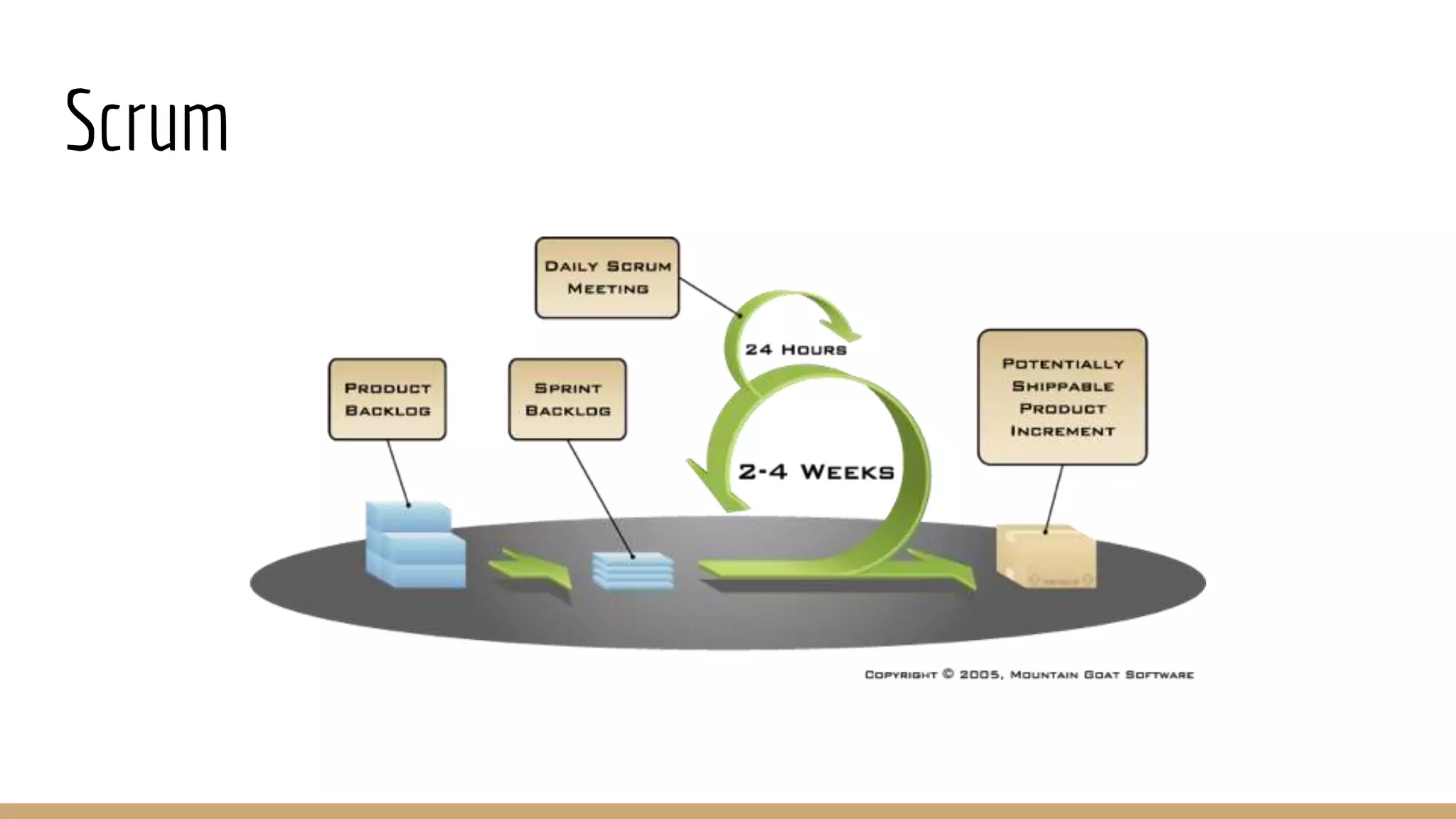
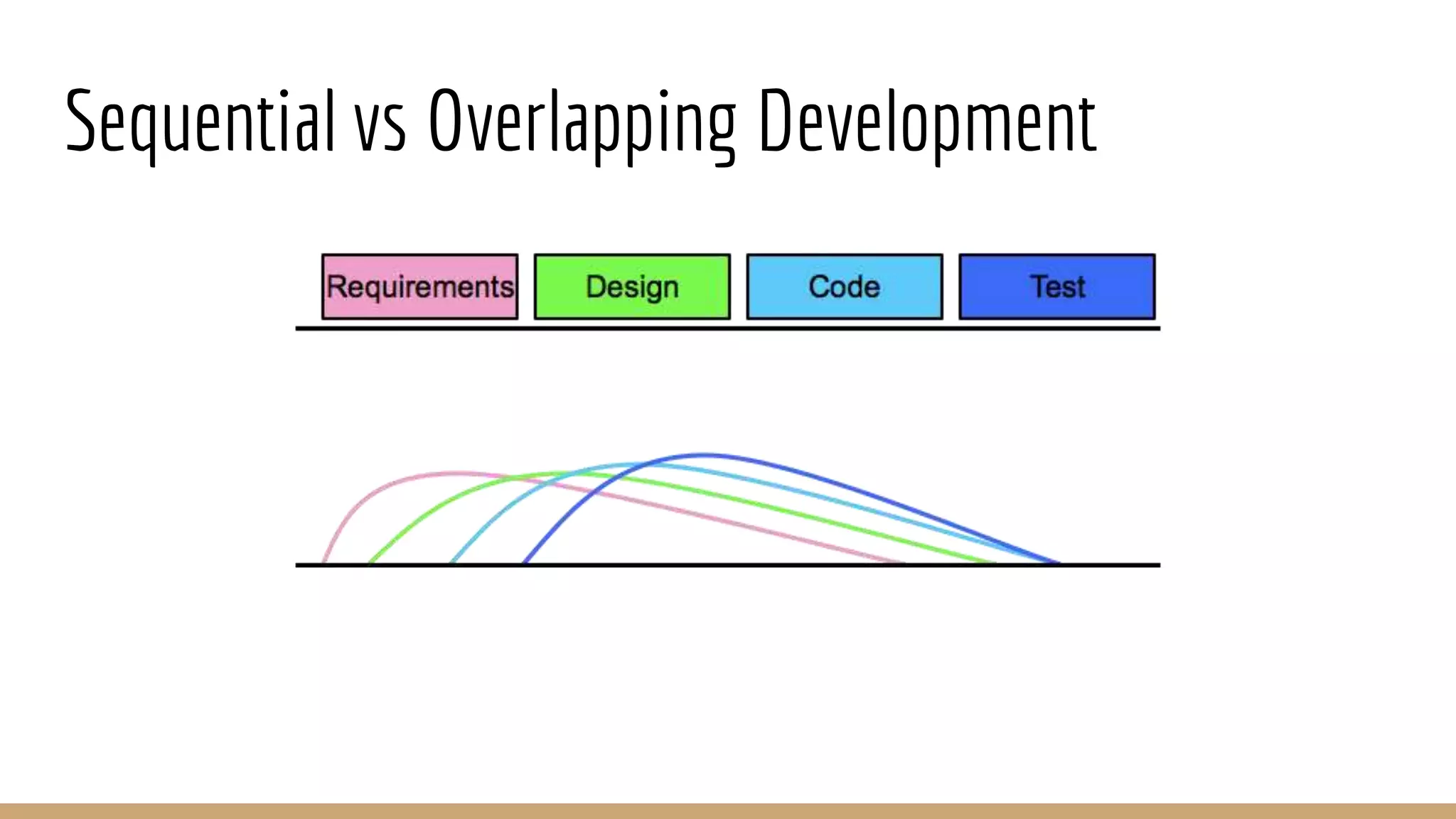
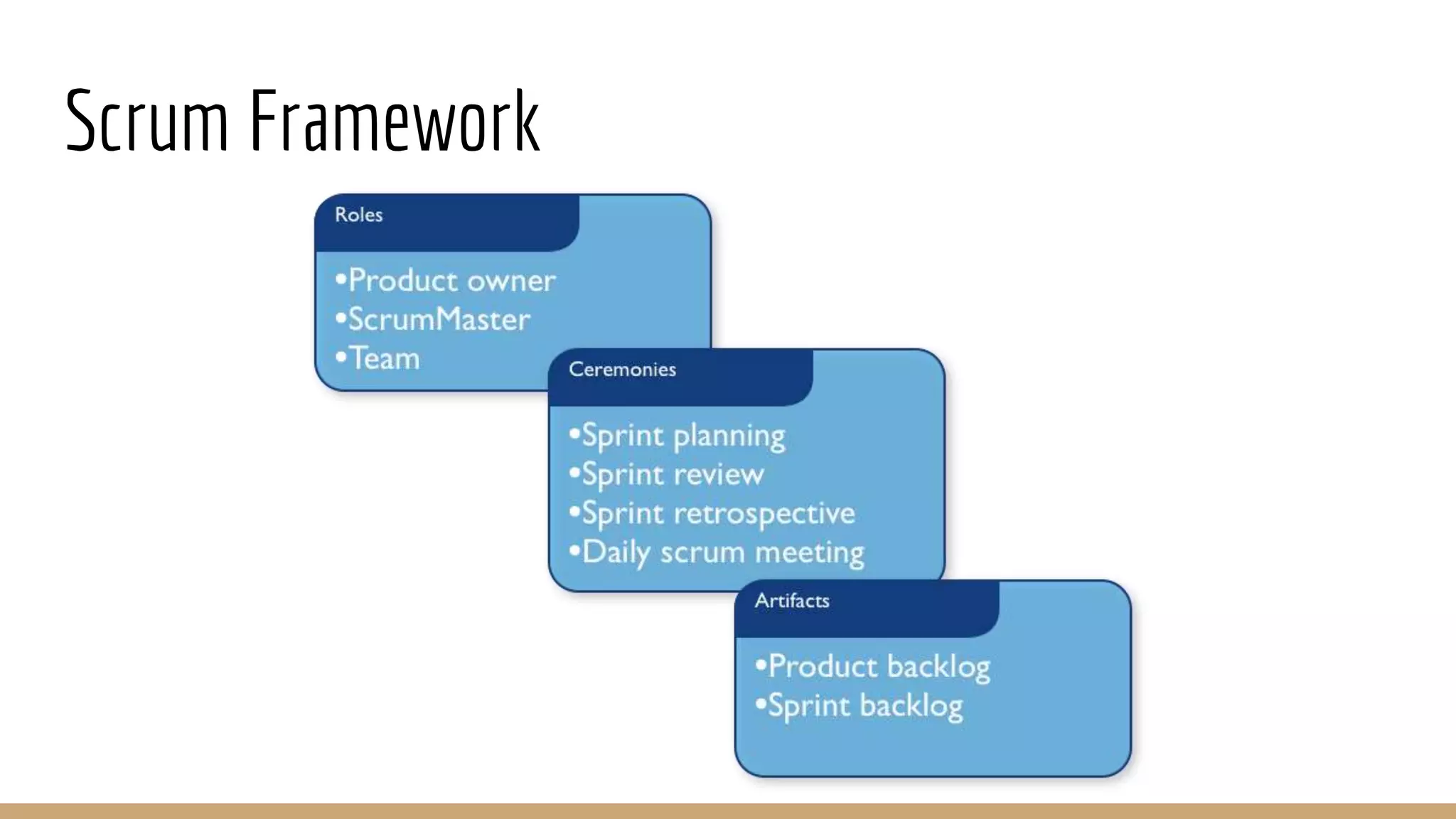
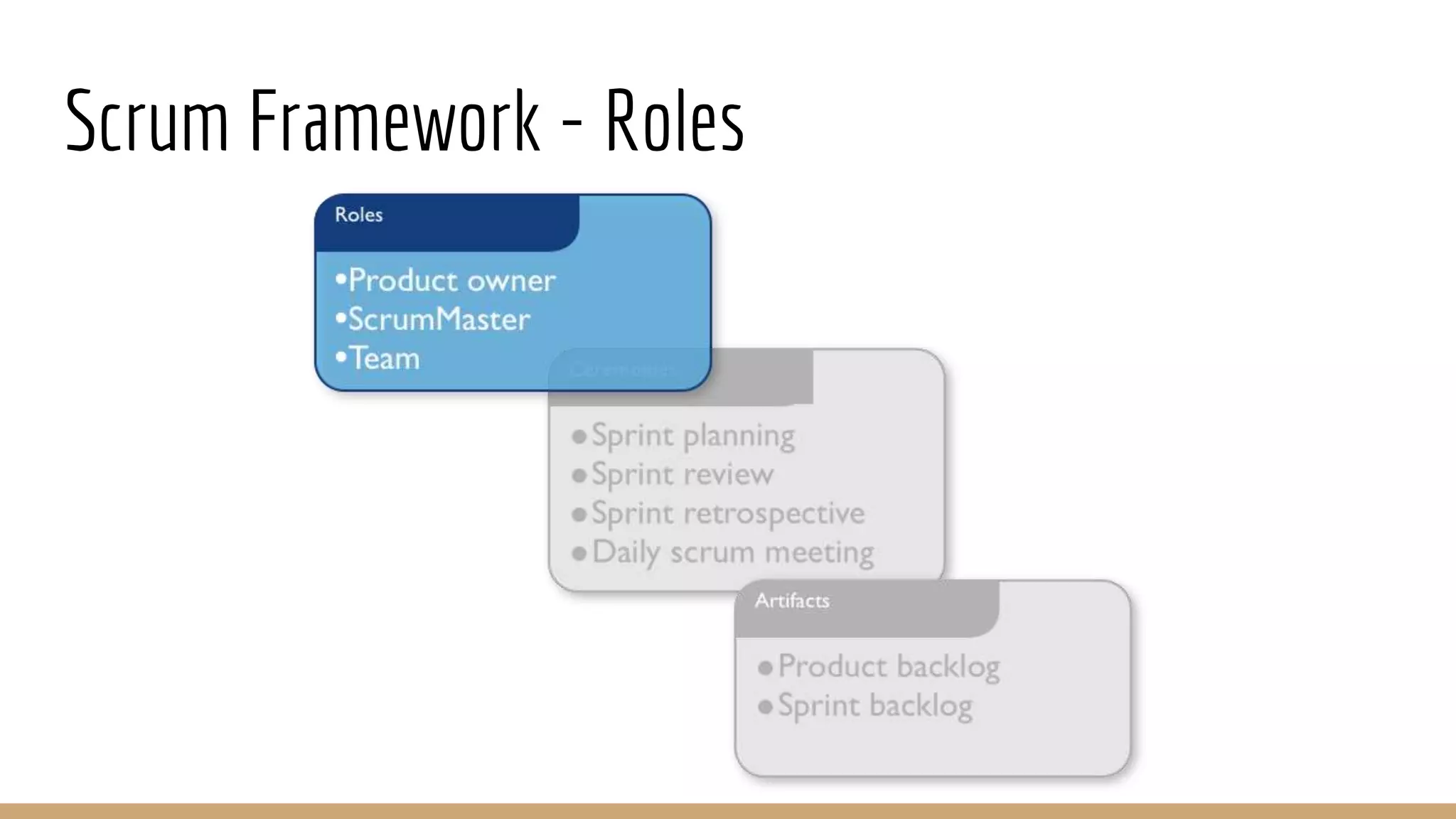
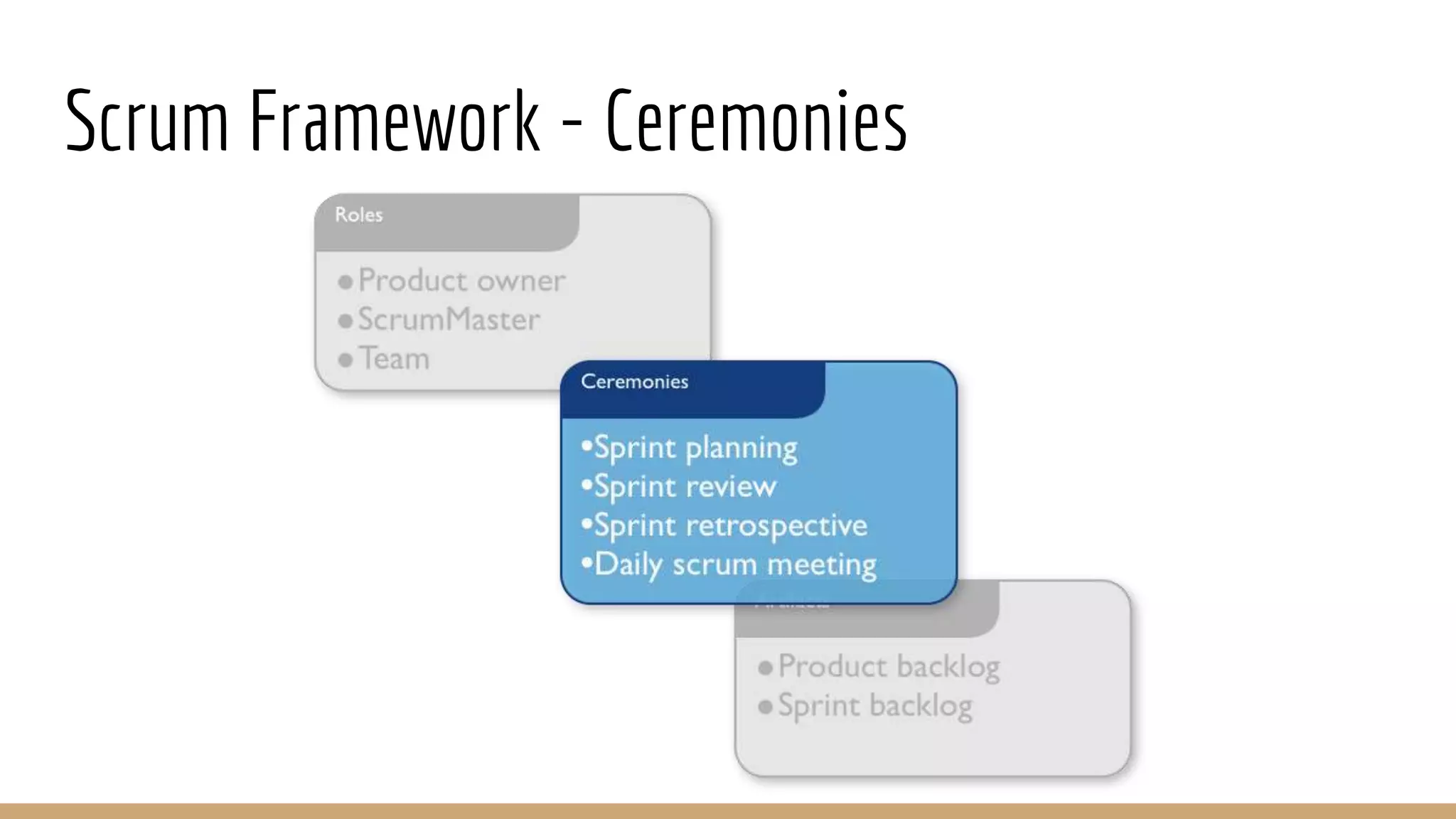
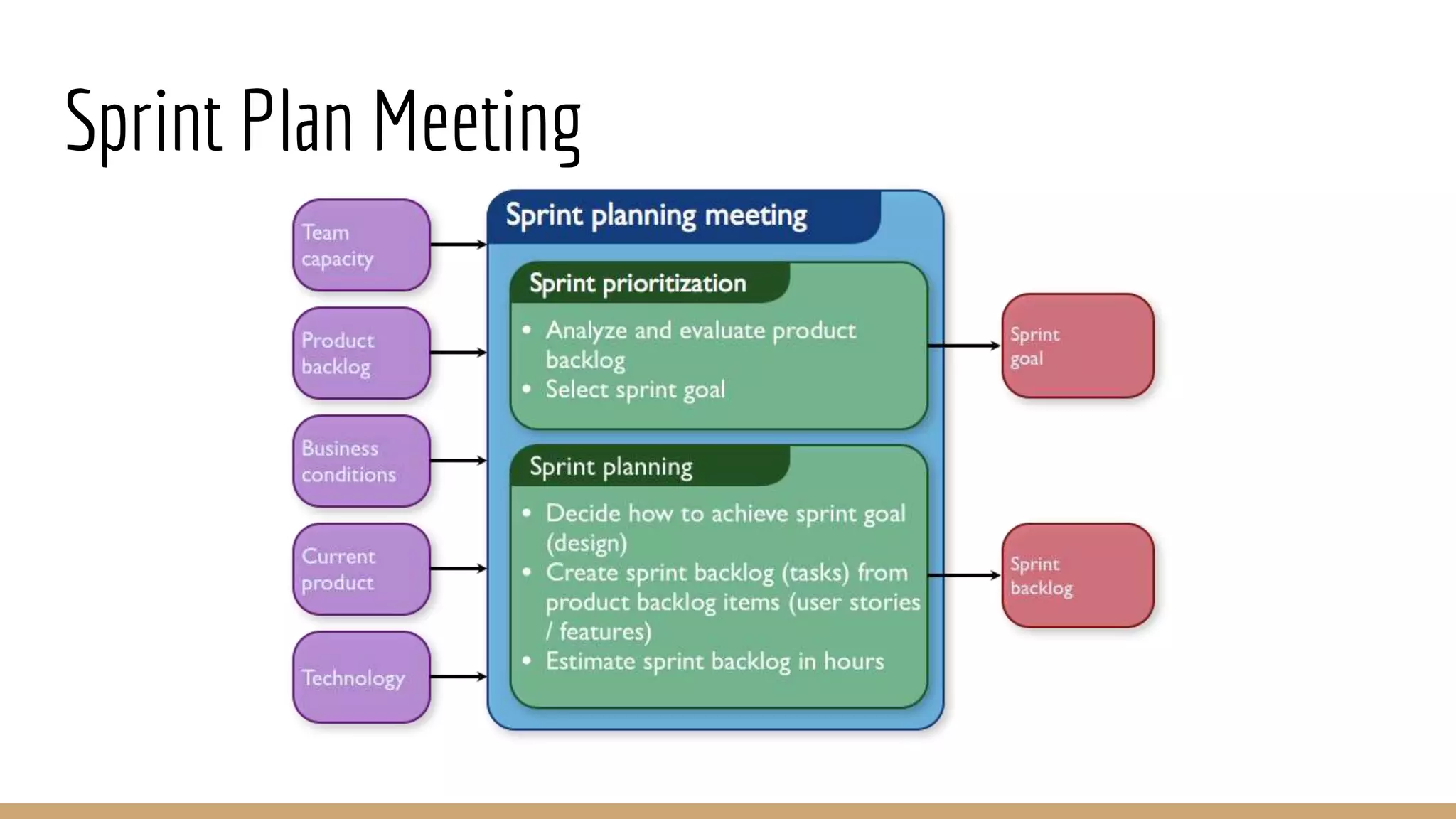
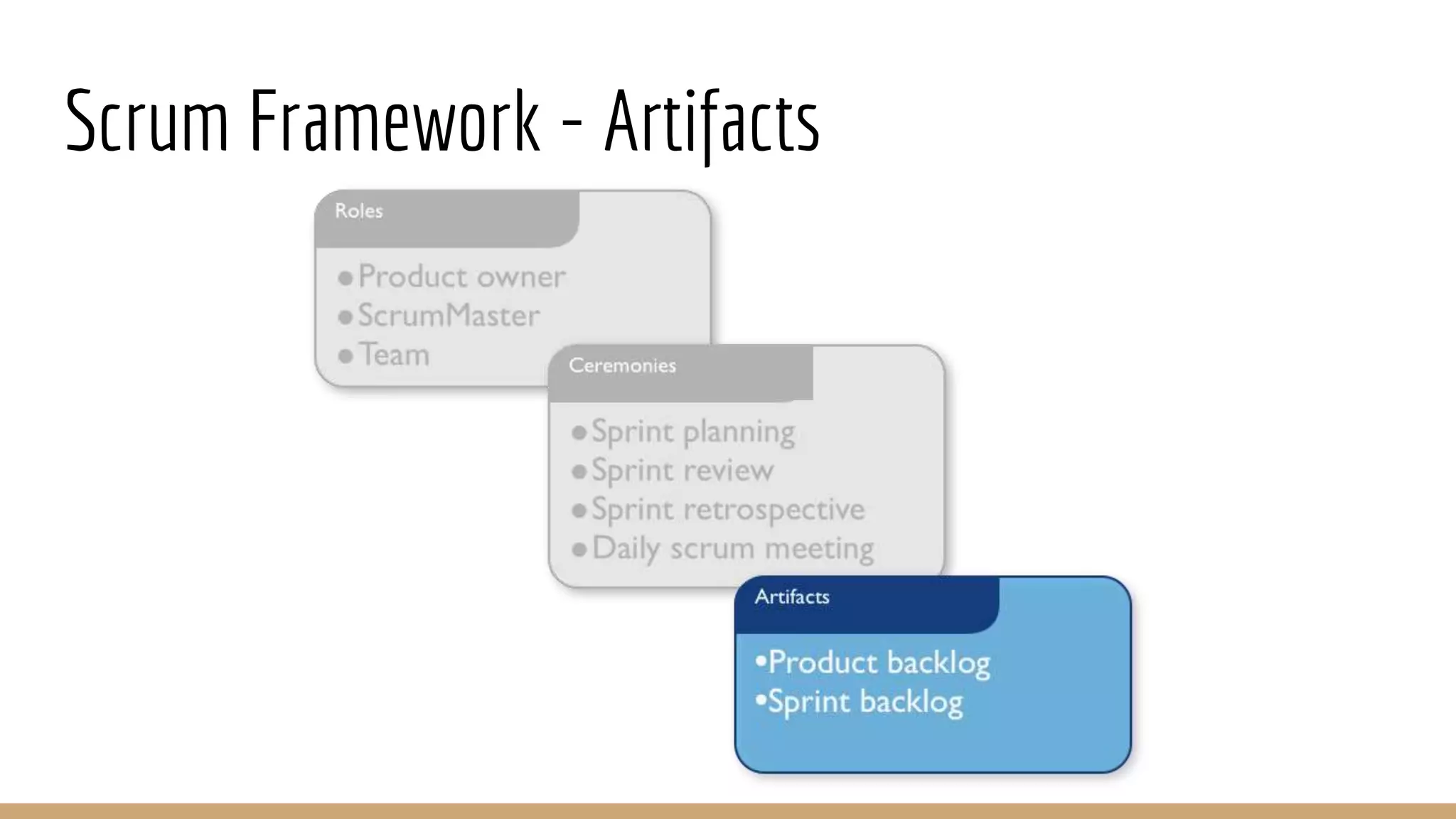
This document provides an overview of agile software development methodologies, focusing on Scrum. It describes the traditional waterfall methodology and its limitations. Agile methodologies like Scrum promote iterative development through collaboration between cross-functional teams. Scrum uses sprints, daily stand-ups, sprint reviews and retrospectives. Key roles include the product owner, Scrum master, and self-organizing development team. The product backlog and sprint backlog are key artifacts that help manage work in progress.