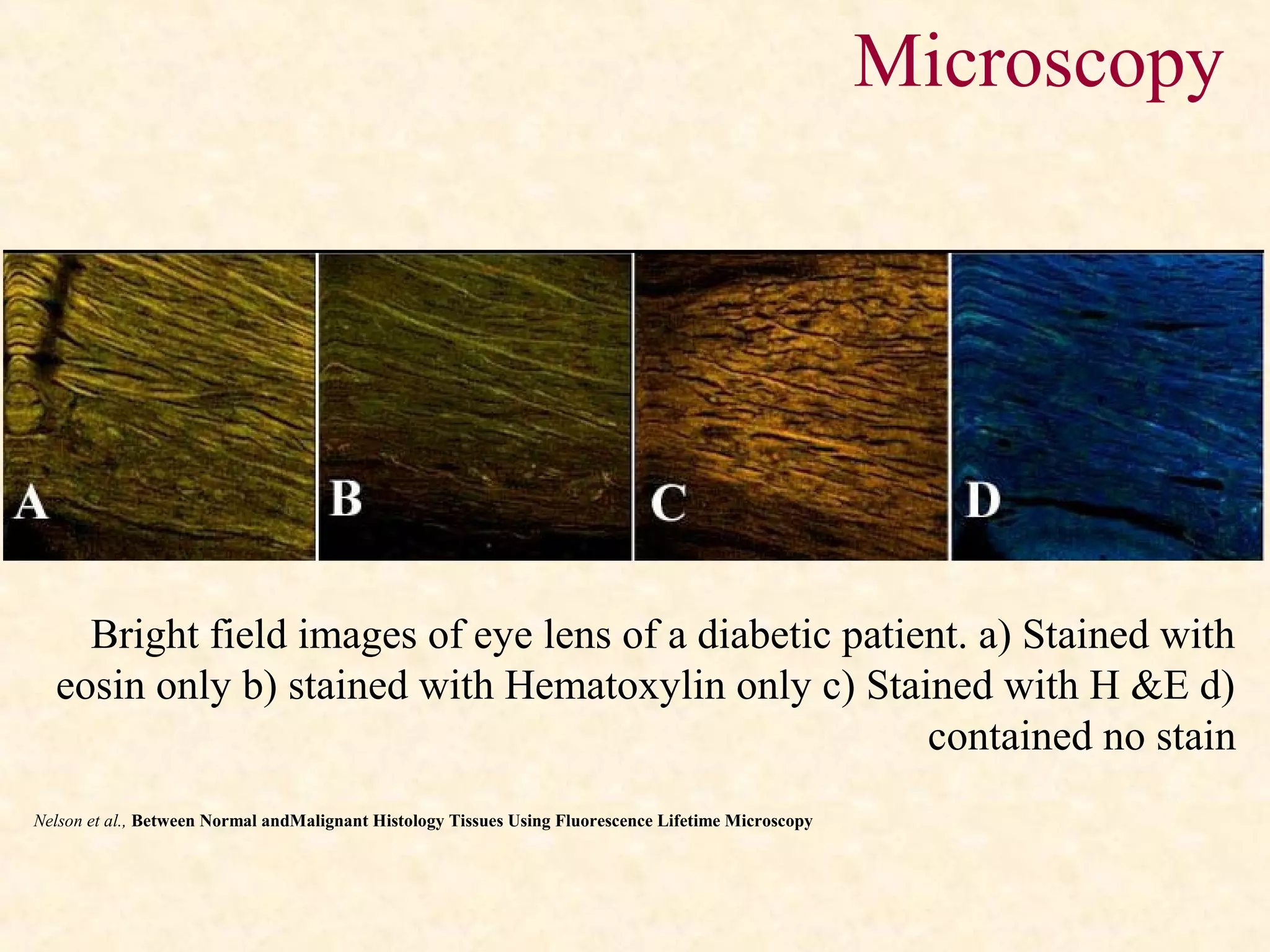
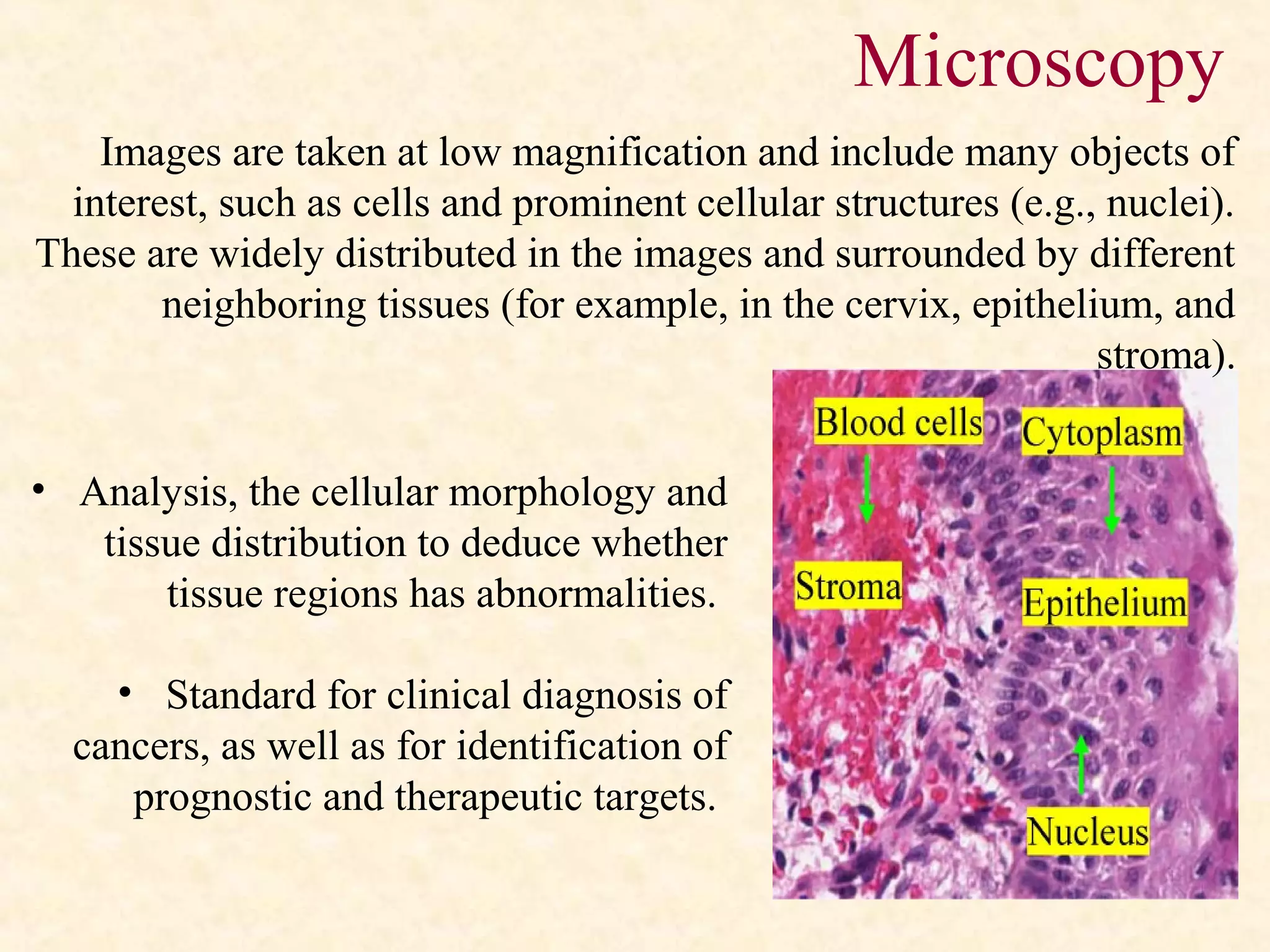
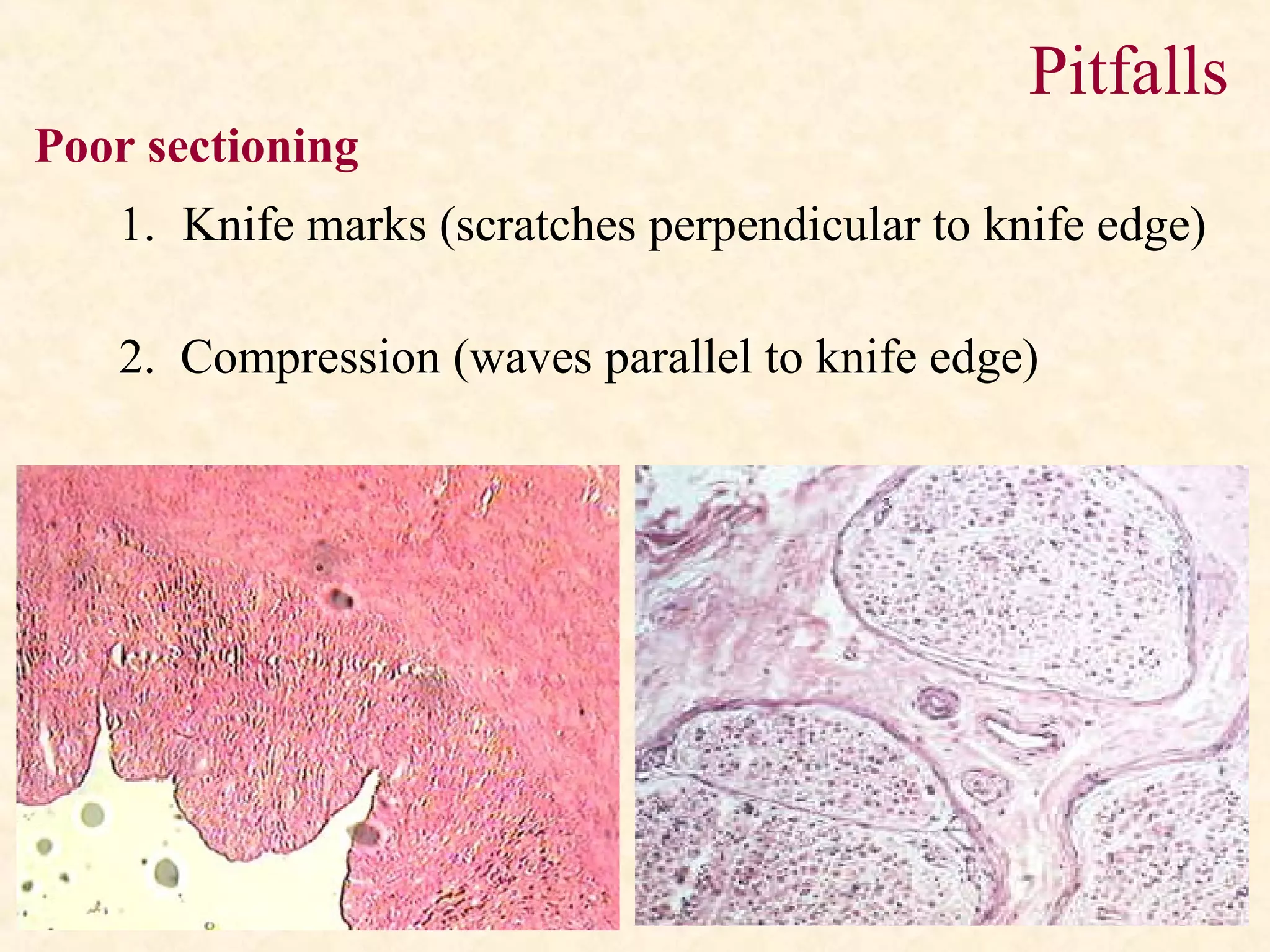
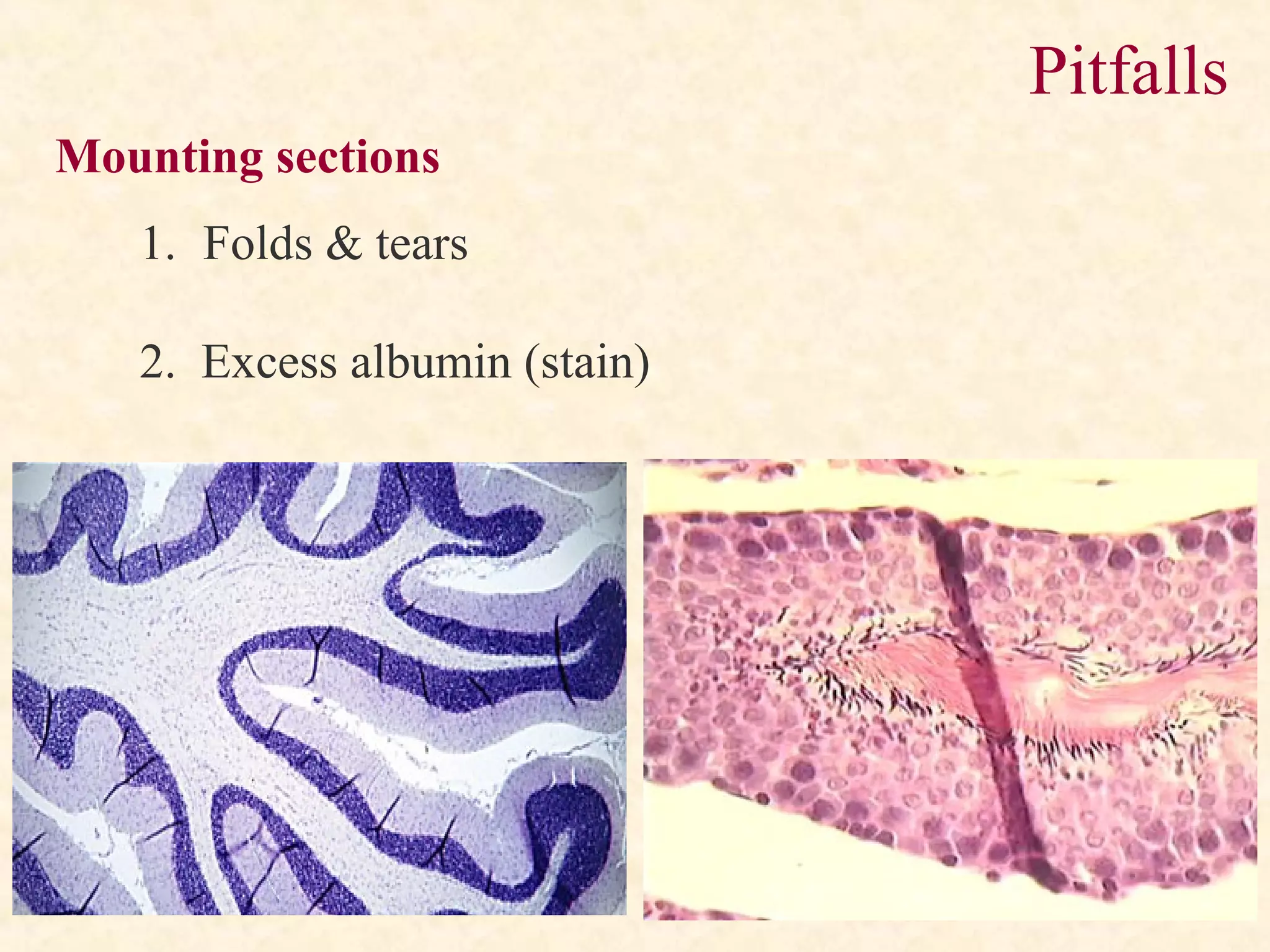
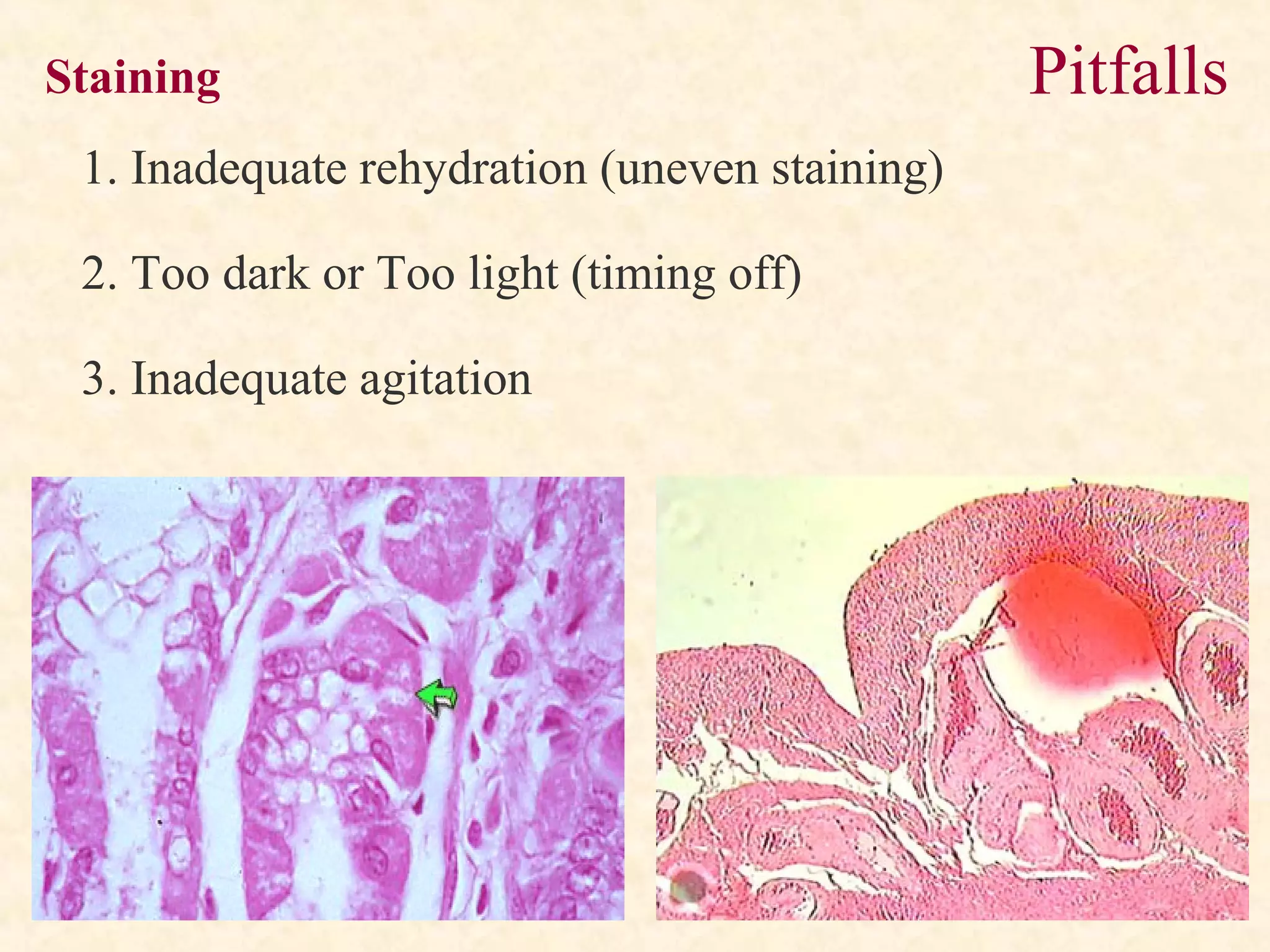
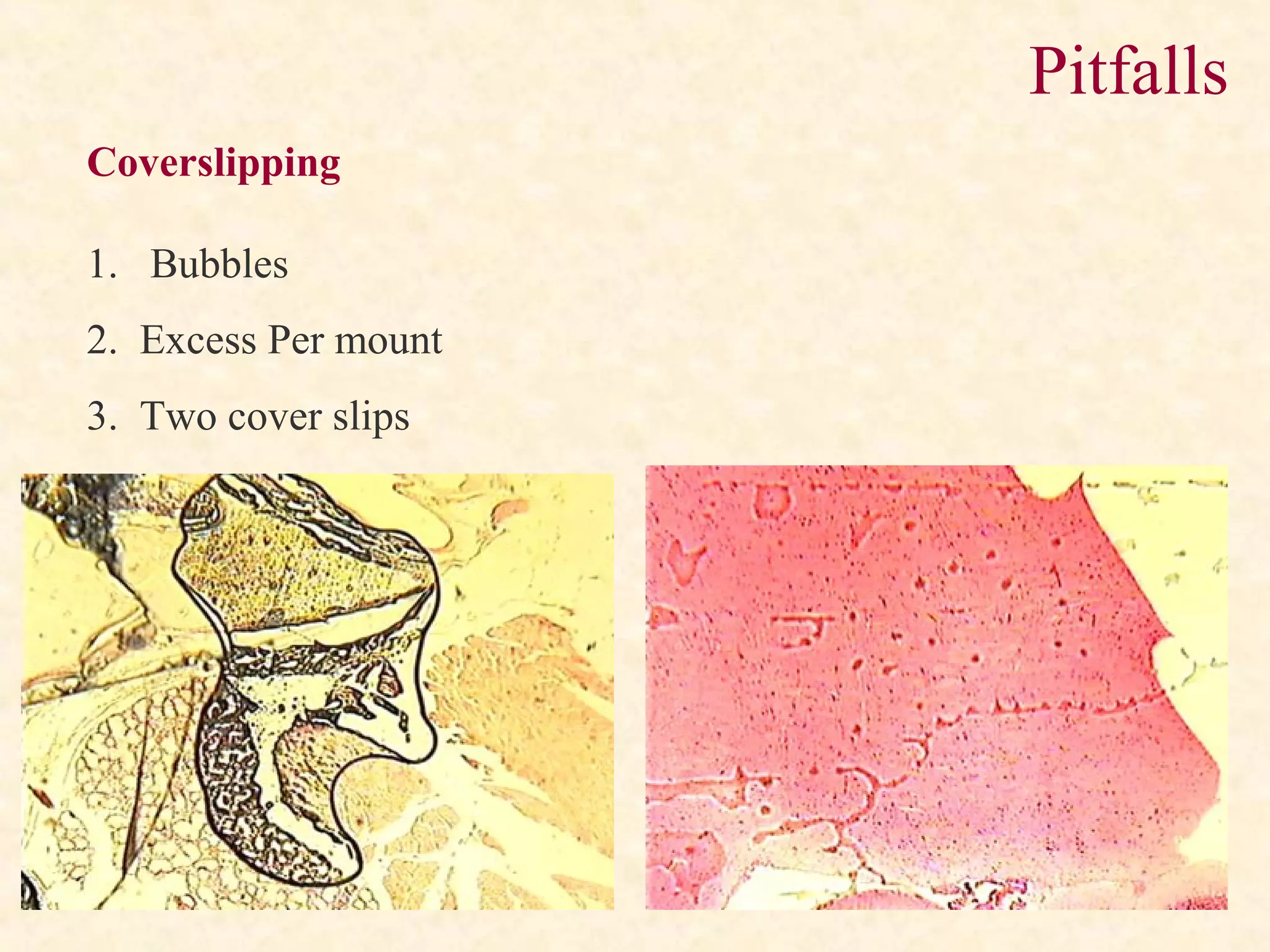
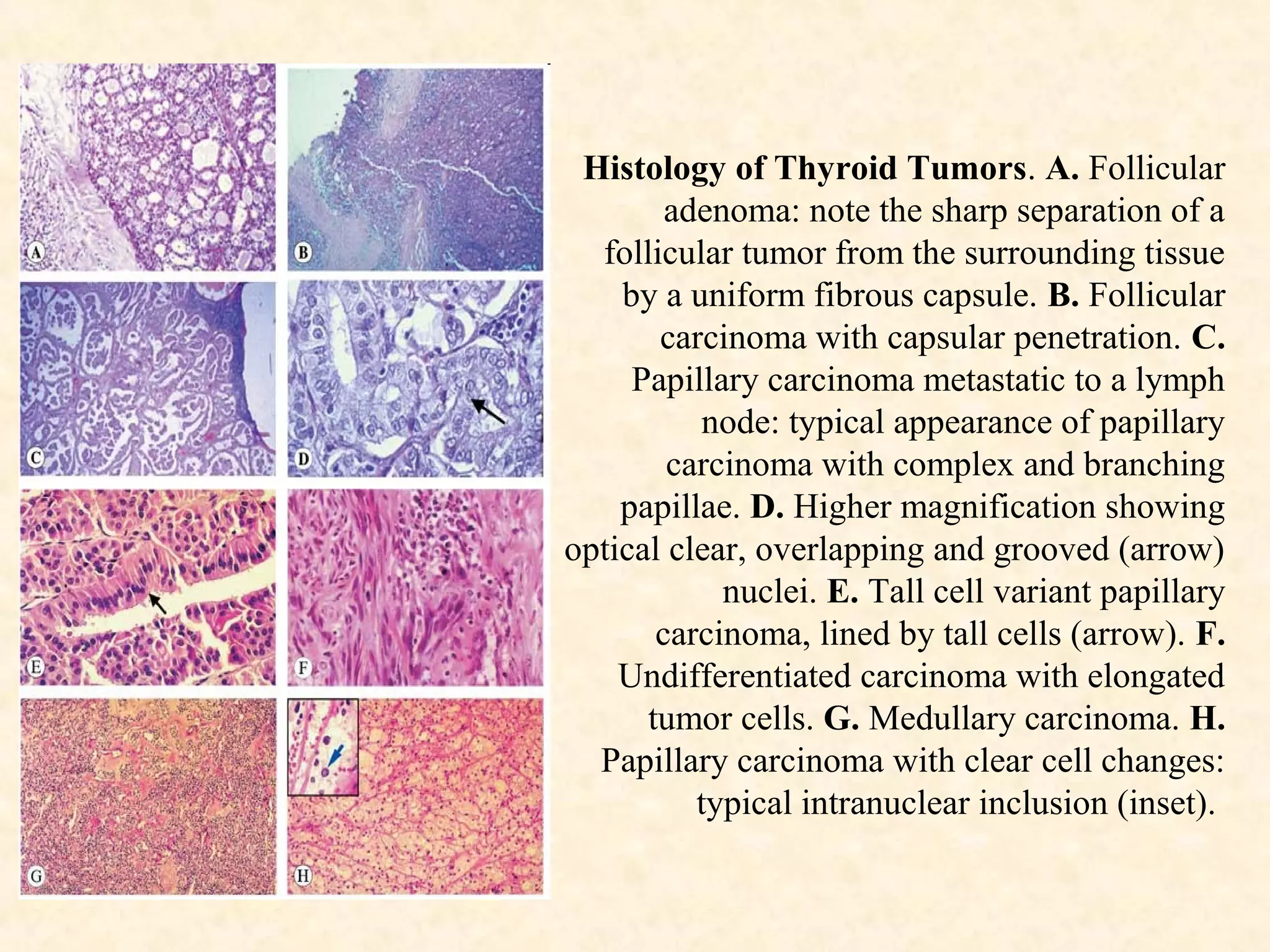
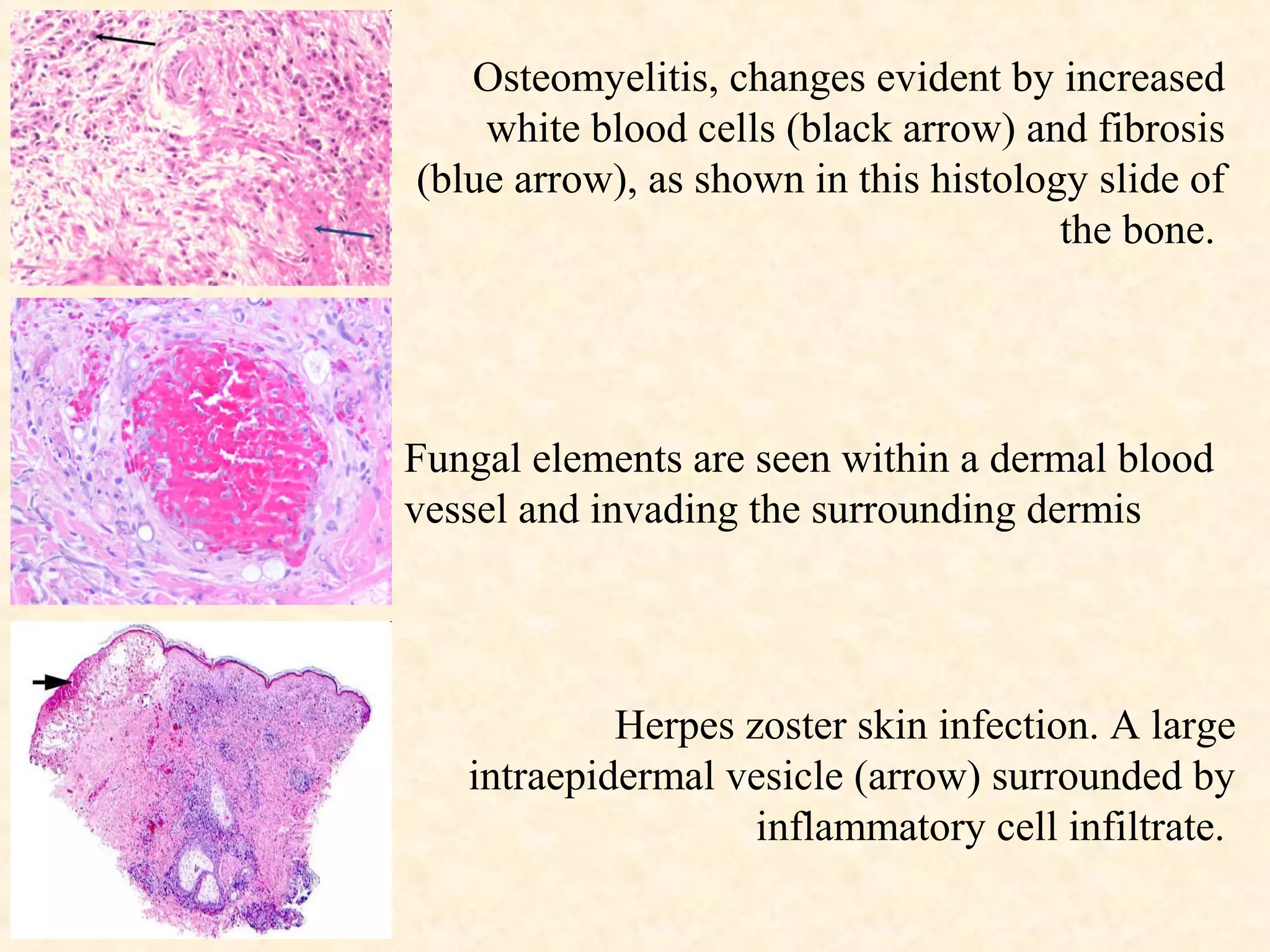
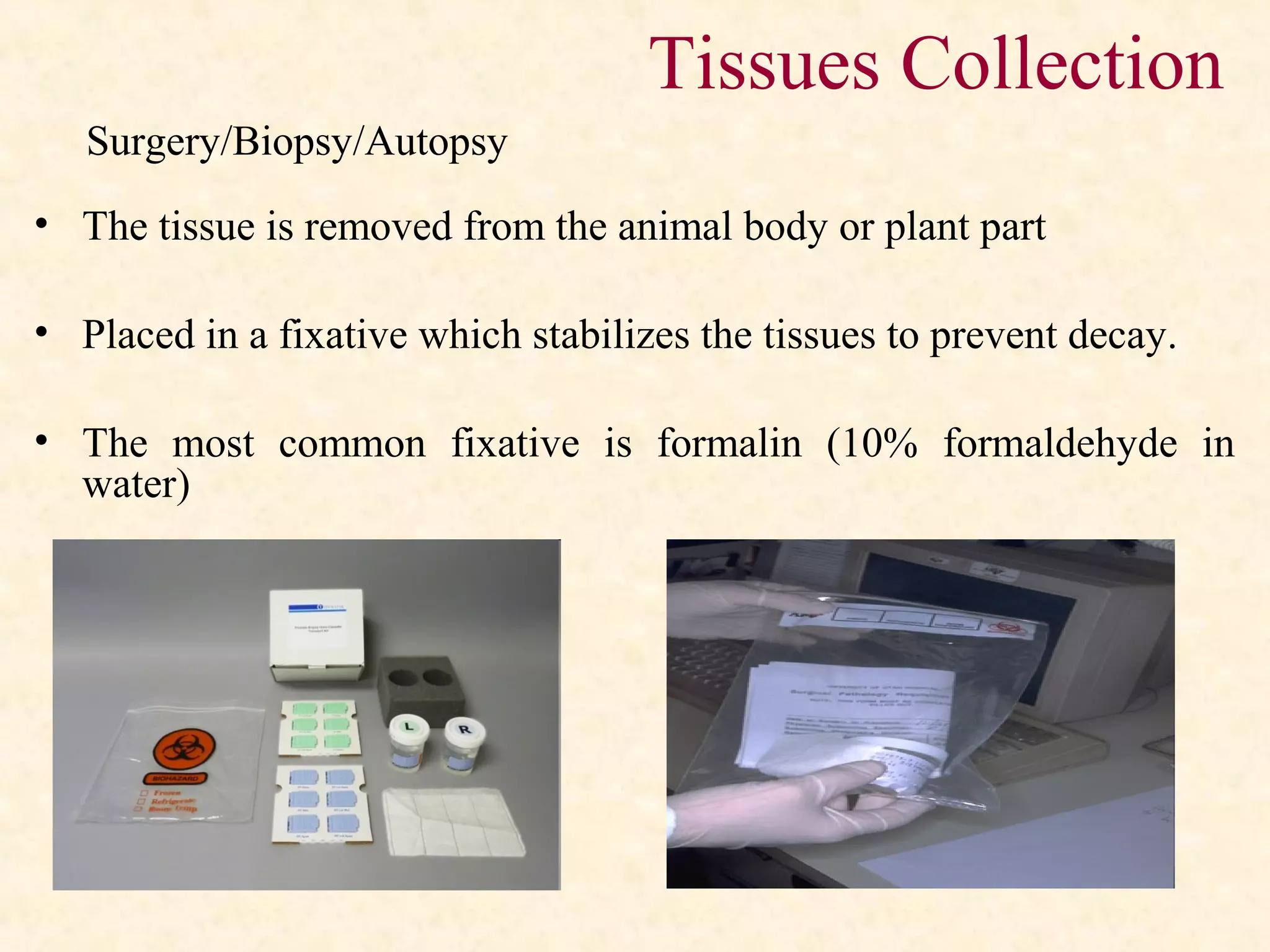
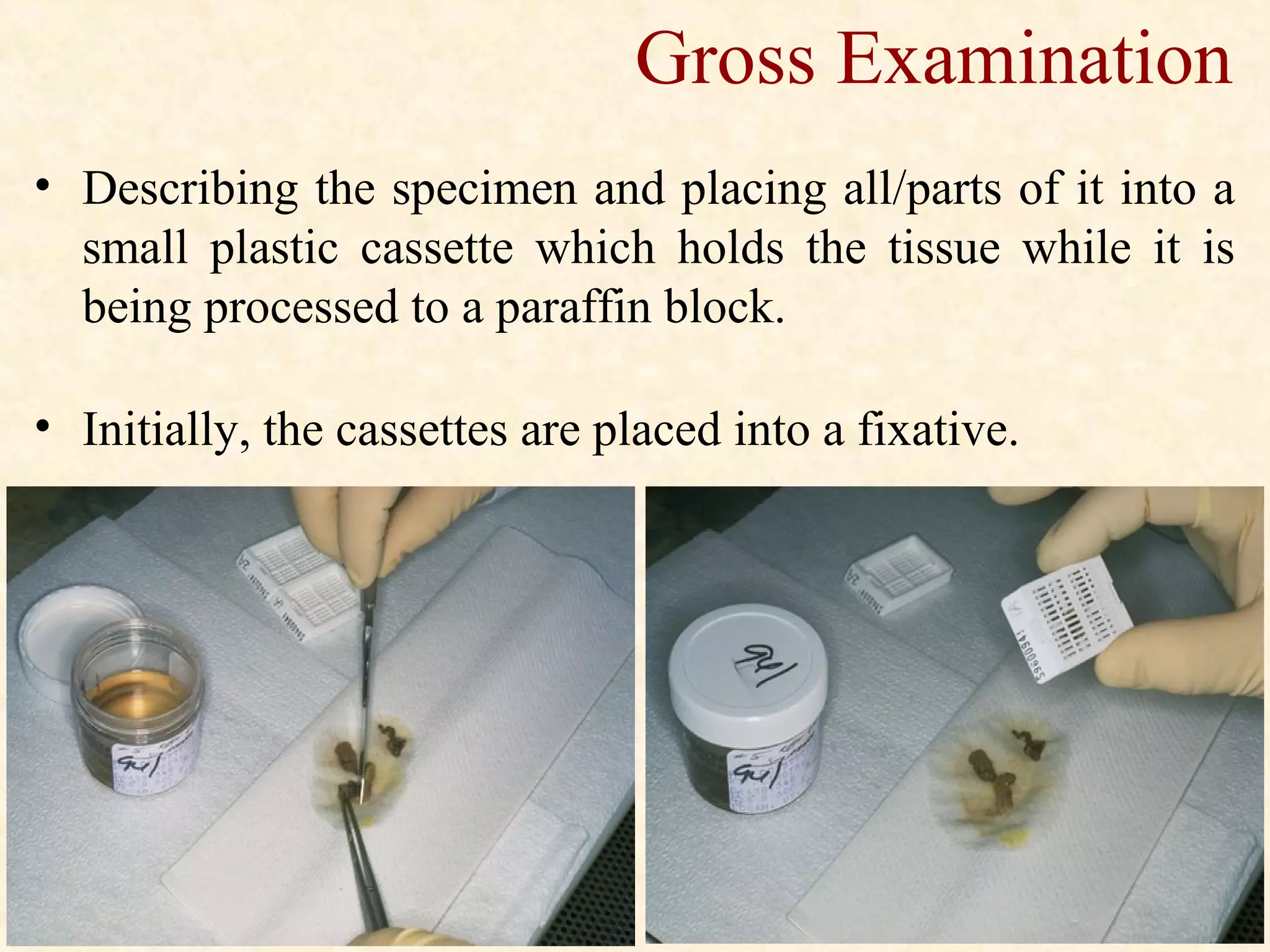
The document discusses the methods and processes involved in histopathology, detailing the history and classification of tissues, tissue processing techniques including fixation, dehydration, and embedding, as well as staining procedures for microscopic examination. It also covers the importance of histopathological evaluations in diagnosing diseases, including malignancies and infections, and outlines potential pitfalls in tissue processing and staining. A comprehensive overview of histological techniques such as using a microtome for sectioning and the use of staining methods like hematoxylin and eosin is provided.


















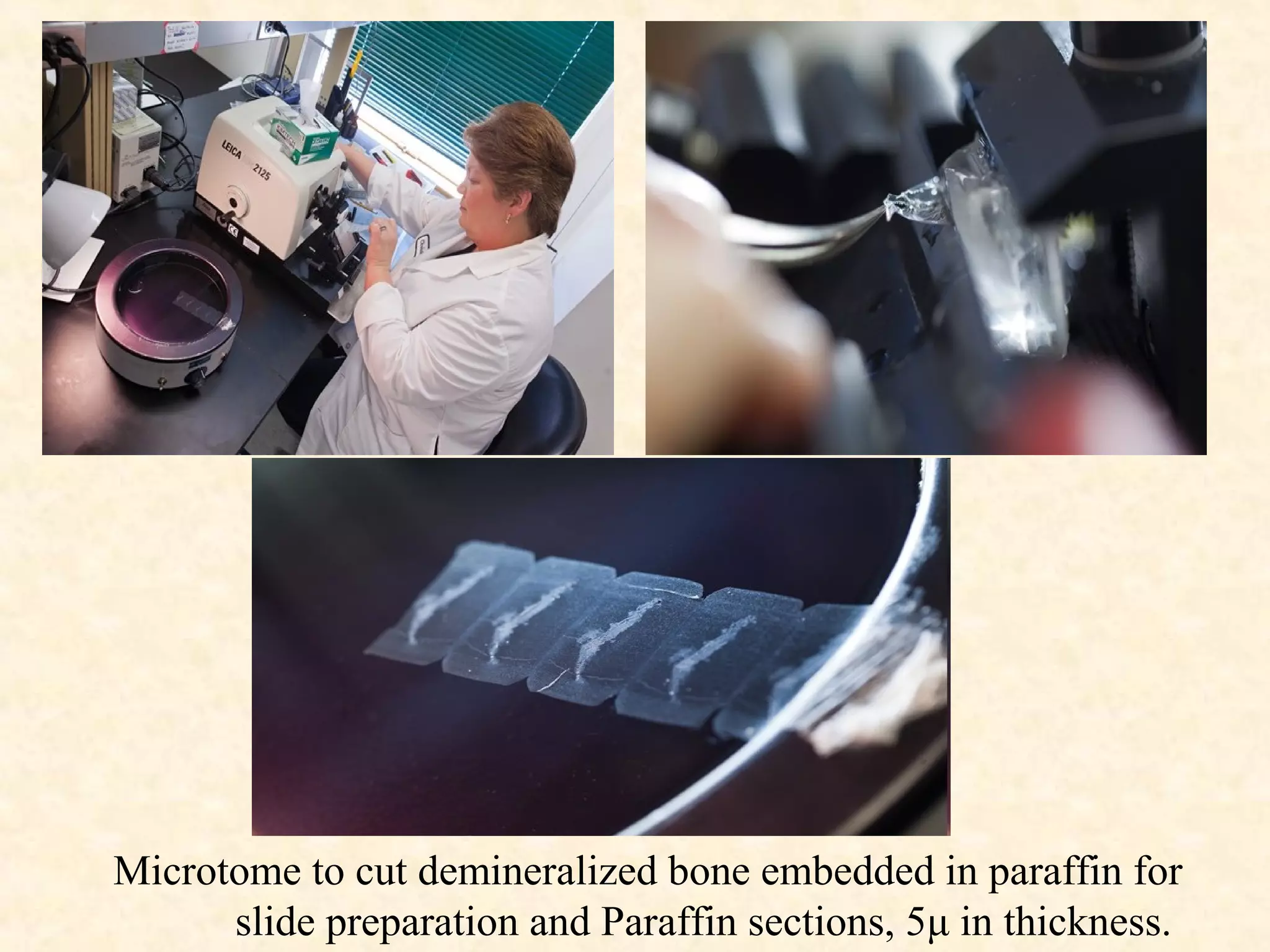
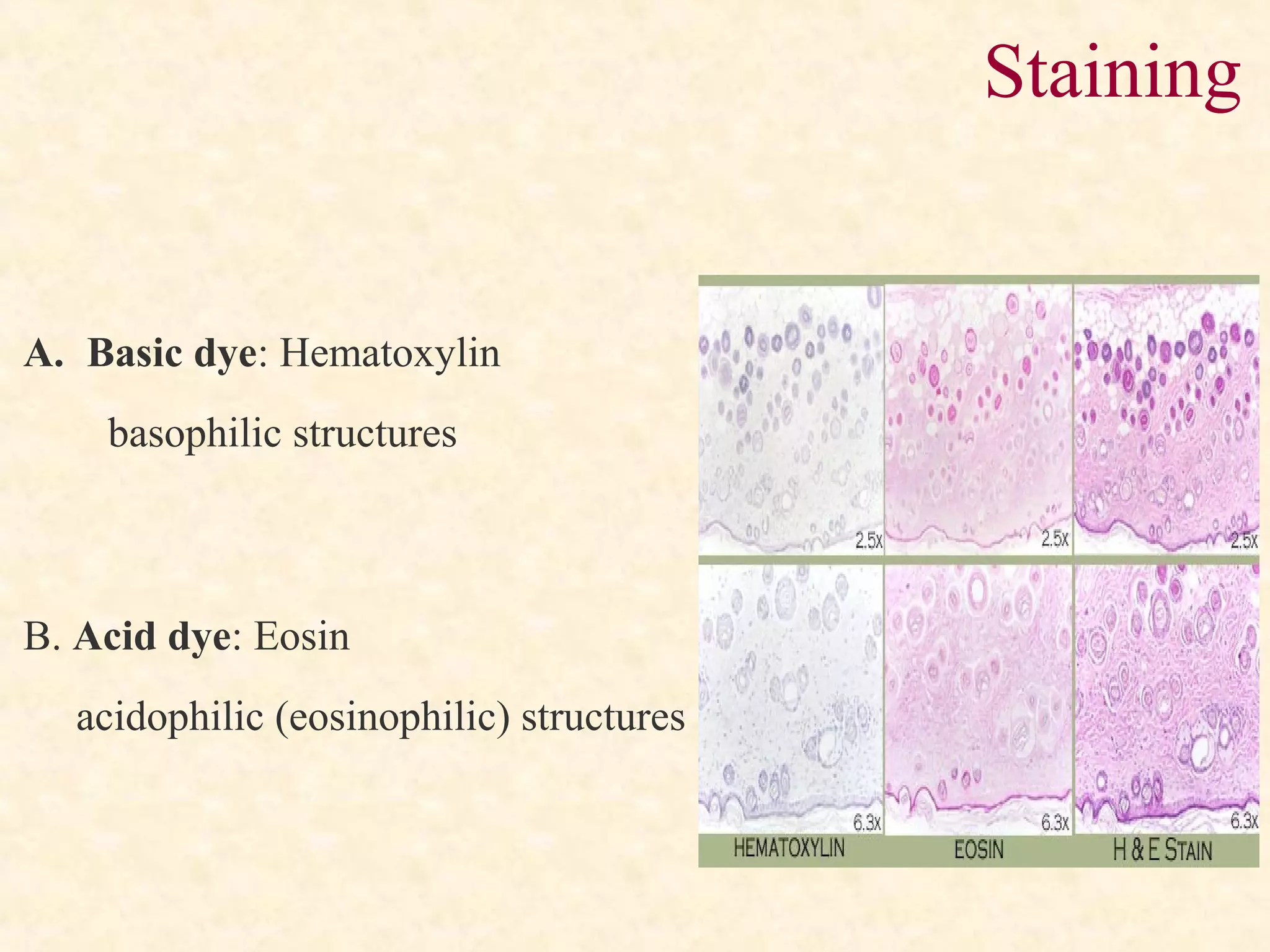



![Fibroblasts with dark nuclei [A] are
seen here along with thick collagen
fibers [B], thin elastic fibers [C] and
very fine reticular fibers [D].
Microscopic view of a histological
specimen of human lung tissue stained
with hematoxylin and eosin.
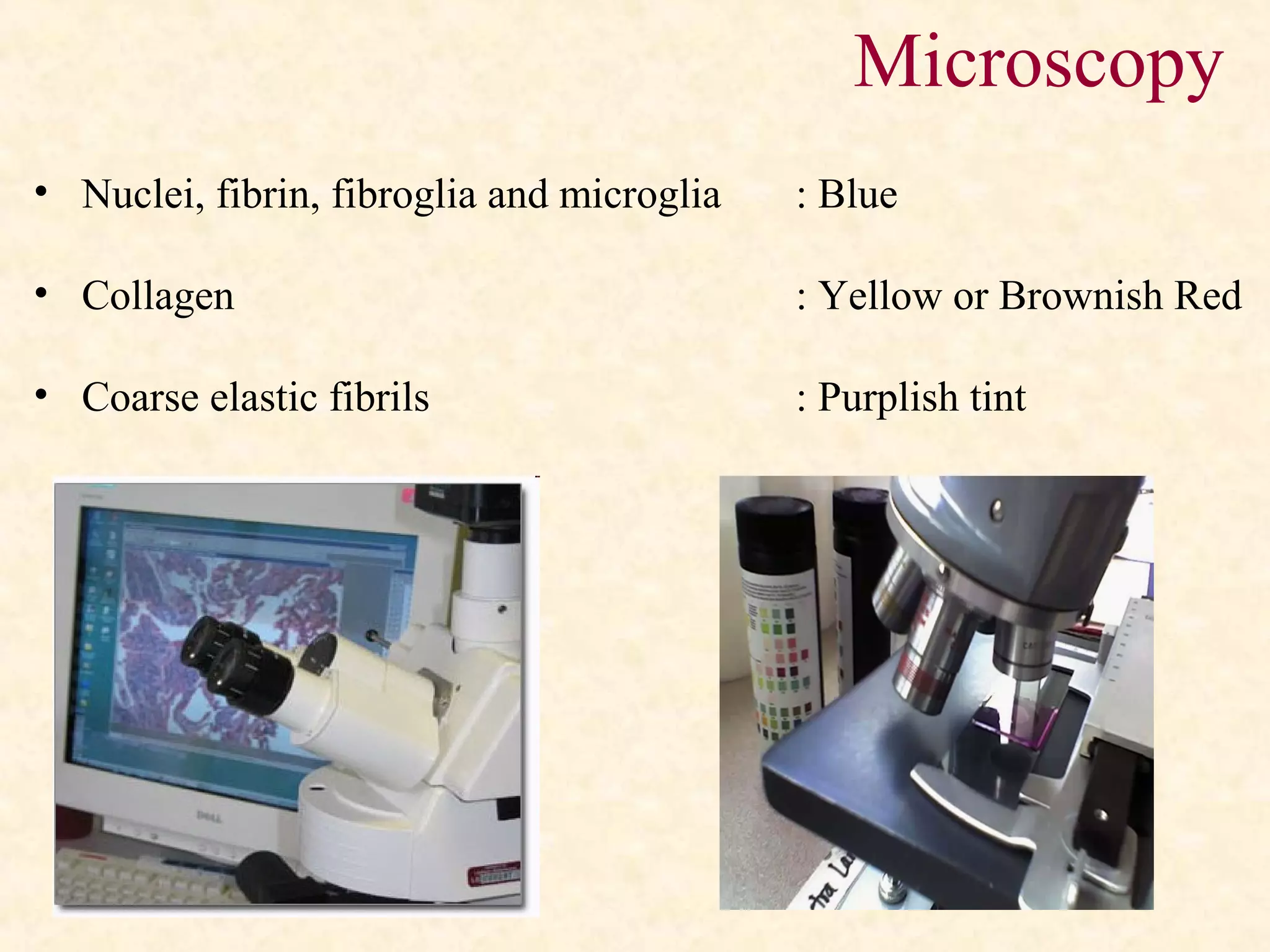
Microscopy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tissproc1-180324051812/75/Tissue-Processing-in-Histopathology-33-2048.jpg)