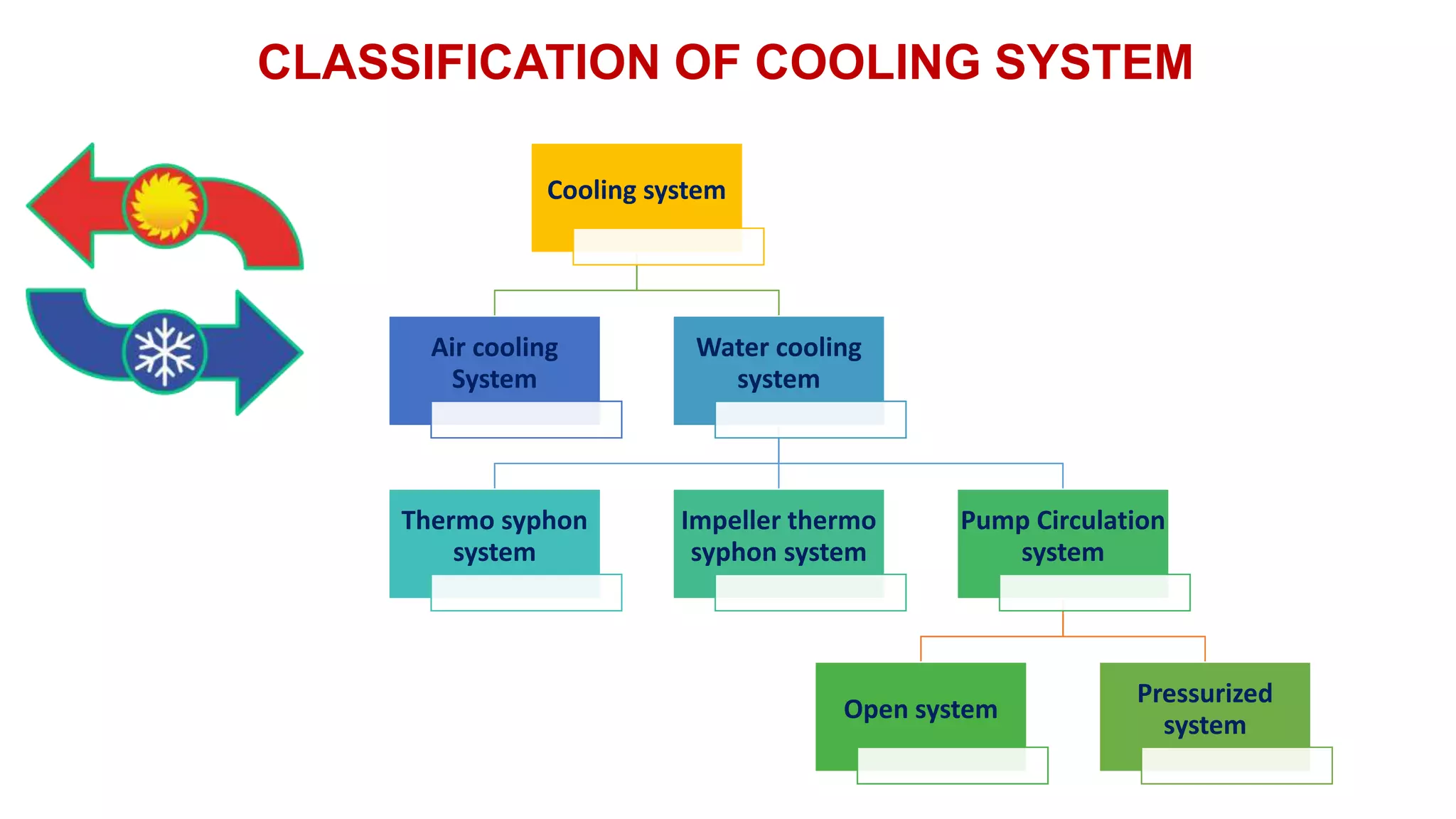
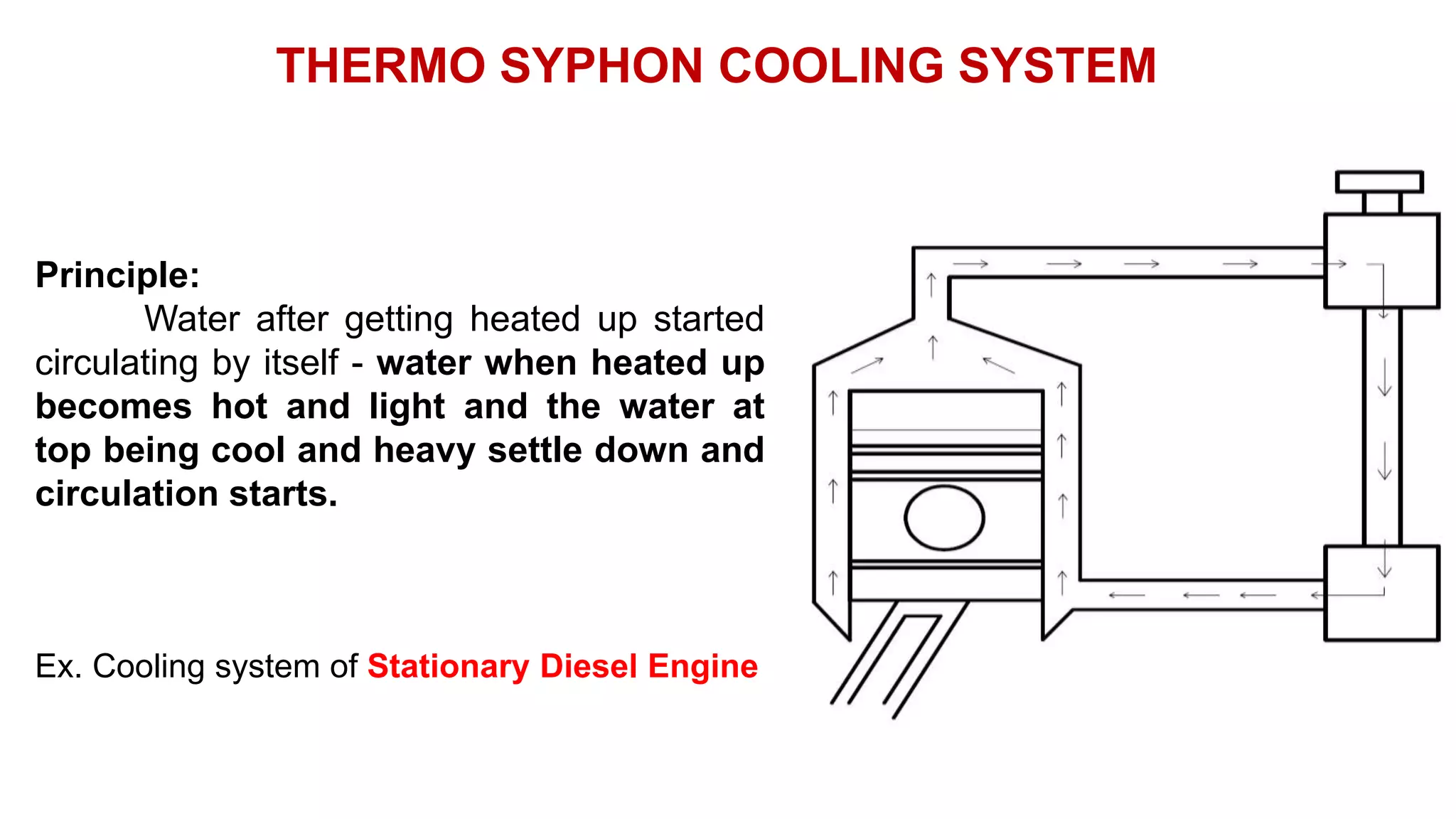
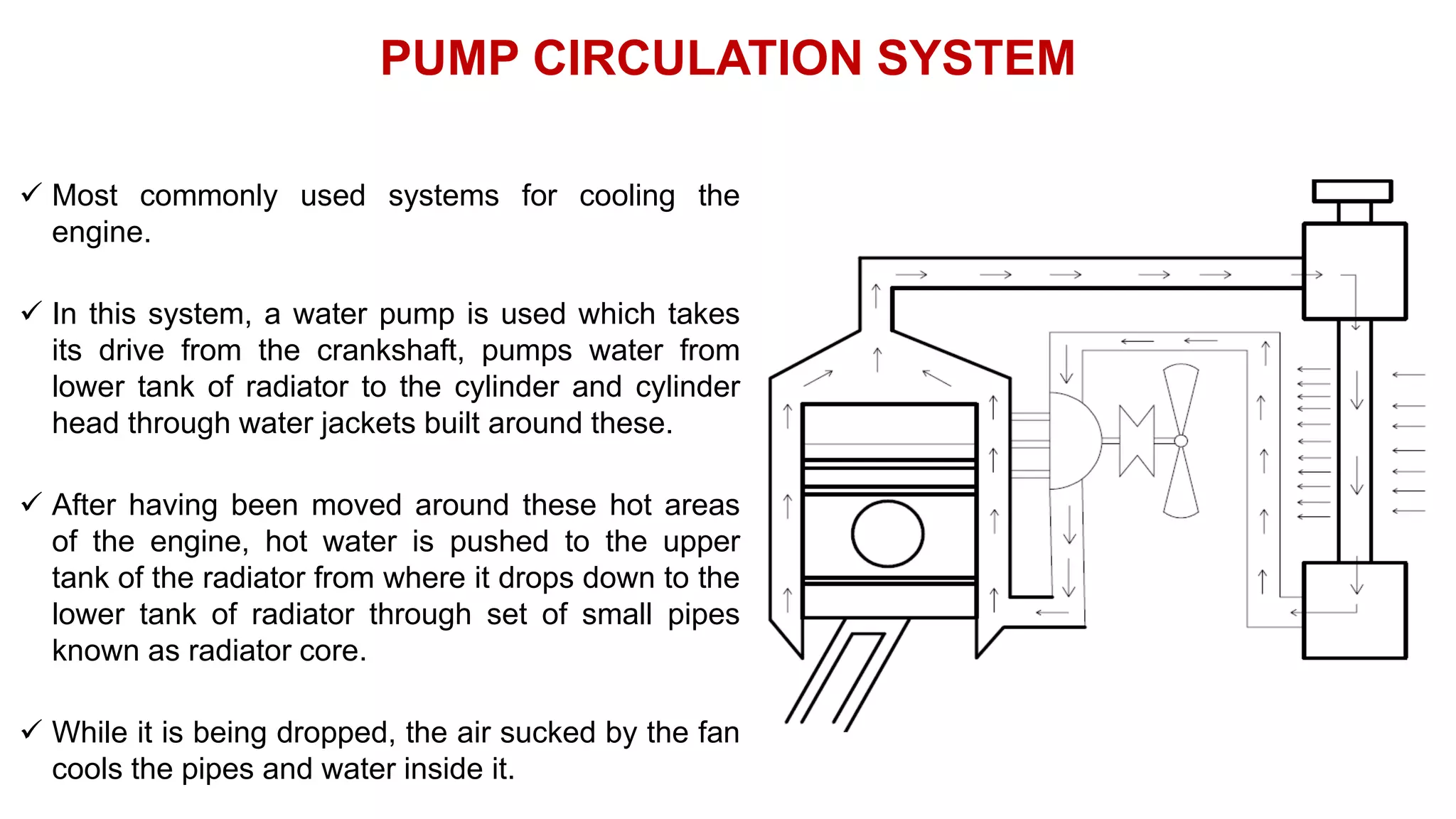
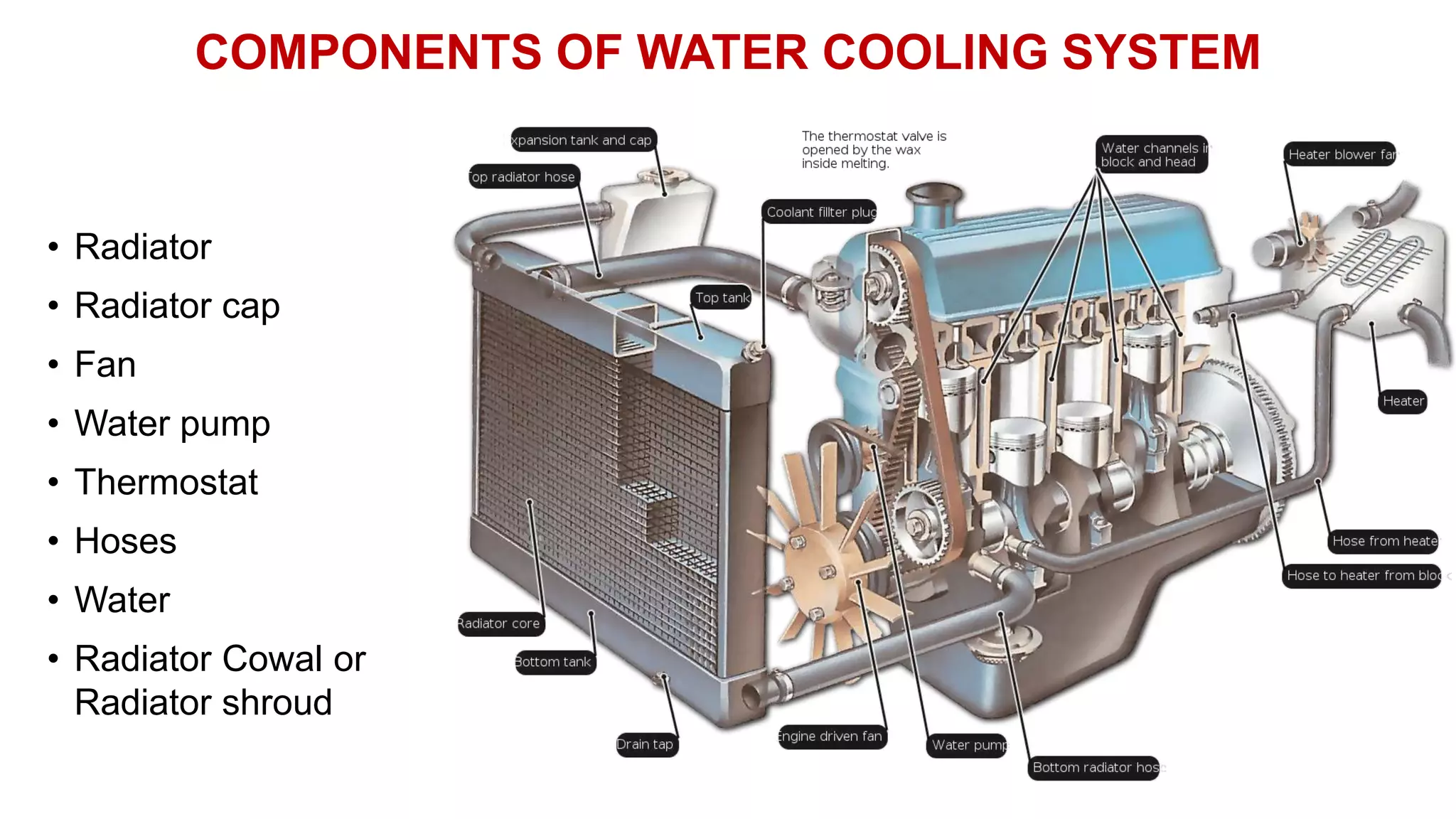
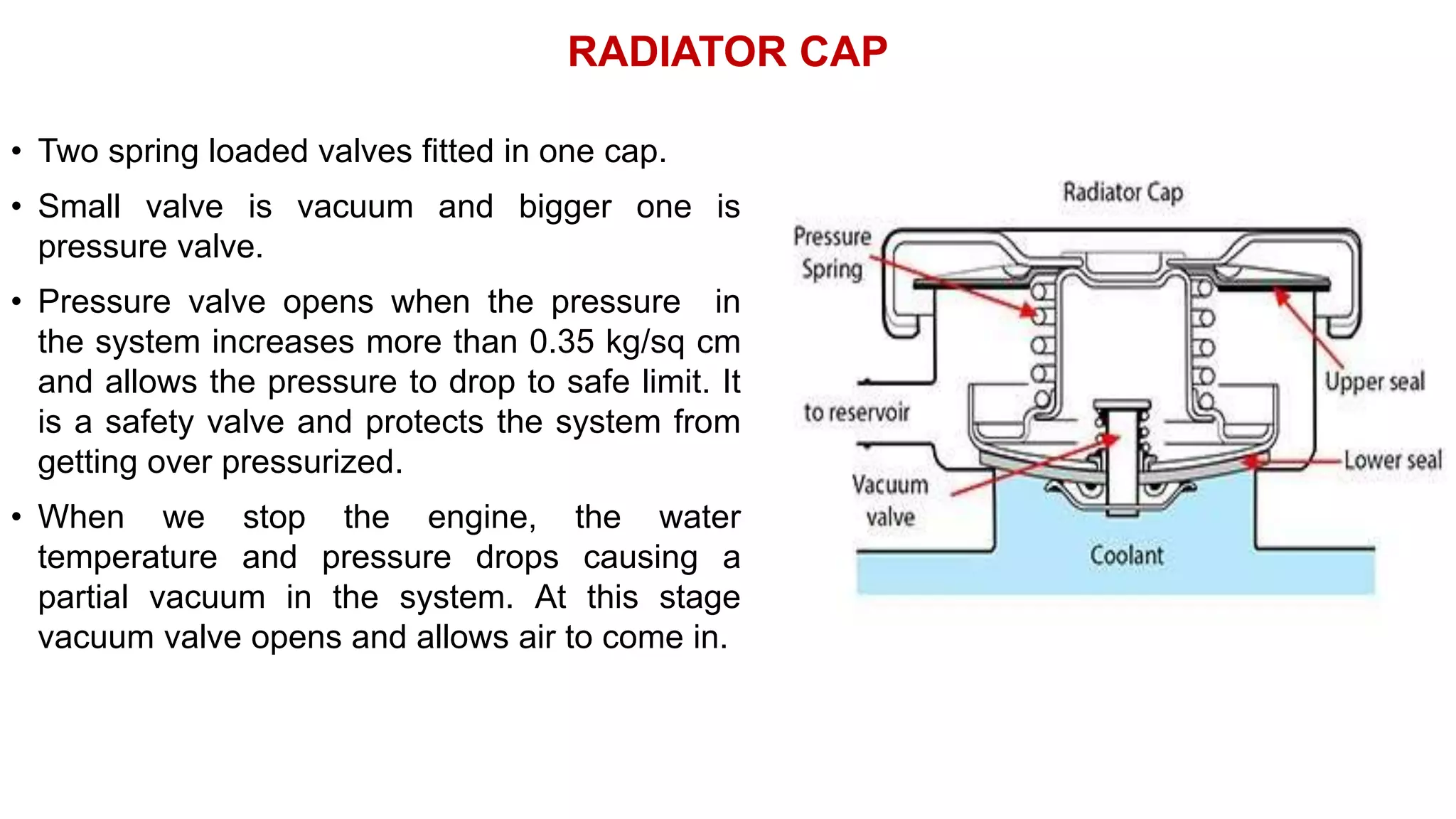
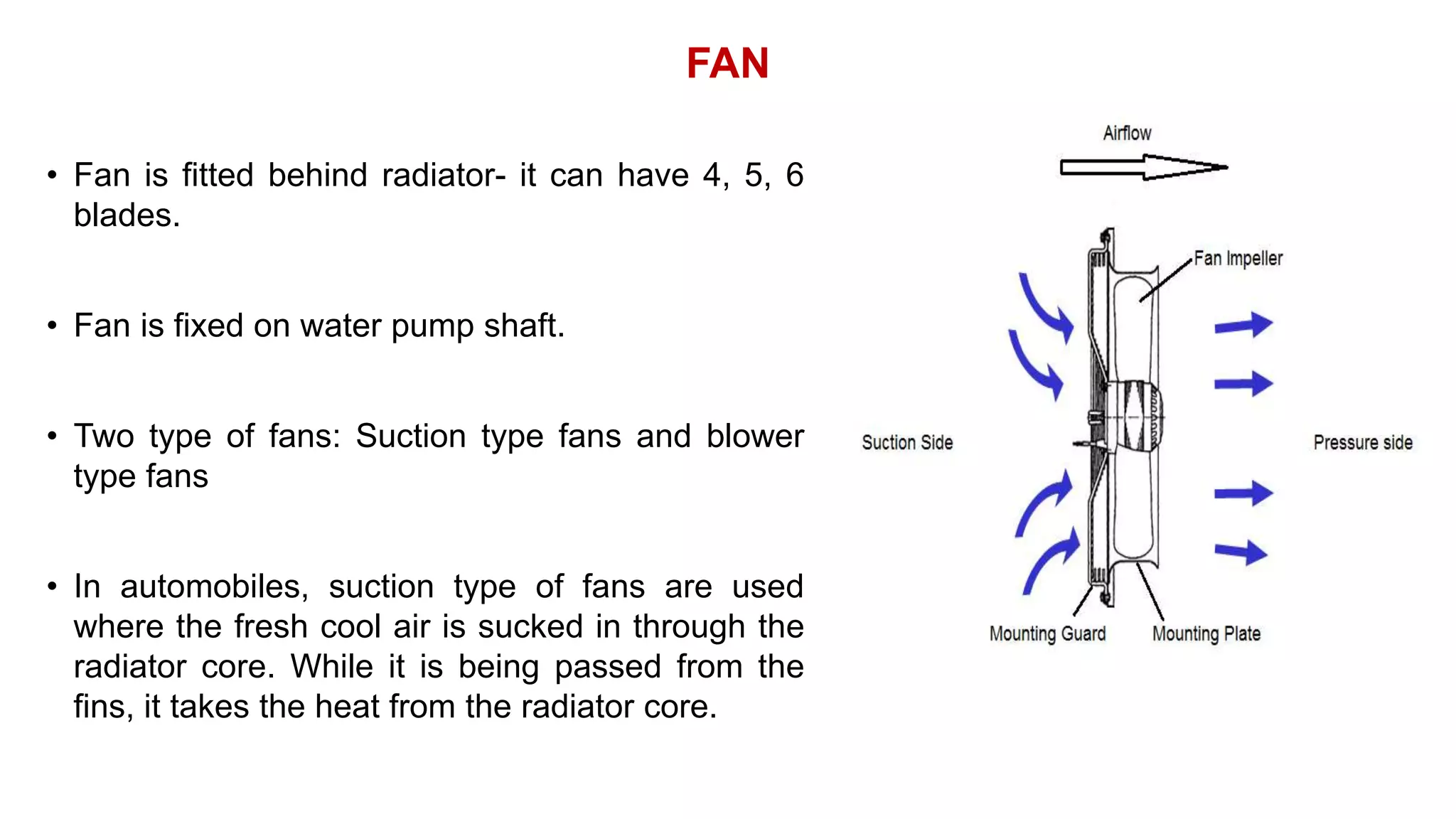
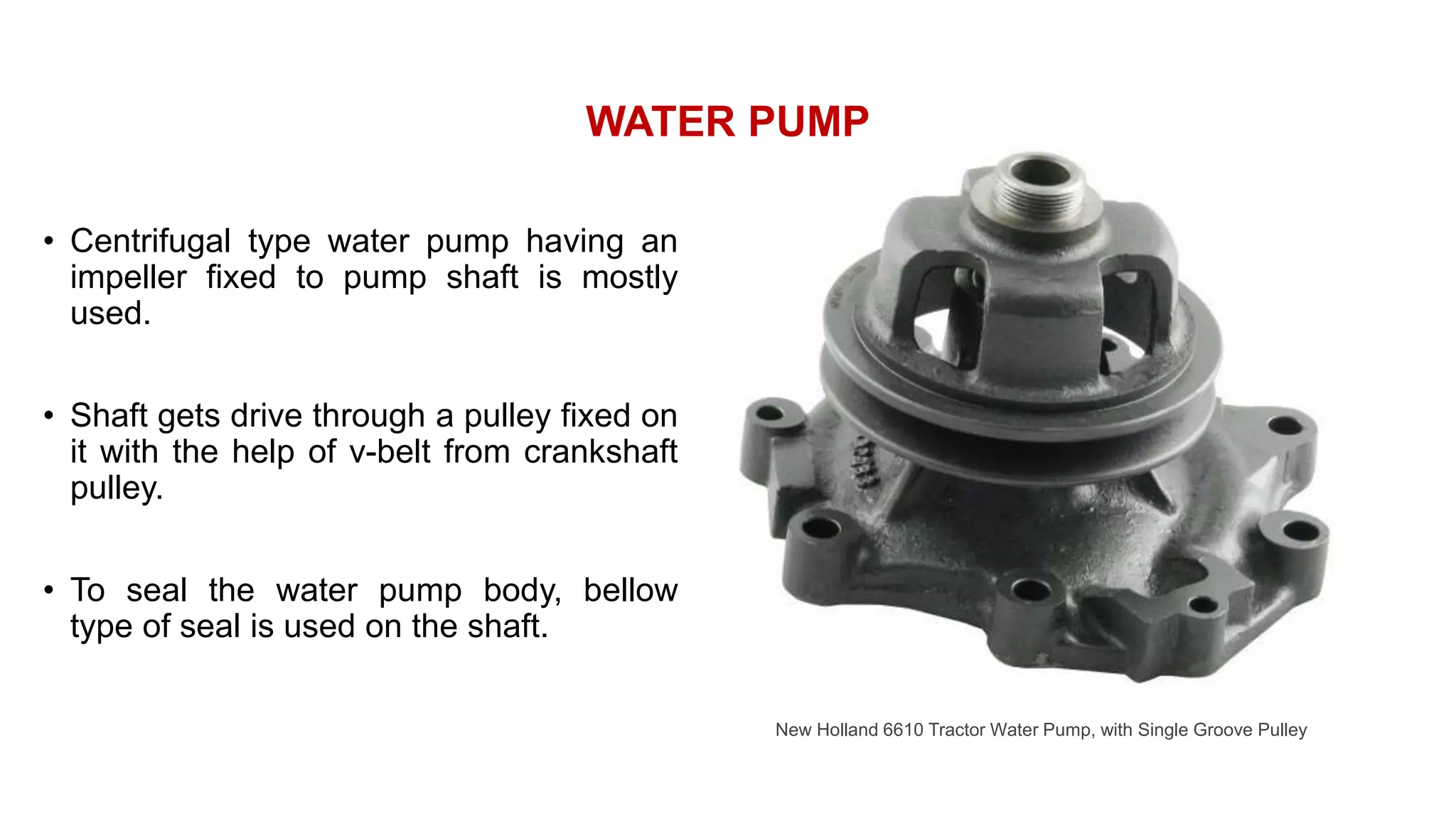
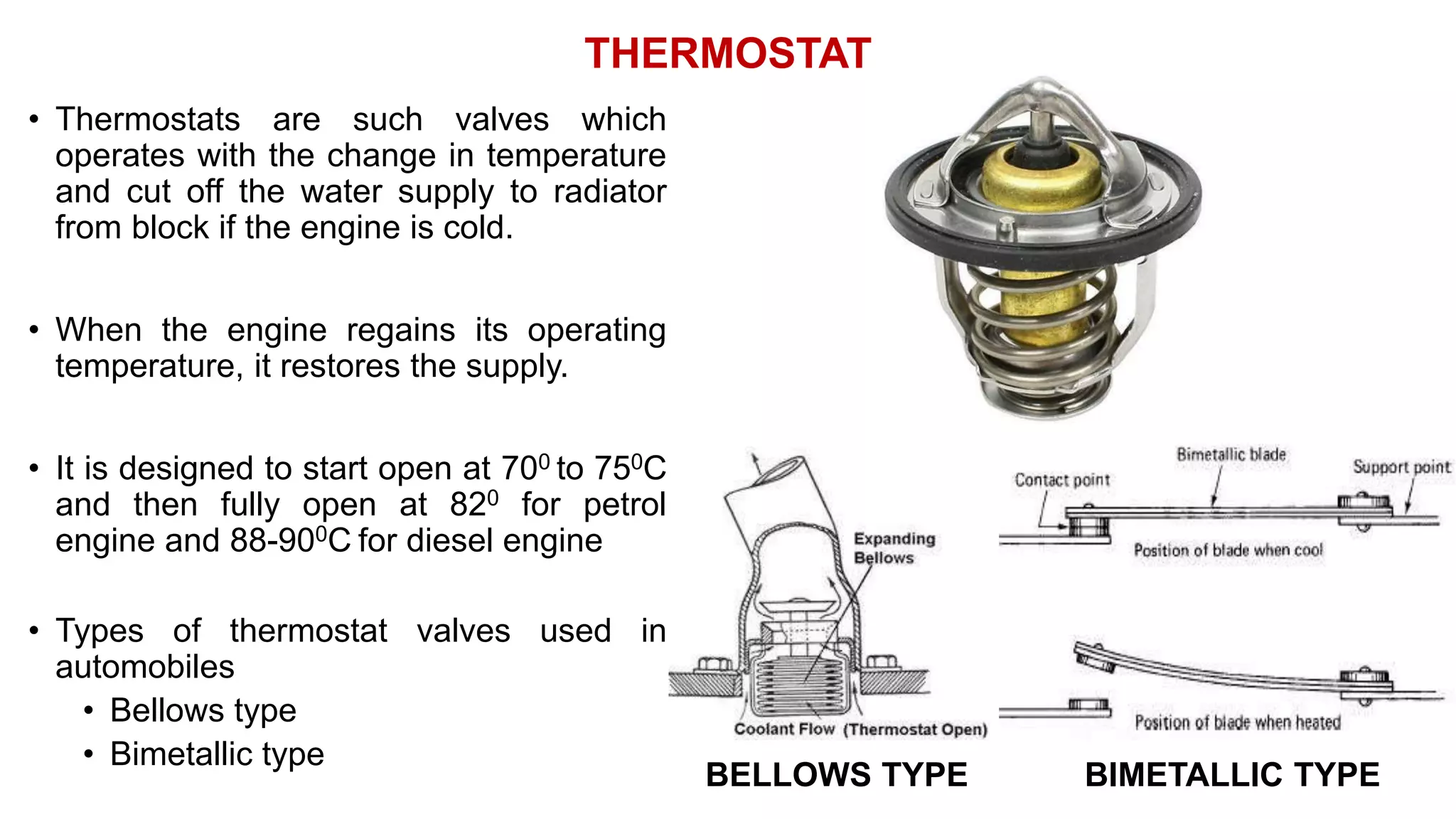
The document comprehensively details tractor cooling systems, explaining various types such as air cooling and water cooling systems along with their advantages and disadvantages. It highlights the importance of maintaining optimum engine temperature to ensure efficient operation and prevent issues like overheating or excessive wear. Additionally, it elaborates on the components of cooling systems, their functions, and necessary maintenance practices.