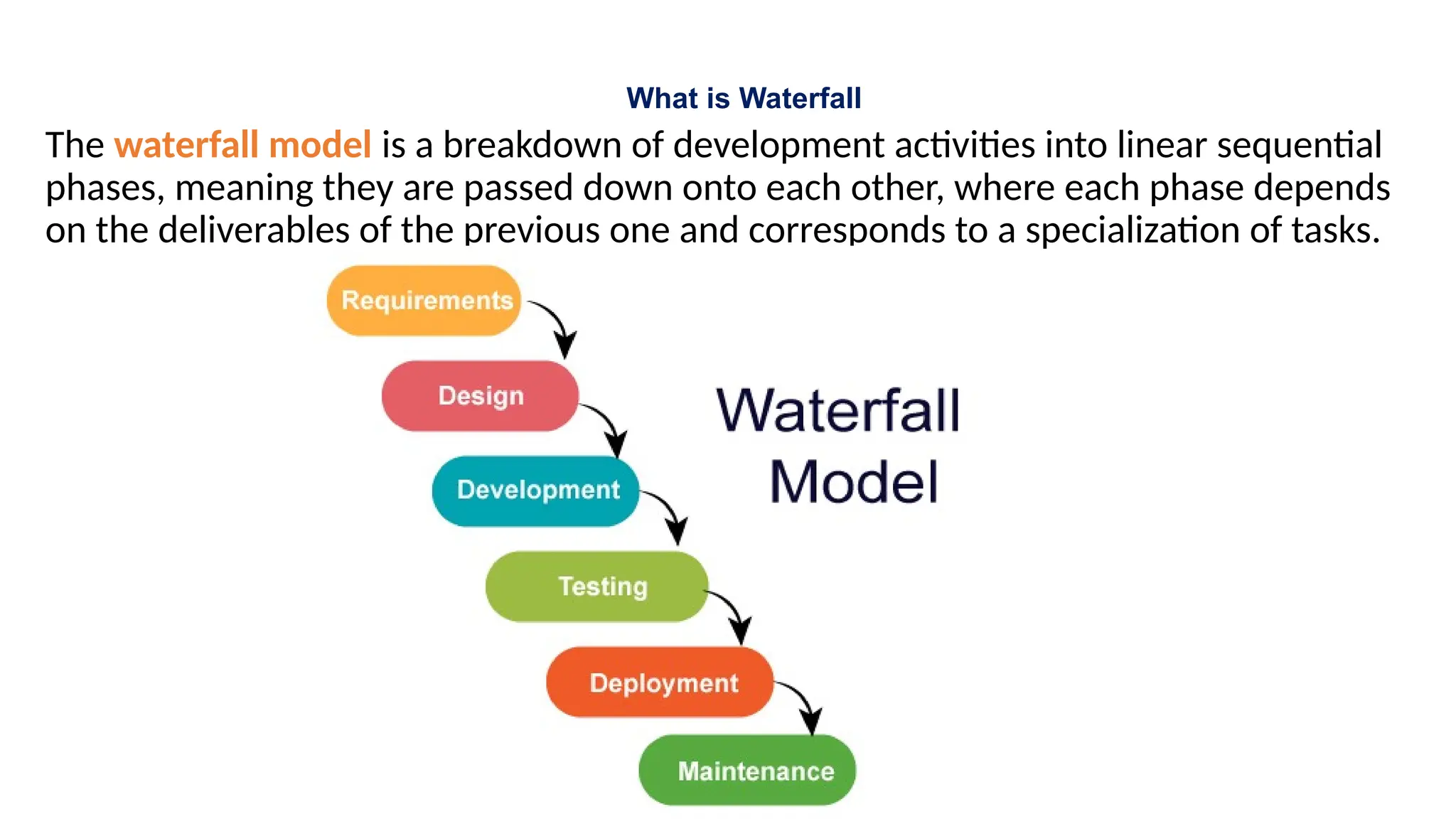
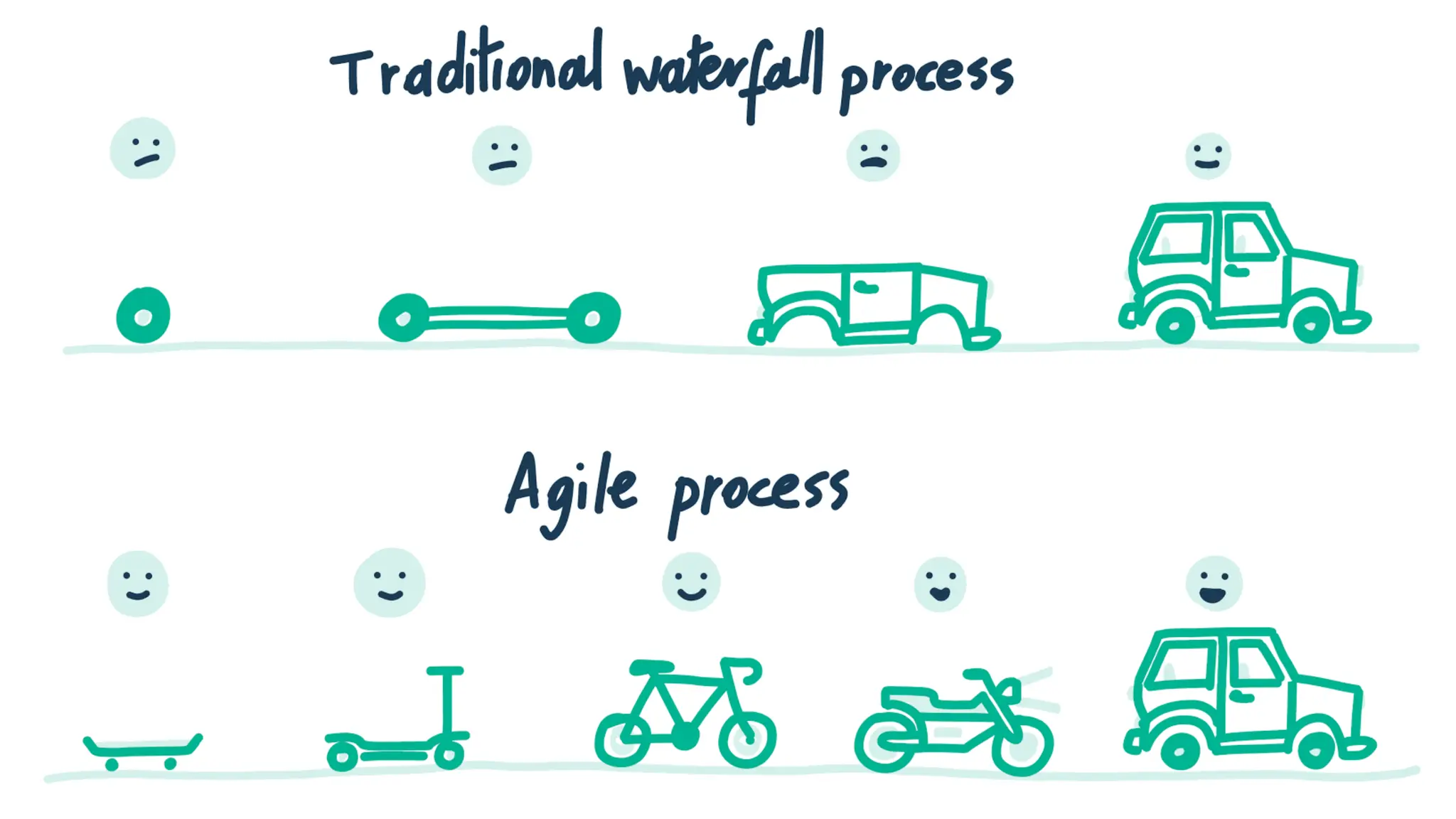
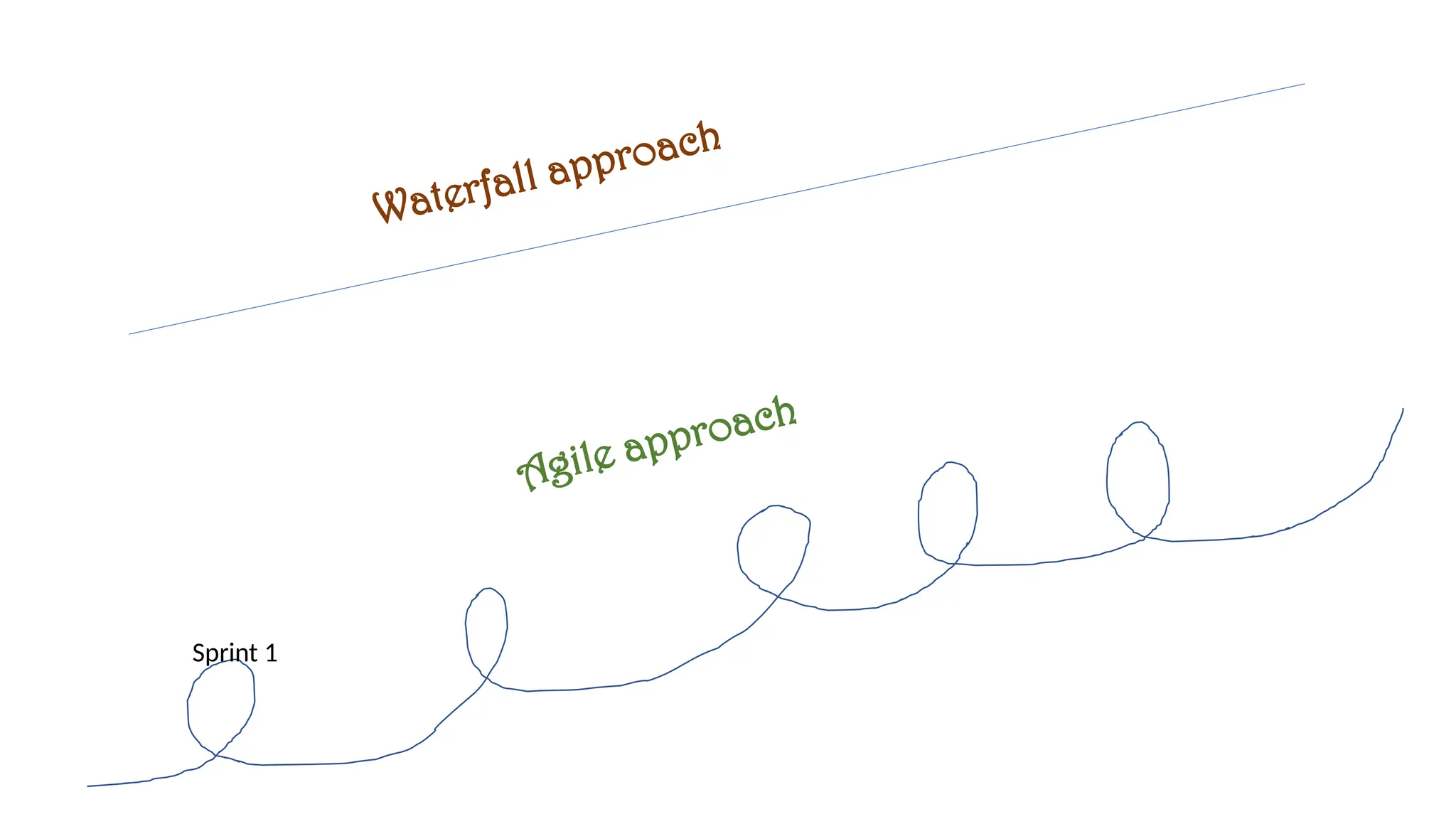
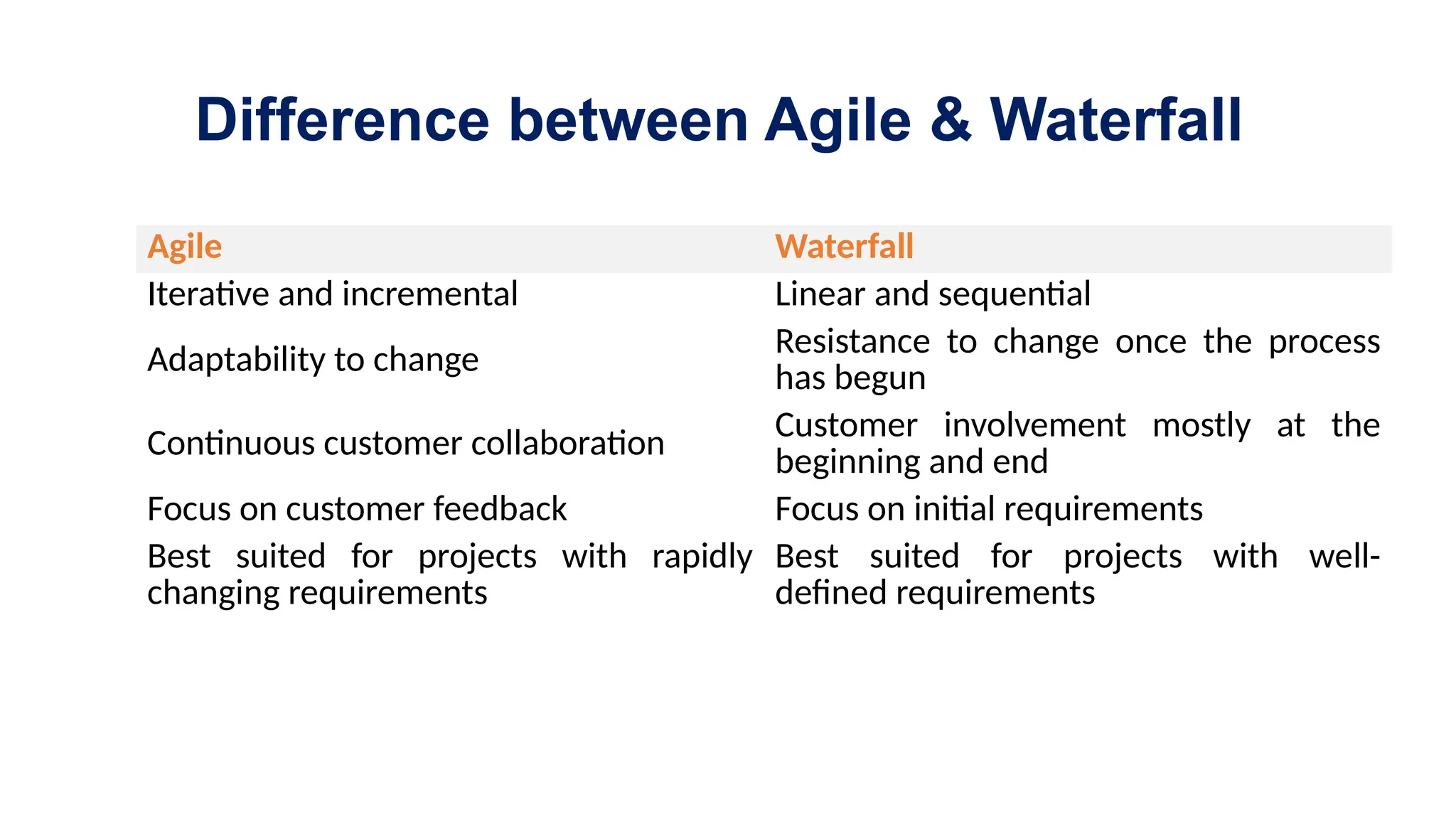
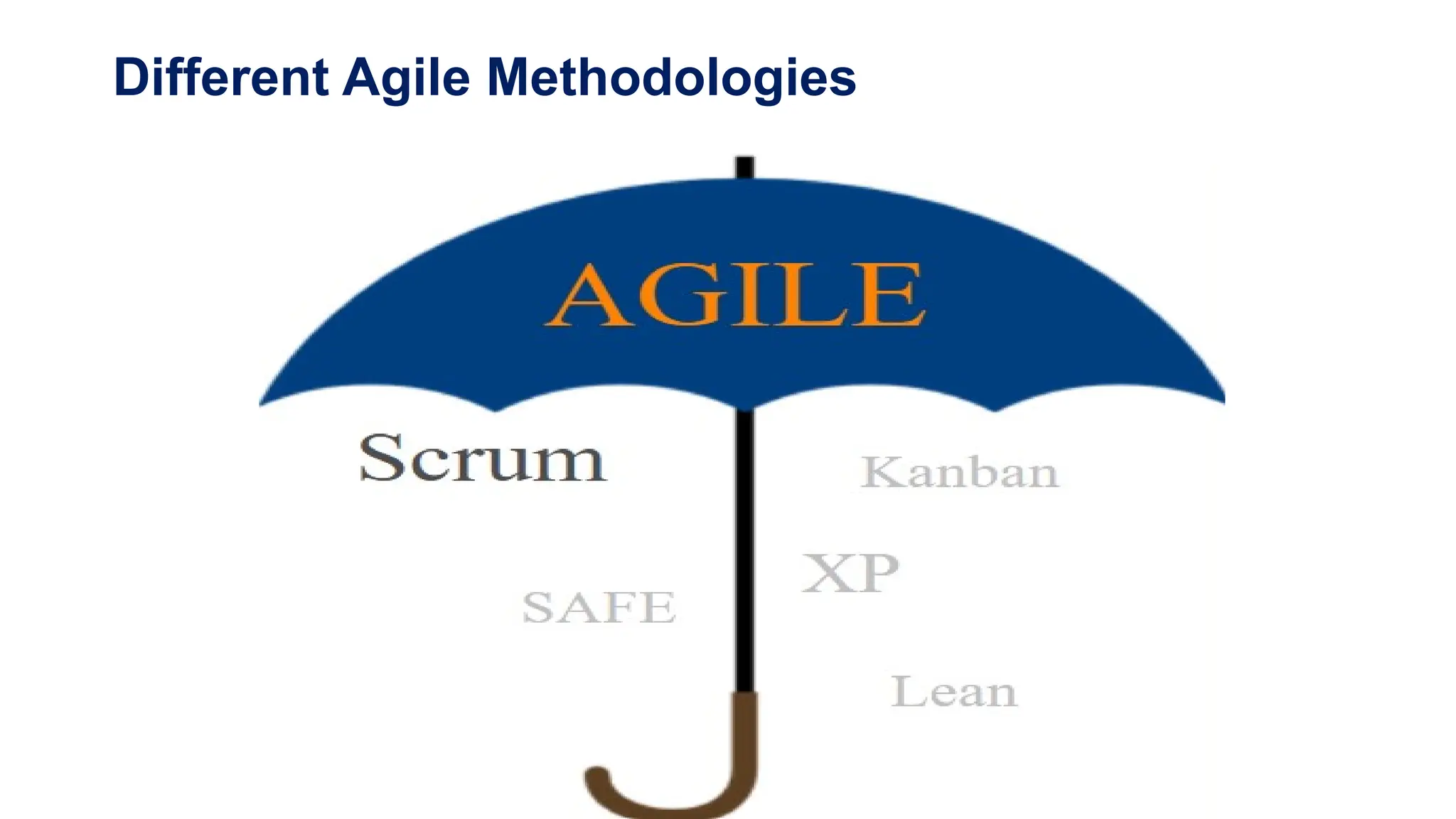
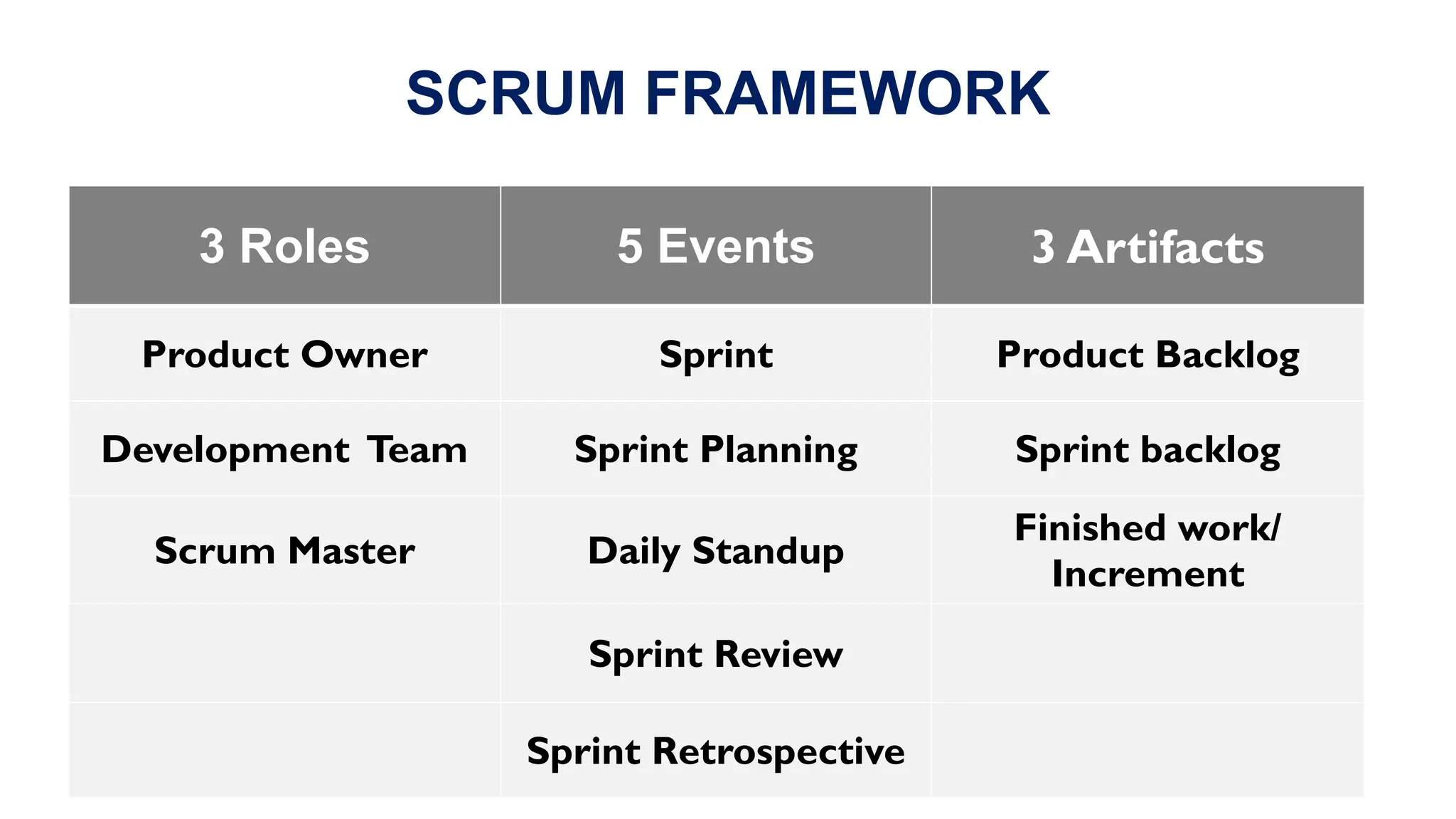
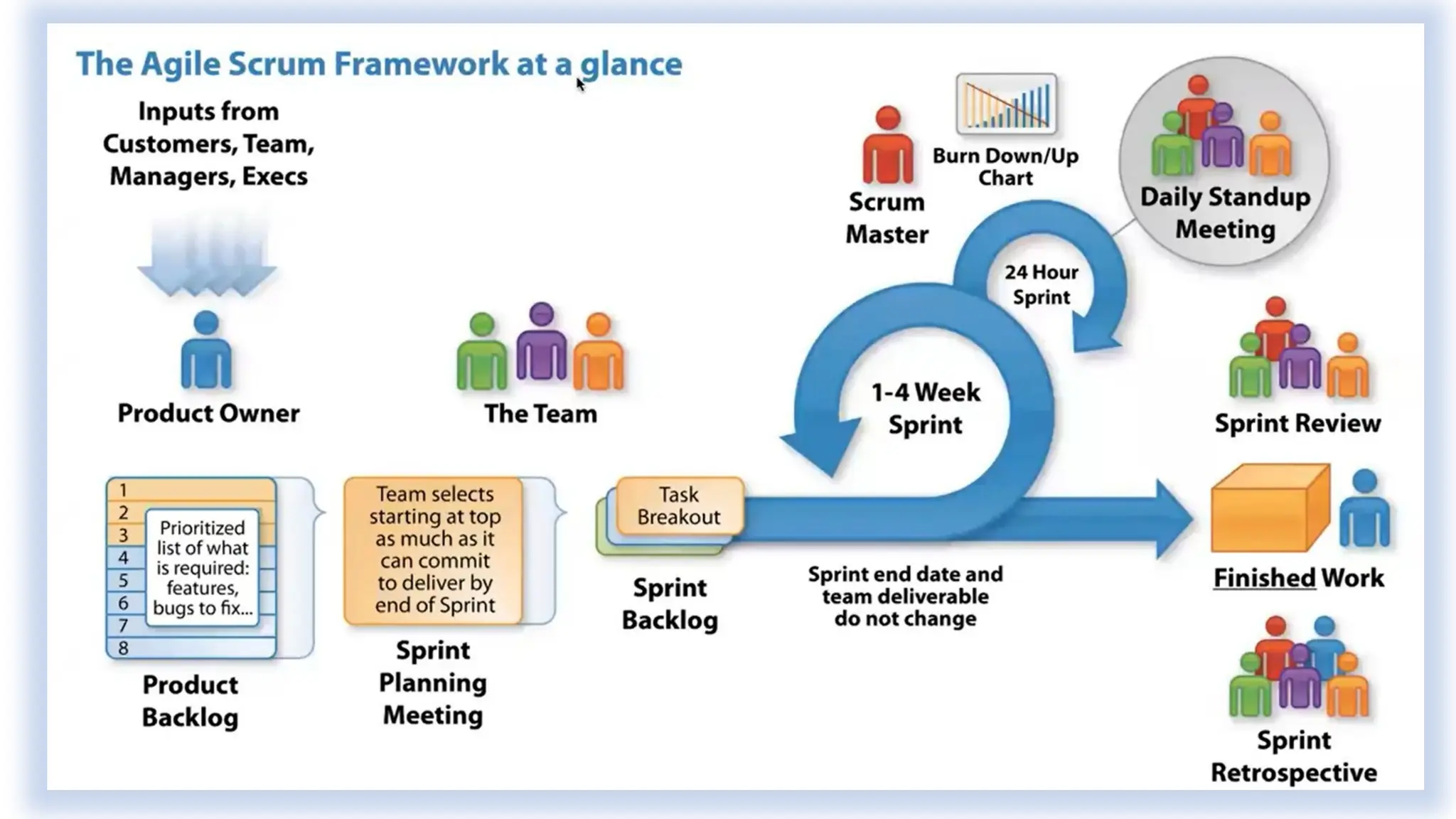
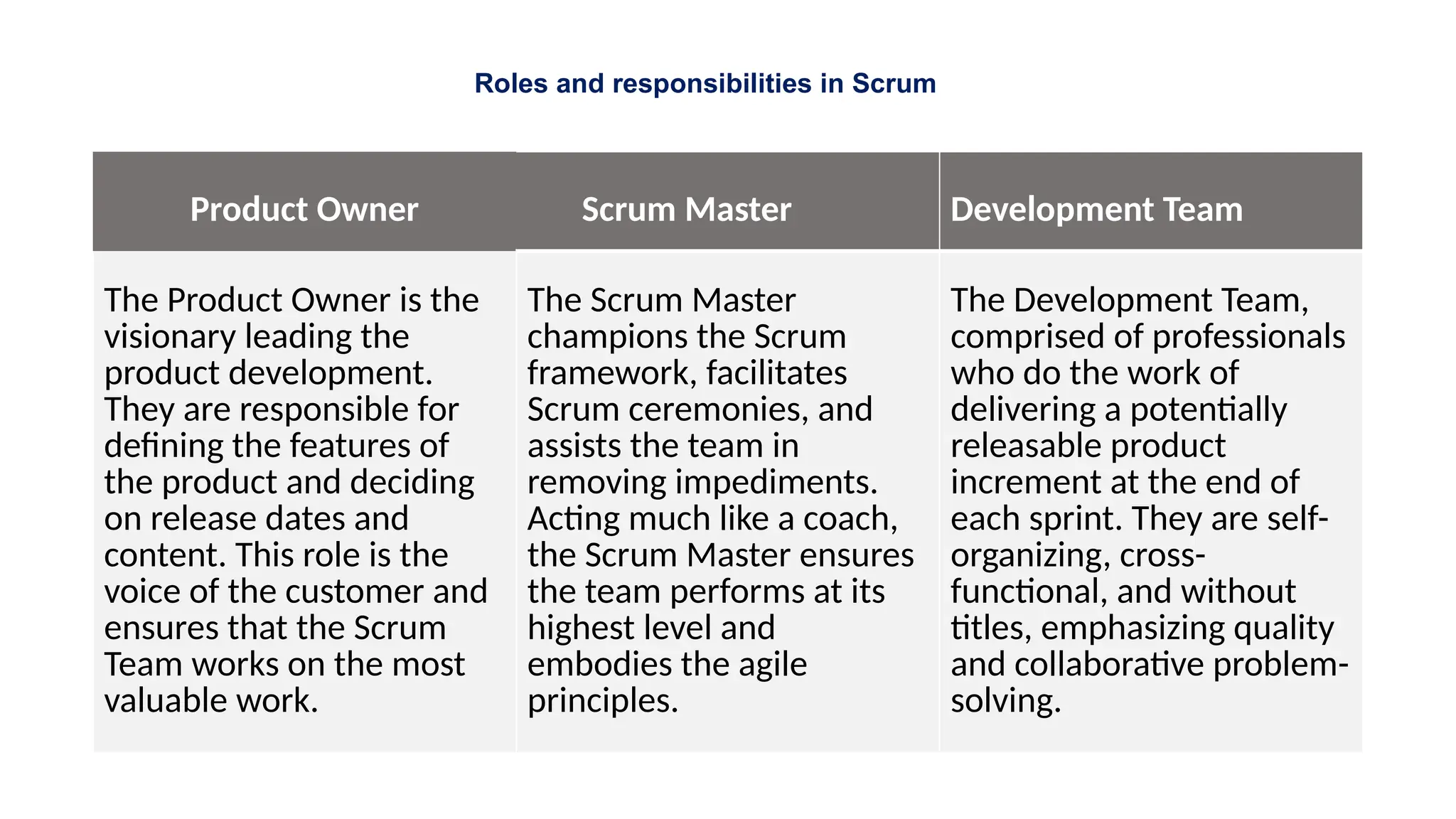
The document contrasts the waterfall and agile project management approaches, highlighting that waterfall follows a linear development process, while agile emphasizes iterative delivery and adaptability to change. It details the principles and roles within the Scrum framework, including the responsibilities of the product owner, scrum master, and development team, as well as key events and artifacts in Scrum. Ultimately, the choice between agile and waterfall depends on project requirements, complexity, and the level of client involvement desired.