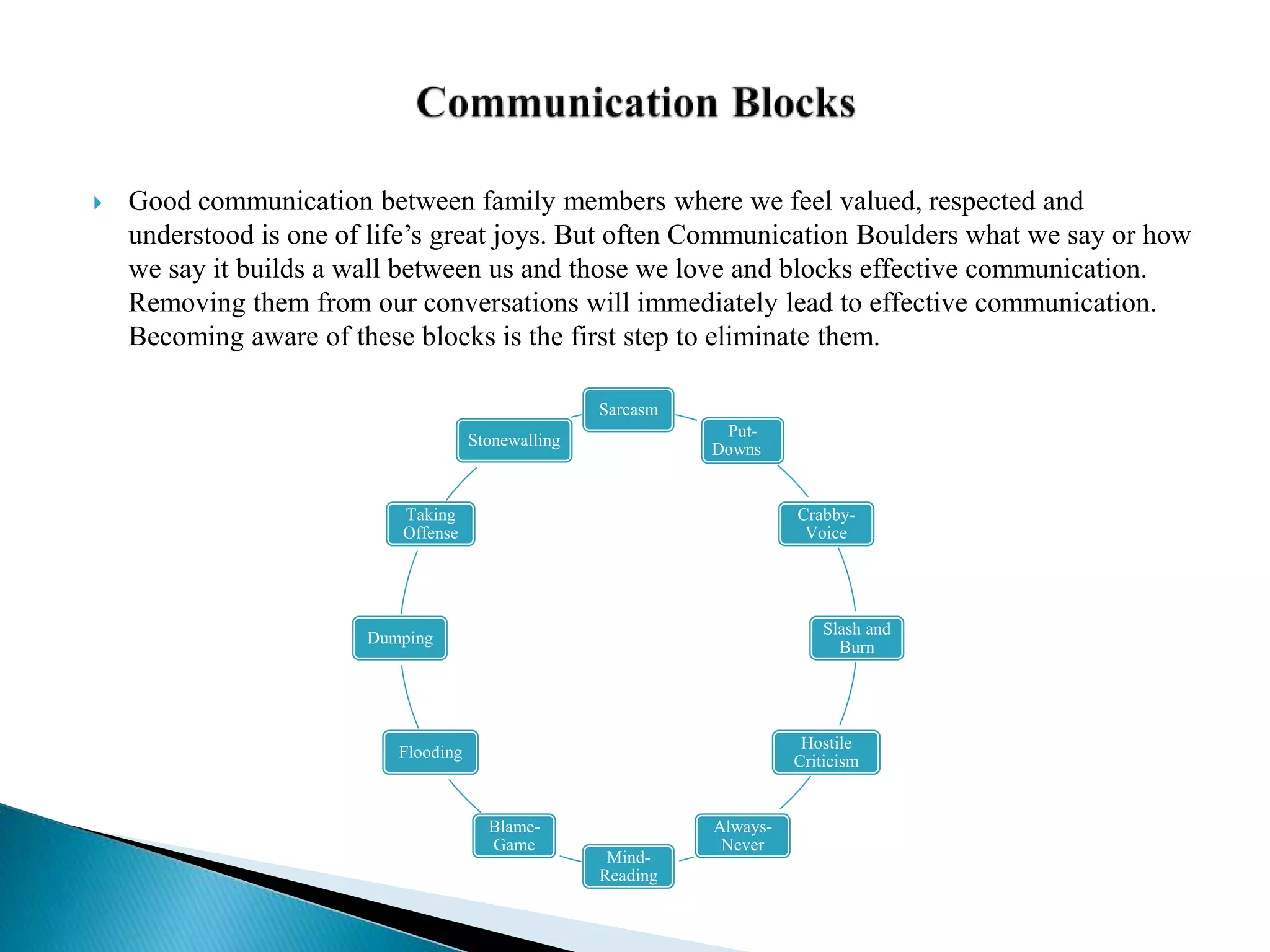
Family communication refers to both instrumental and affective exchanges between members. Instrumental communication shares factual information, while affective communication shares emotions. Healthy families communicate well in both areas. There are also two dimensions of family communication - conversation orientation, which is the openness of interaction and discussion of thoughts/feelings, and conformity orientation, which is the emphasis on similar attitudes, beliefs, and values. The four patterns of family communication are laissez-faire, protective, consensual, and pluralistic, which vary based on levels of conversation and conformity orientation.