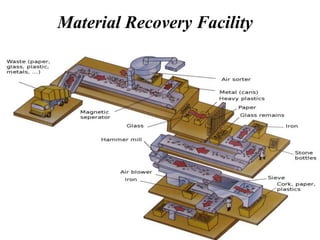
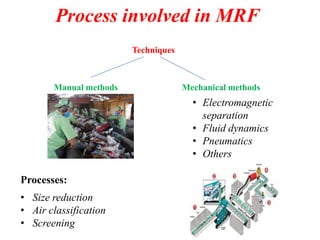
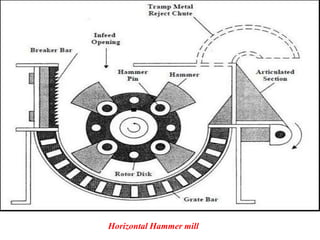
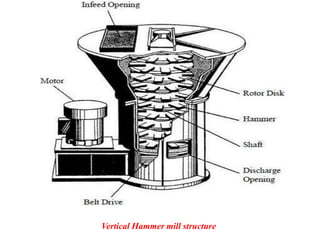
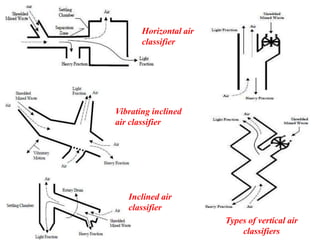
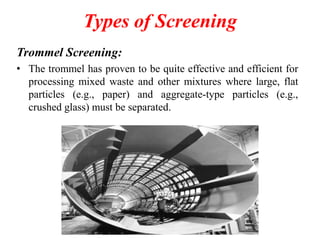
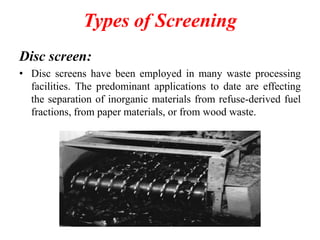
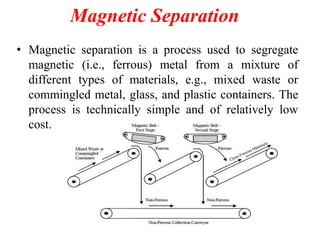
The document discusses material recovery facilities (MRFs) which separate recyclable materials from solid waste for marketing to manufacturers. MRFs use both manual and mechanical methods of separation. Manual sorting removes contaminants while mechanical processes like size reduction, air classification, screening, magnetic separation, and eddy current separation separate materials based on physical properties. Together these methods efficiently recover resources from waste to support recycling.