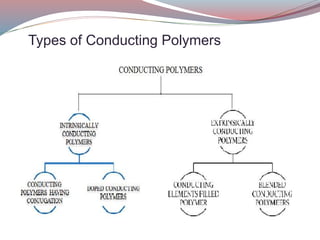
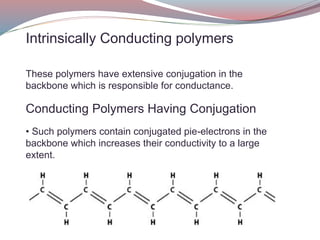
This document discusses conducting polymers. It describes two types of conducting polymers: intrinsically conducting polymers which have conjugation in their backbone providing conductivity, and extrinsically conducting polymers which require external ingredients like carbon black to become conductive. Doping can increase the conductivity of polymers by removing or inserting electrons. Conducting polymers have applications in anti-static coatings, corrosion inhibition, capacitors, smart windows, transistors, LEDs and solar cells. While manufacturing costs are high, conducting polymers could enable flexible transparent displays and be used in biomedical applications if issues like toxicity and processing are addressed.