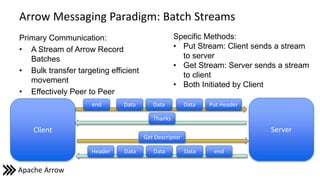
Arrow Flight is a proposed RPC layer for Apache Arrow that allows for efficient transfer of Arrow record batches between systems. It uses GRPC as the foundation to define streams of Arrow data that can be consumed in parallel across locations. Arrow Flight supports custom actions that can be used to build services on top of the generic API. By extending GRPC, Arrow Flight aims to simplify the creation of data applications while enabling high performance data transfer and locality awareness.