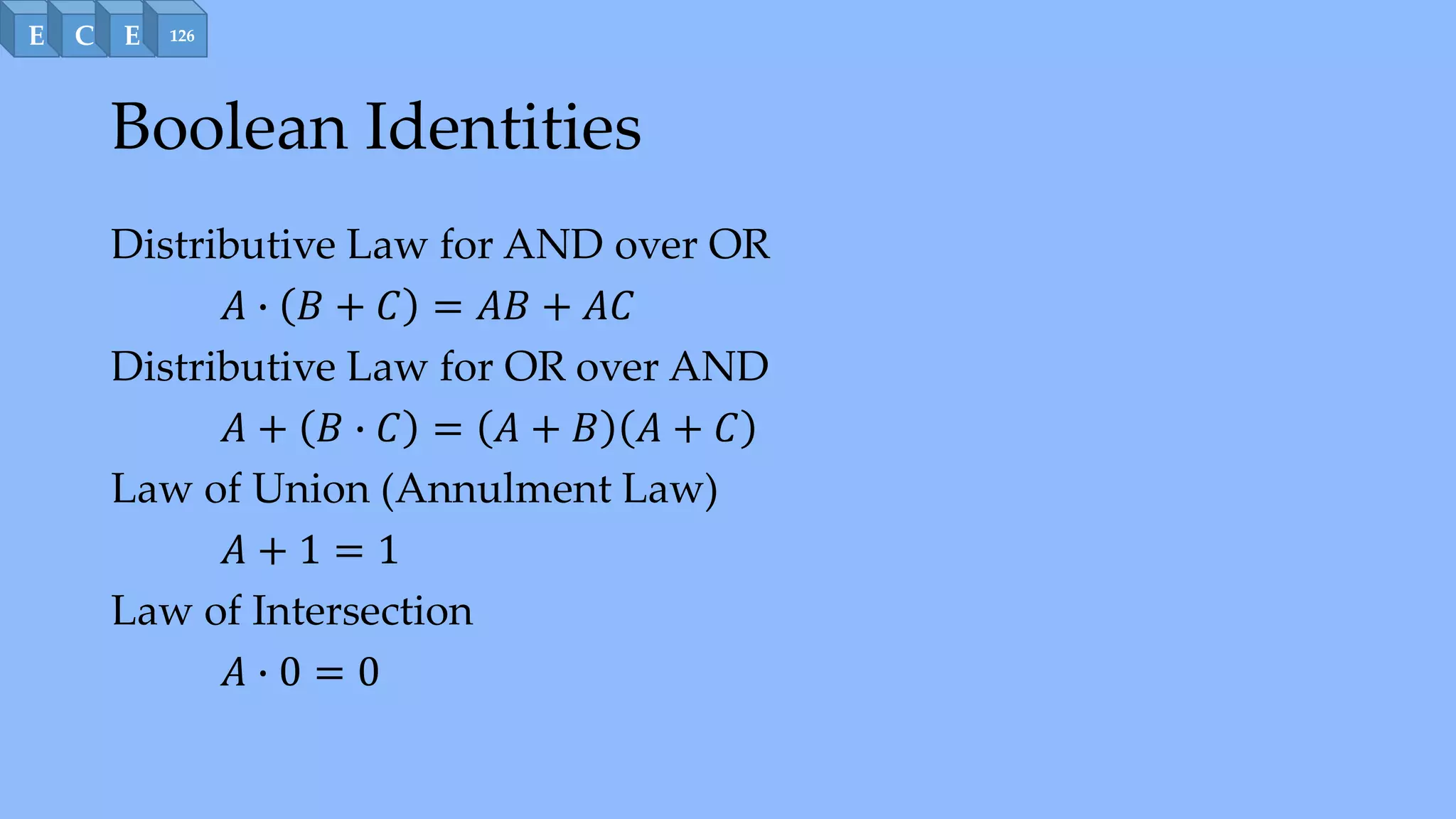
Boolean algebra uses only two values - 0 and 1 - to represent logic states in digital circuits. It defines basic logical operations like AND, OR, and NOT. Various identities govern how these operations interact, such as distribution, absorption, complement, DeMorgan's laws, and duality. Boolean algebra is used to simplify and optimize logic expressions that represent digital circuit behavior.