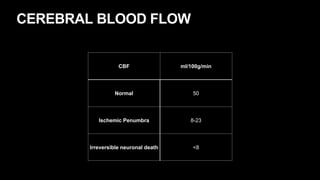
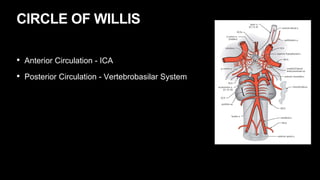
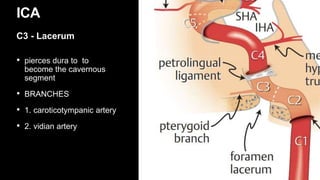
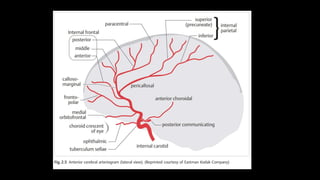
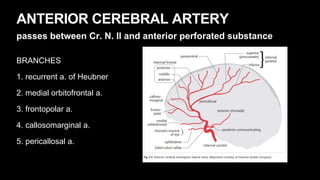
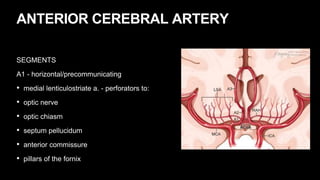
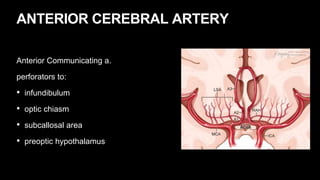
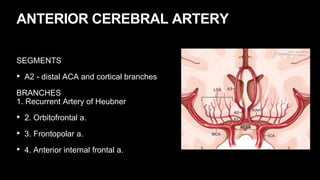
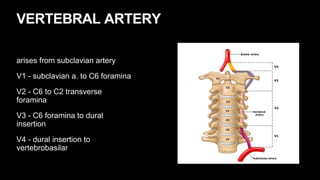
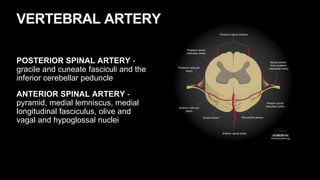
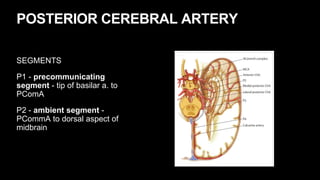
This document provides an overview of cerebral vascular anatomy, including the major arteries supplying blood to the brain. It describes the internal carotid artery and its segments. It then discusses the anterior, middle, and posterior cerebral arteries, their segments, and key branches. The document also reviews the posterior circulation, including the vertebral artery, basilar artery, and posterior cerebral artery. Finally, it briefly mentions venous drainage from the brain.