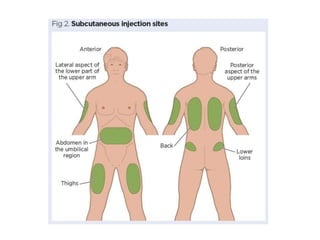
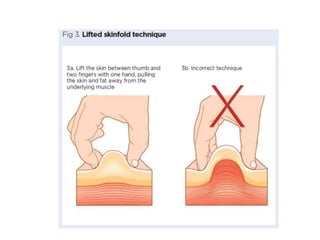
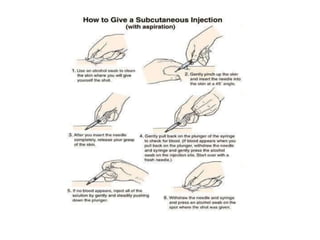
Subcutaneous injections involve injecting medication into the subcutaneous tissue just below the skin using a short needle. This route provides slower absorption than intramuscular injections, which is beneficial for drugs that need continuous absorption like insulin or heparin. Recommended sites for subcutaneous injections include the upper arms, thighs, and abdomen. Proper technique involves lifting a skin fold and inserting the needle at a 90 degree angle to deliver the drug slowly. Factors like injection site rotation help prevent issues like lipohypertrophy.