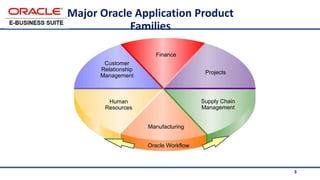
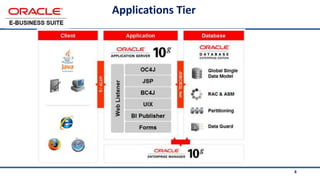
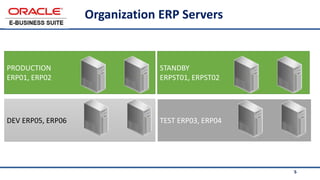
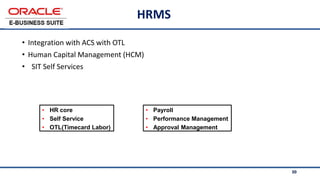
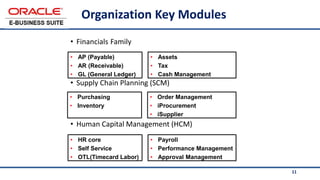
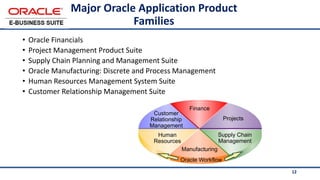
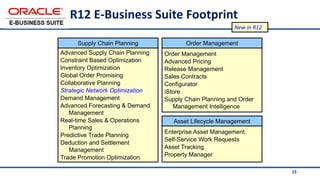
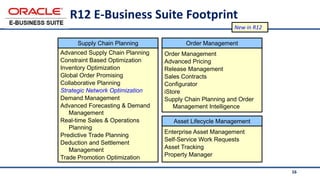
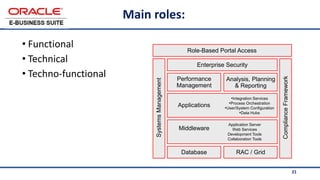
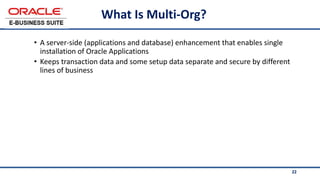
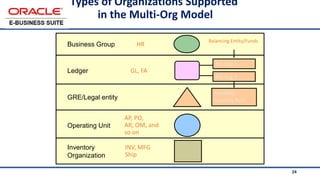
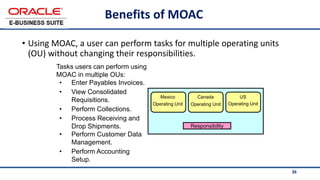
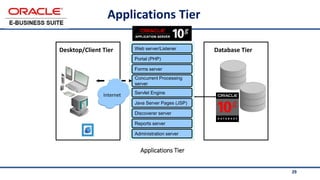
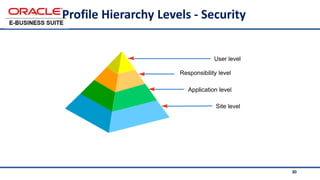
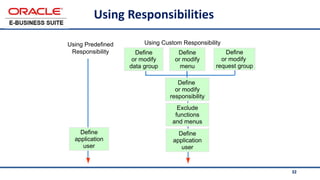
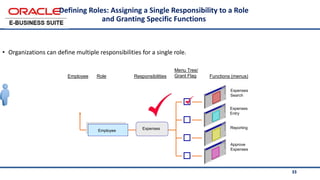
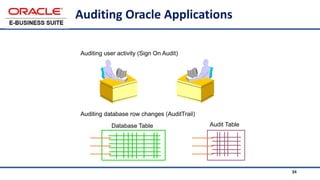
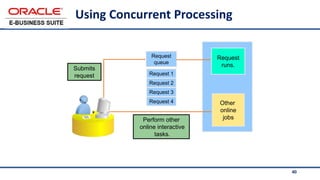
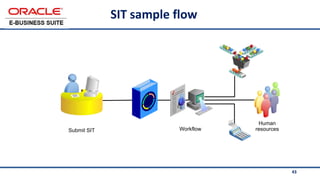
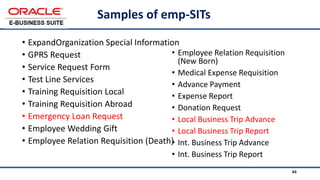
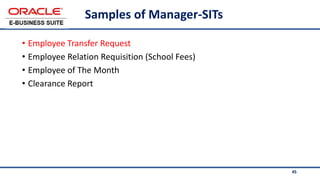
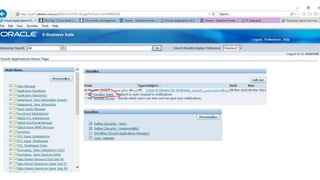
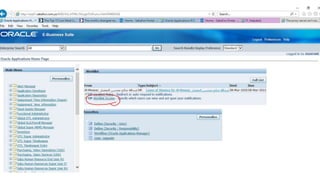
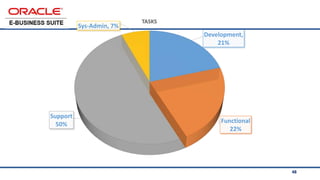
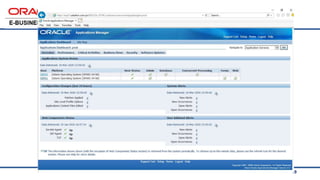
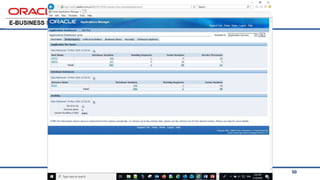
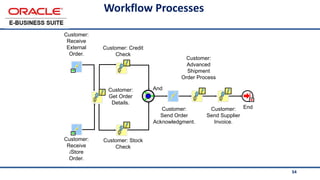
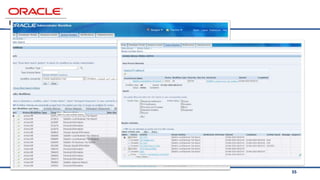
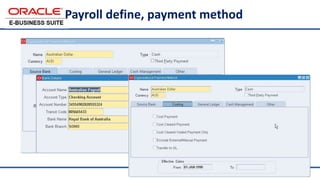
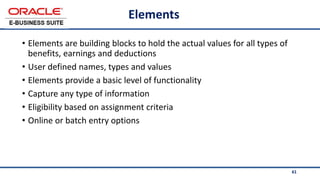
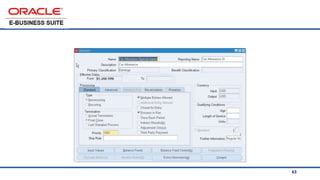
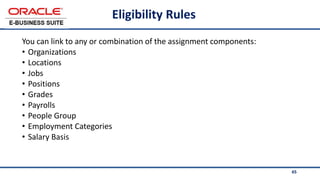
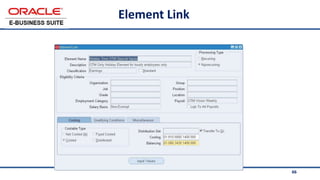
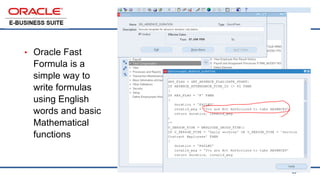
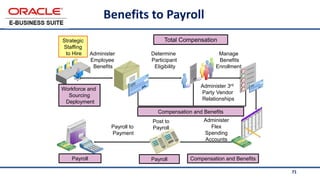
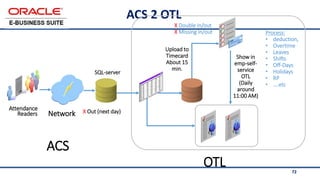
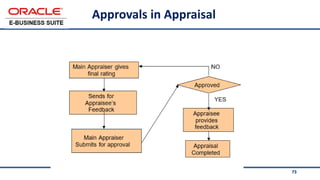
The document provides an overview of Oracle's E-Business Suite R12 and describes its main components and applications. It discusses Oracle's major application product families which include customer relationship management, supply chain management, manufacturing, finance, projects, and human resources. It also describes the applications tier environment, development environments, production environments, and standby environments. It provides examples of the main tasks of an ERP team which include integrating ERP with other systems, involvement in implementation projects, user and system management, report development, and more.