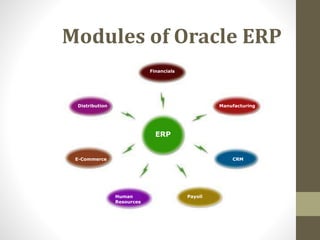
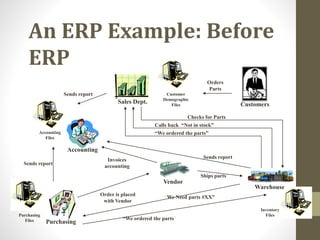
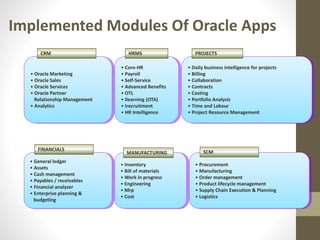
This document provides an overview of Oracle ERP presented by Nitin Maheshwari. It begins with an introduction to ERP systems and then discusses Oracle as an ERP vendor. The core modules of Oracle ERP are outlined, including financials, distribution, human resources, payroll, CRM, manufacturing and more. It then explains how ERP systems work by integrating a centralized database. The document also reviews benefits of ERP such as improved integration, efficiency and access to information. It concludes by emphasizing the large market for ERP services and encouraging attendees to pursue related careers and courses.