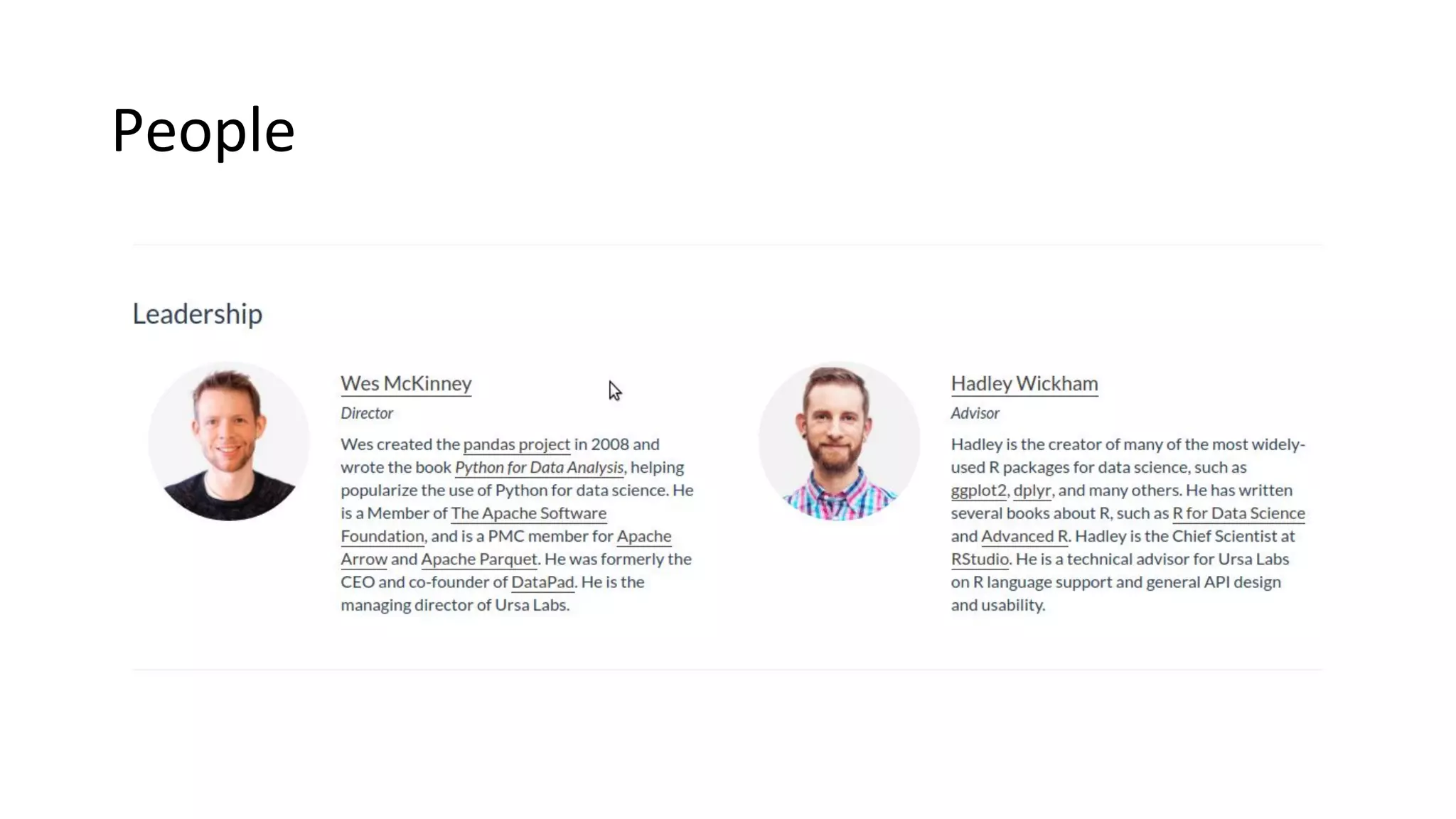
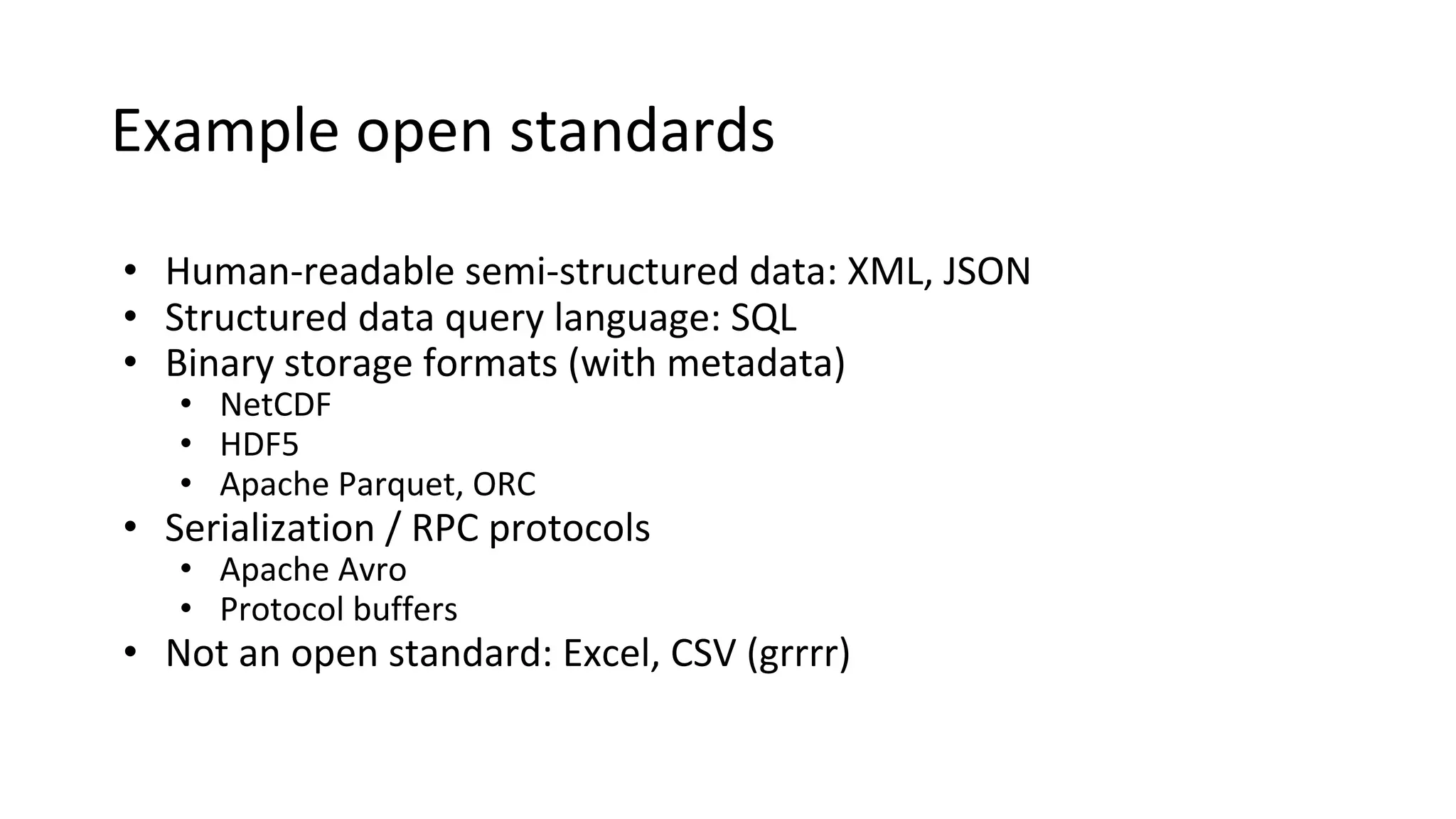
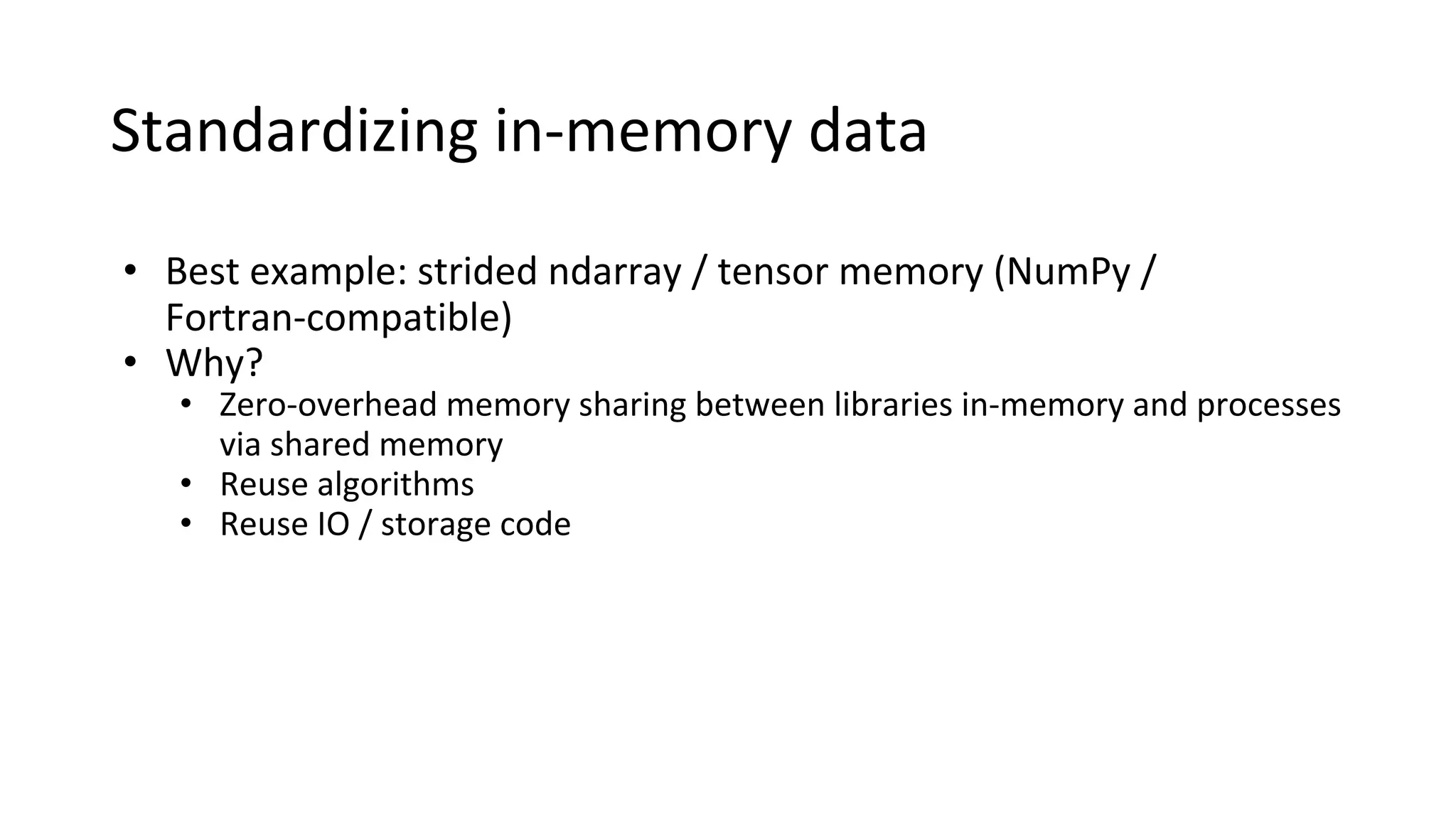
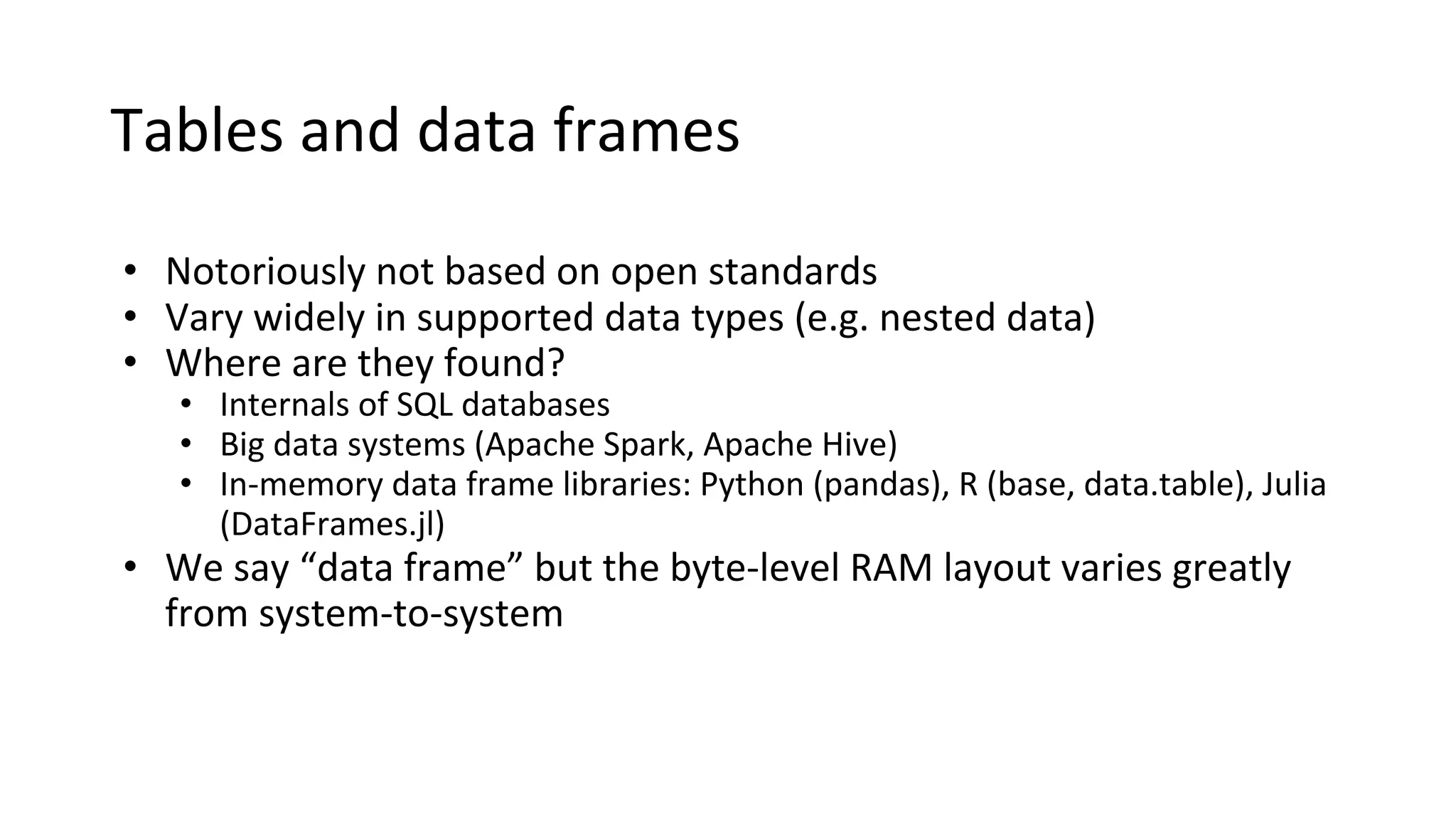
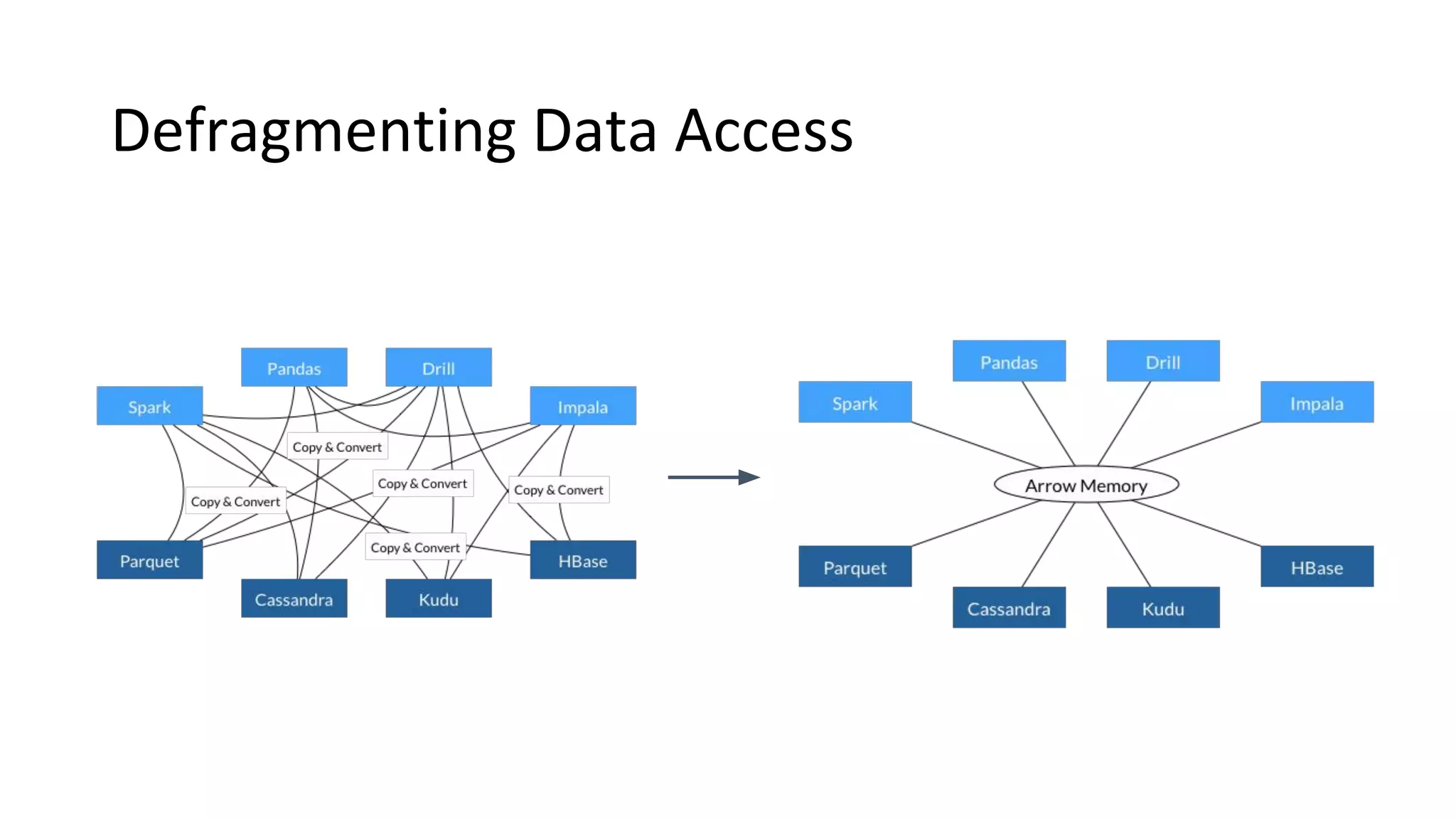
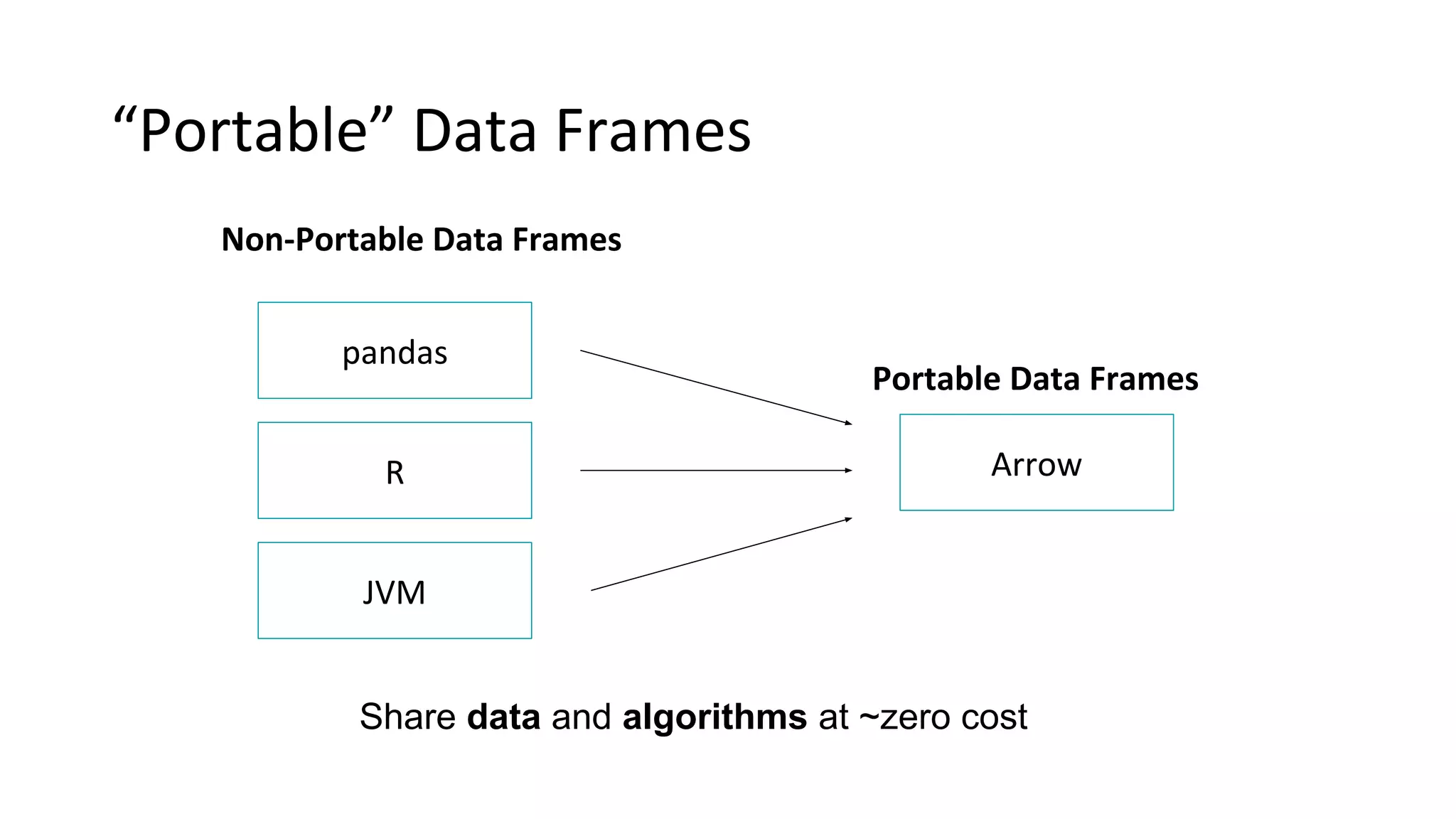
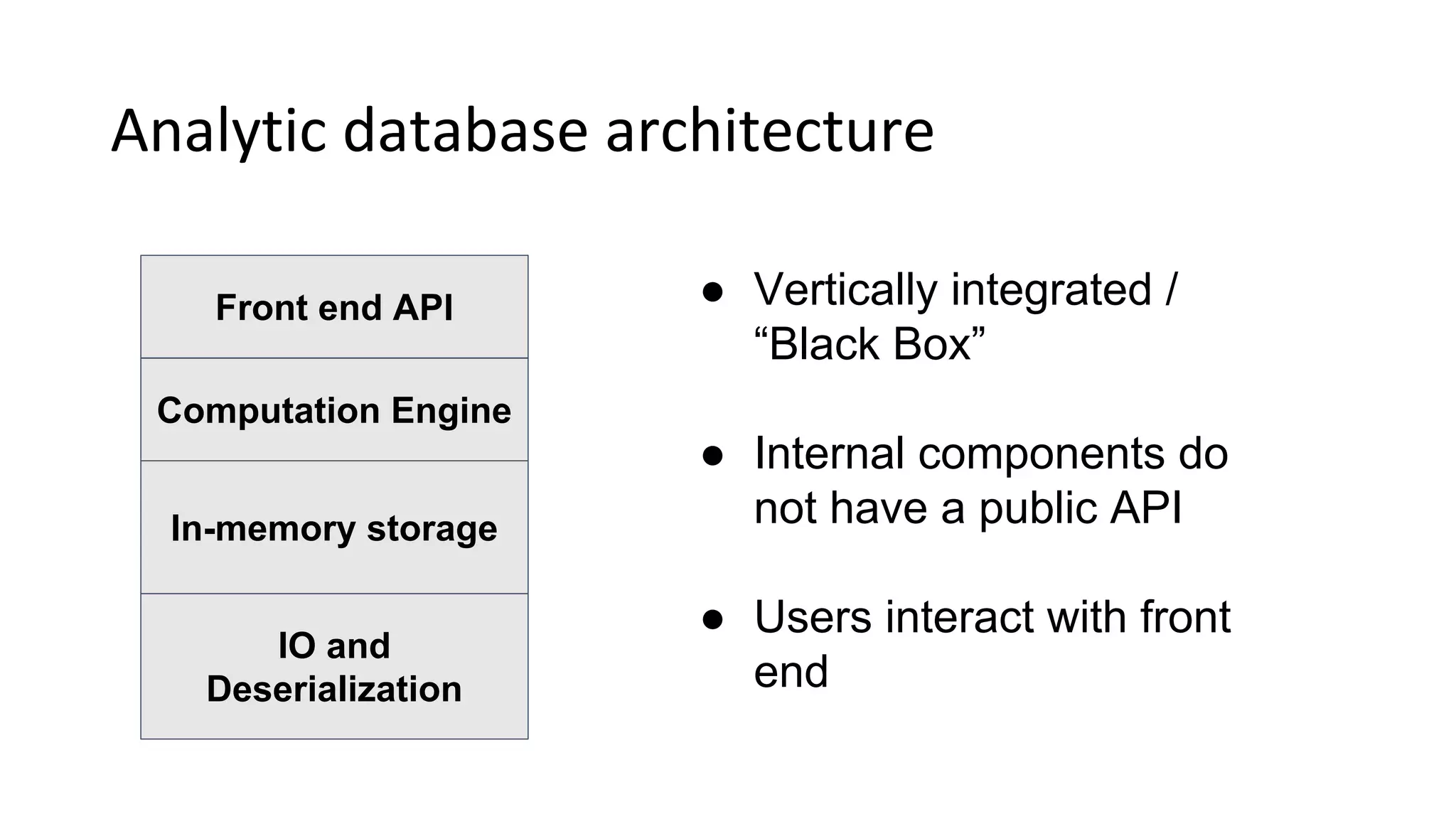
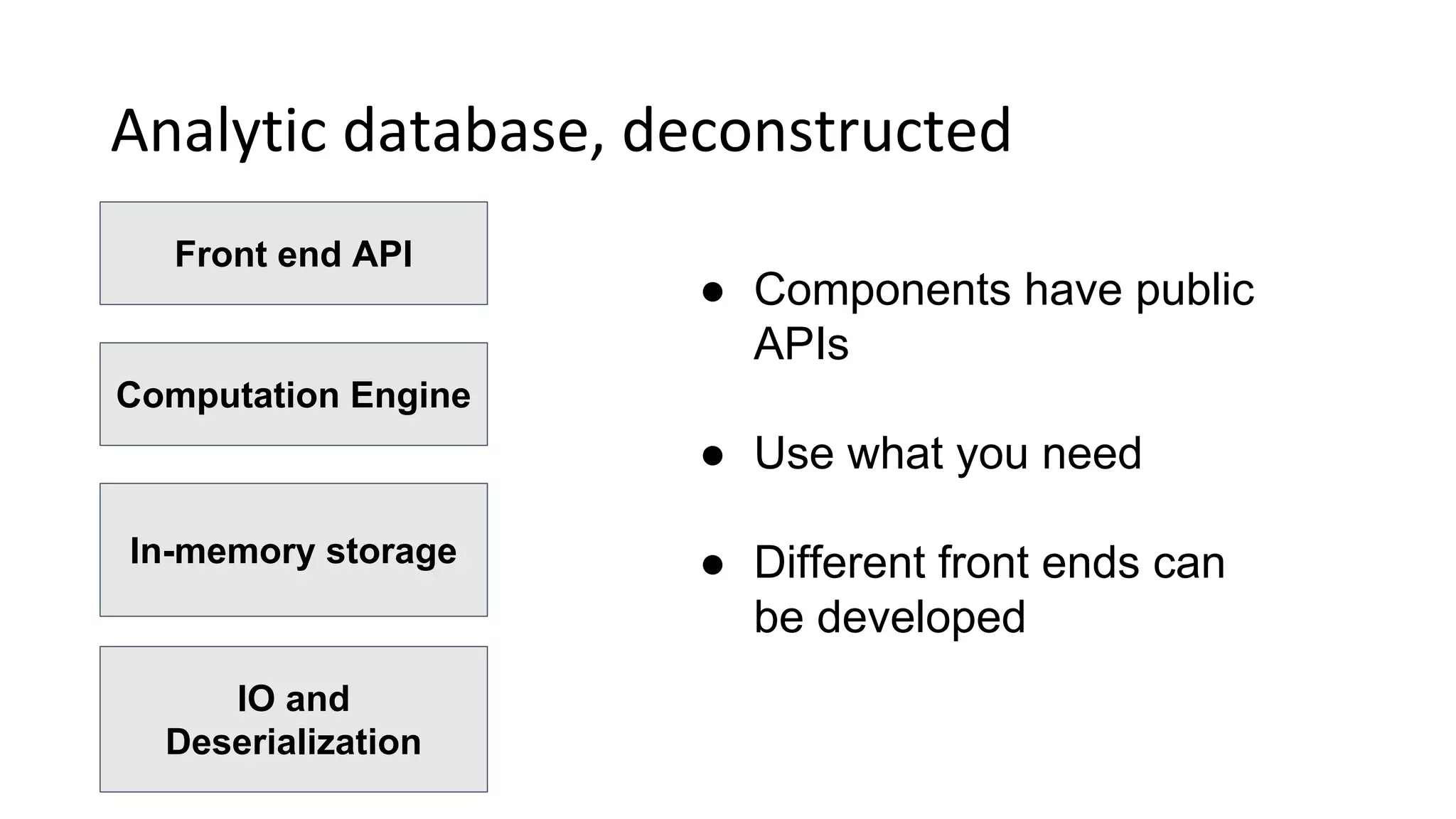
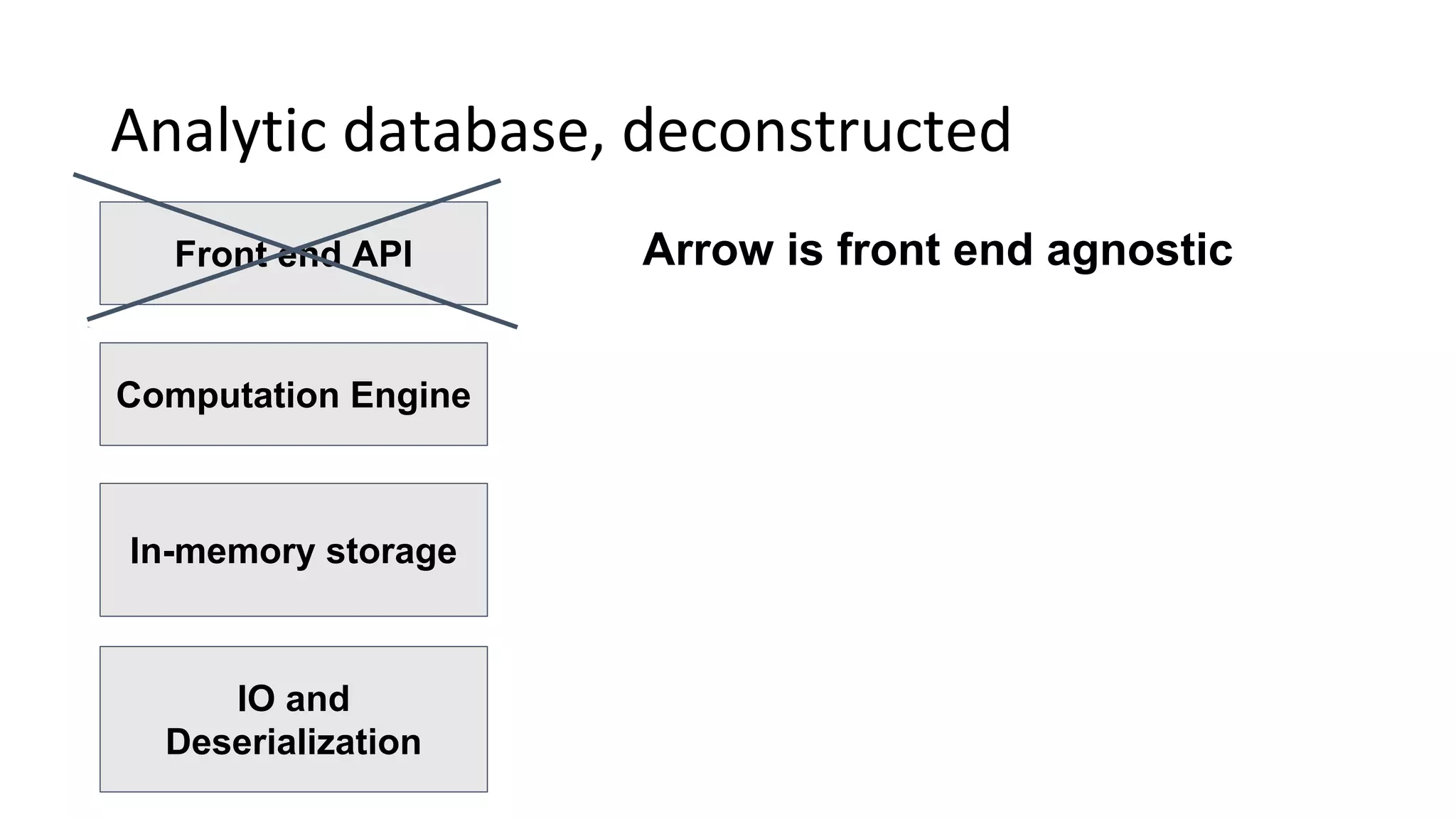
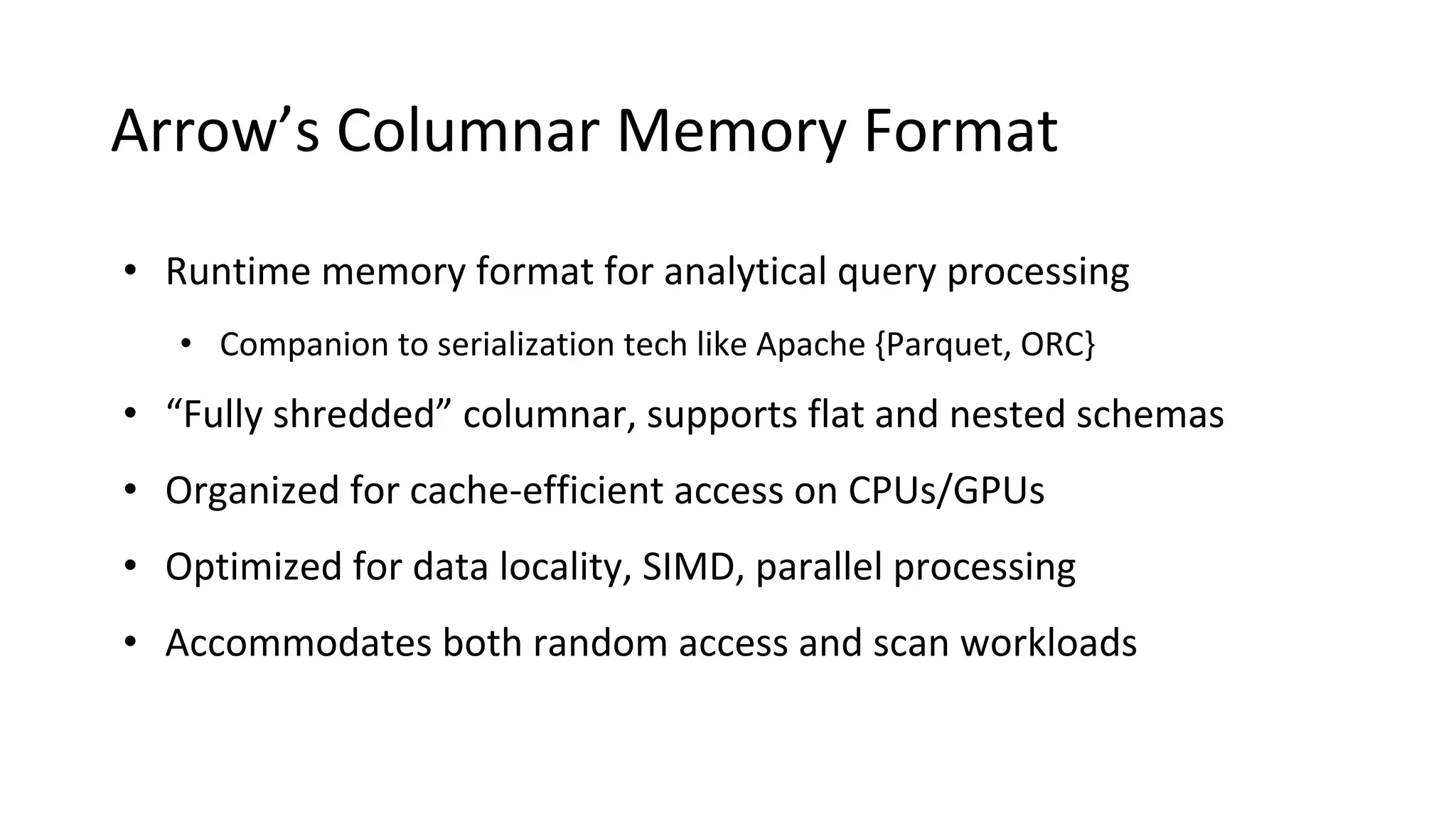
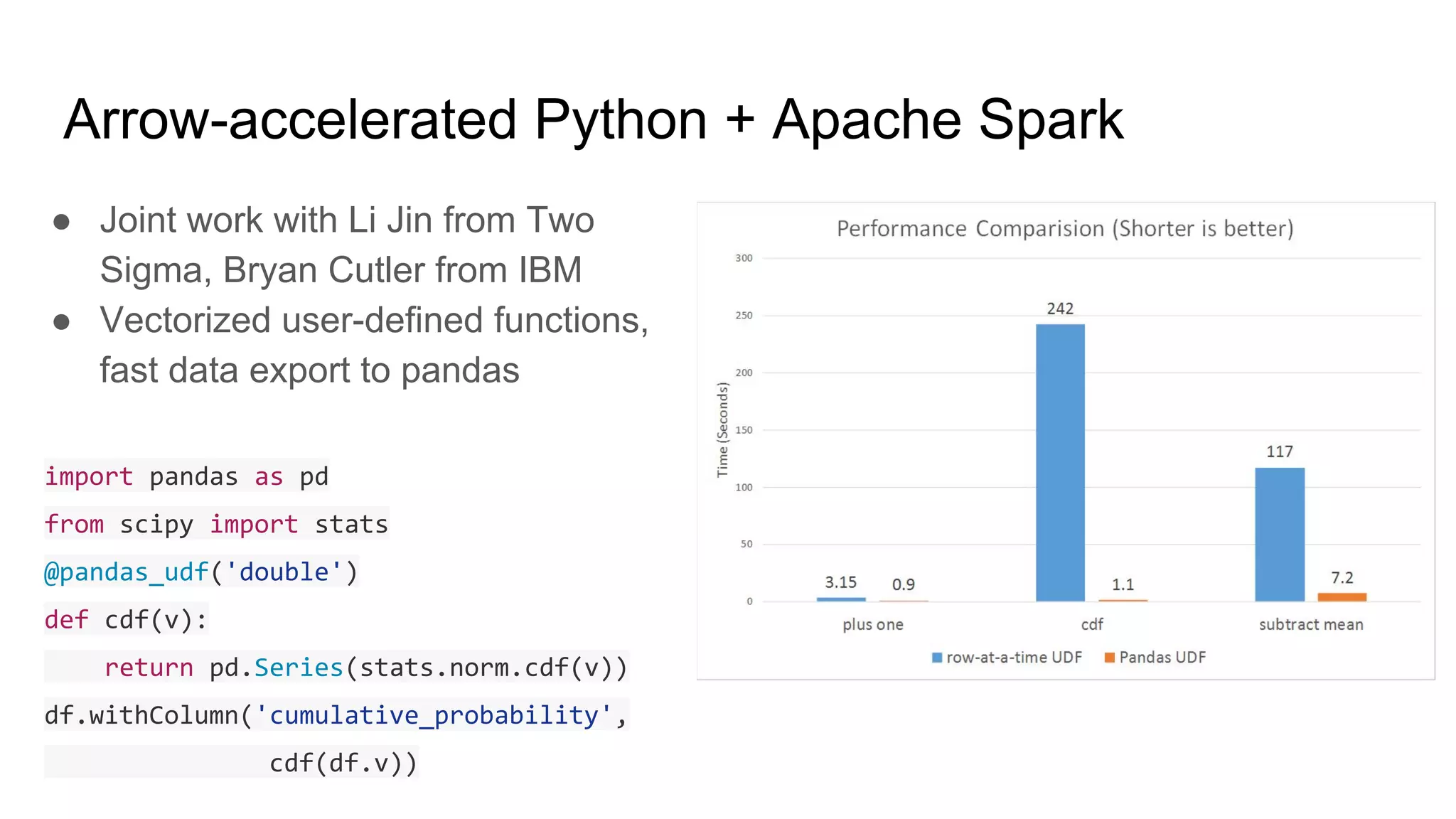
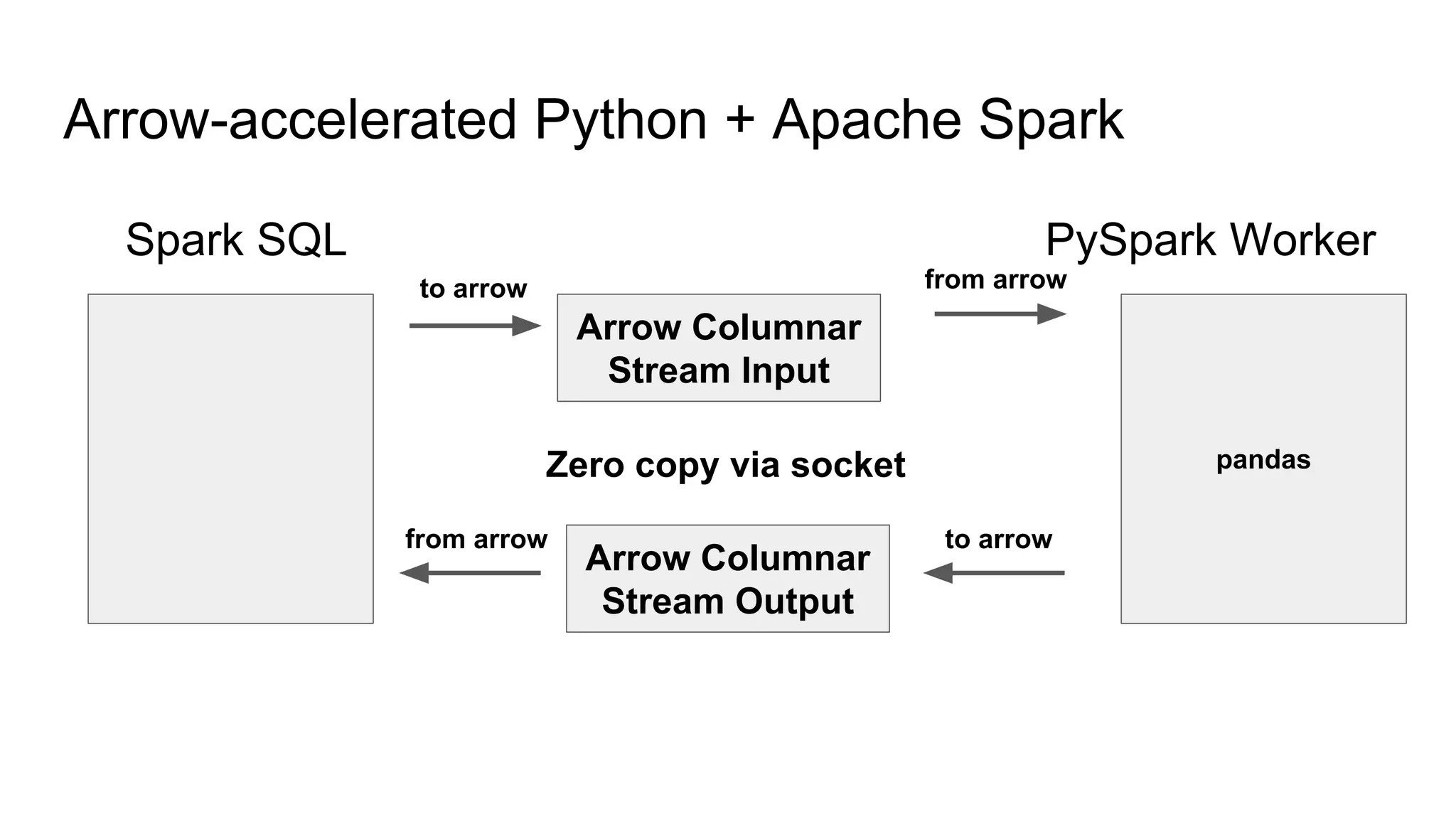
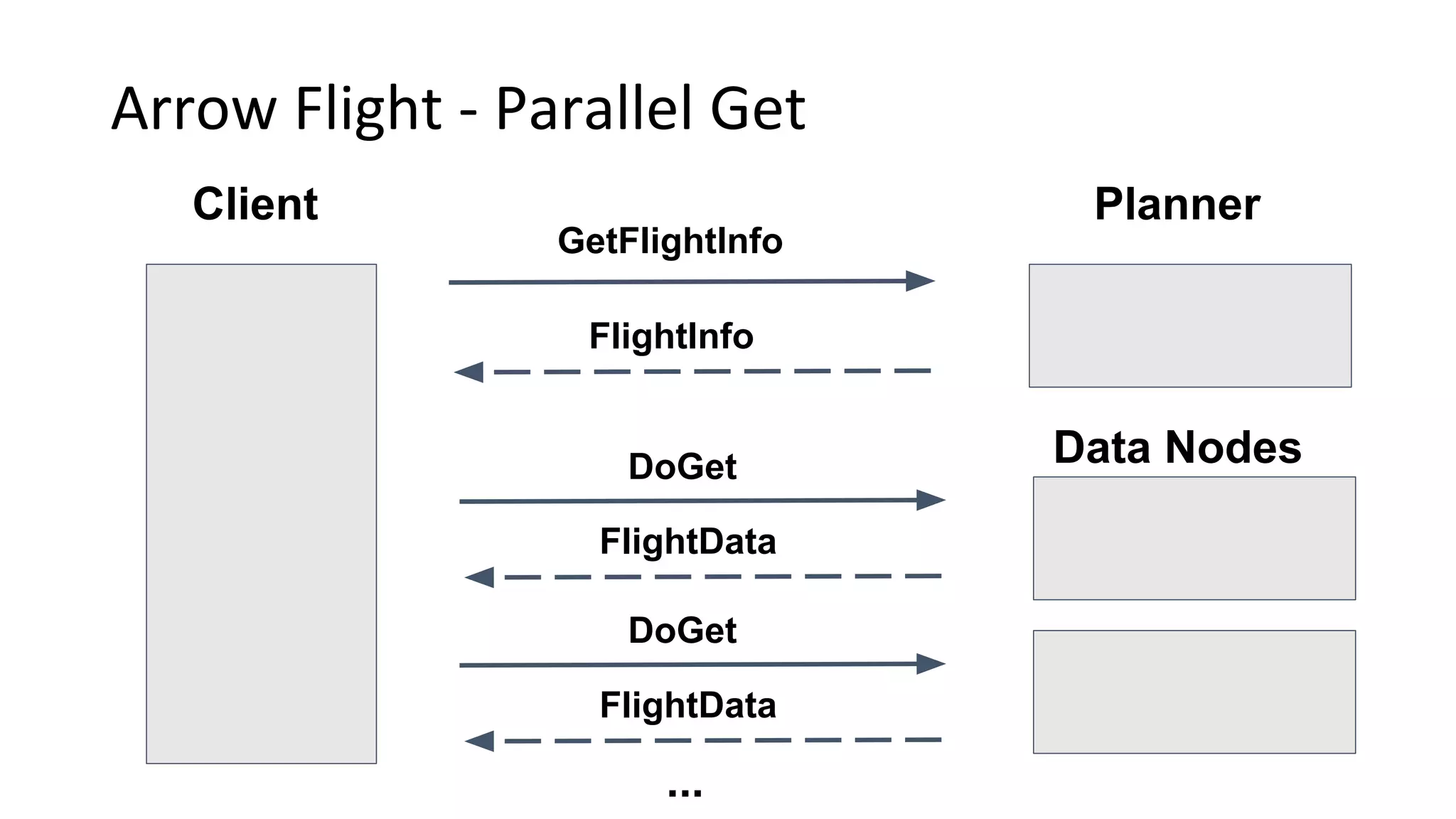
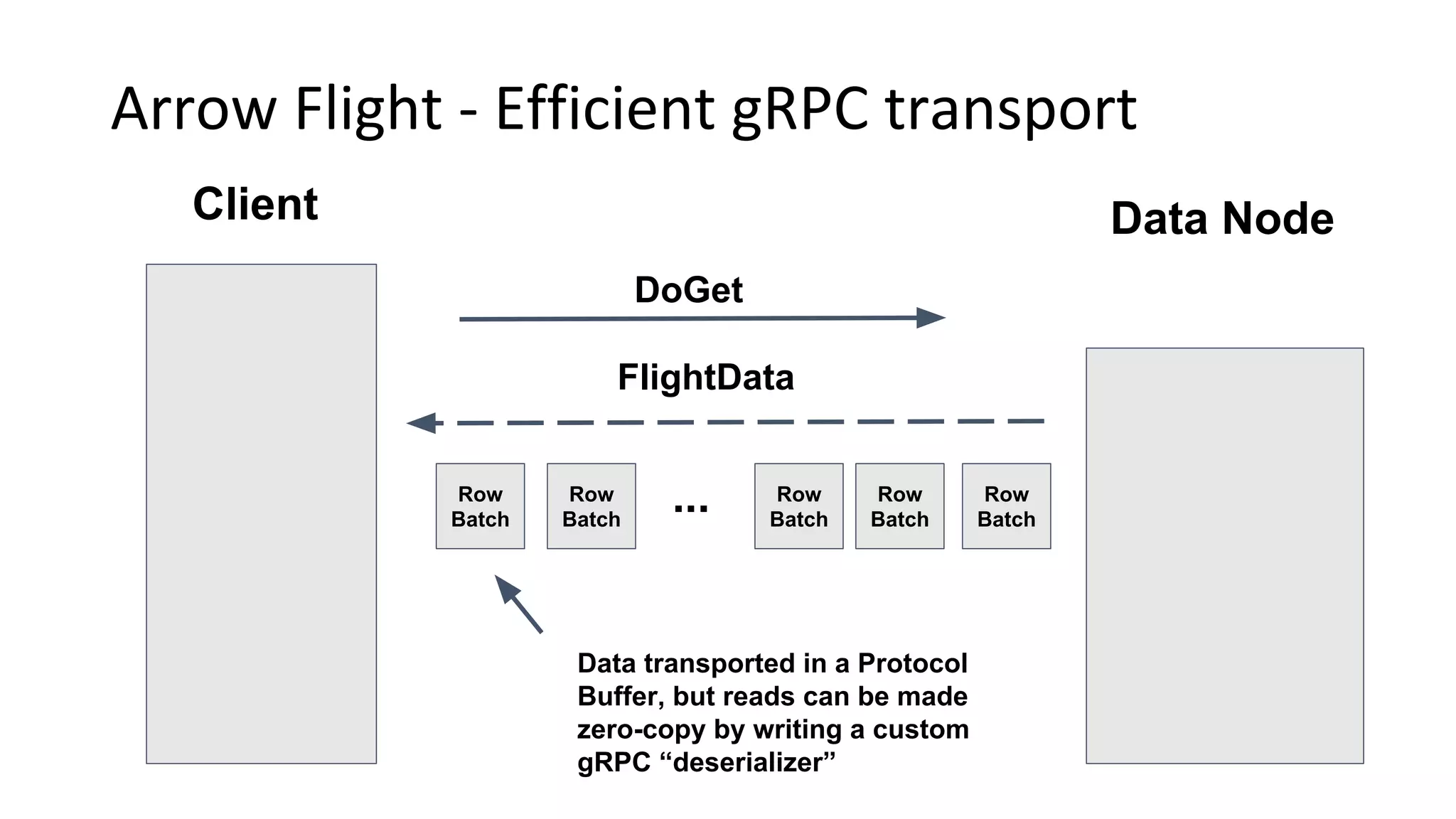
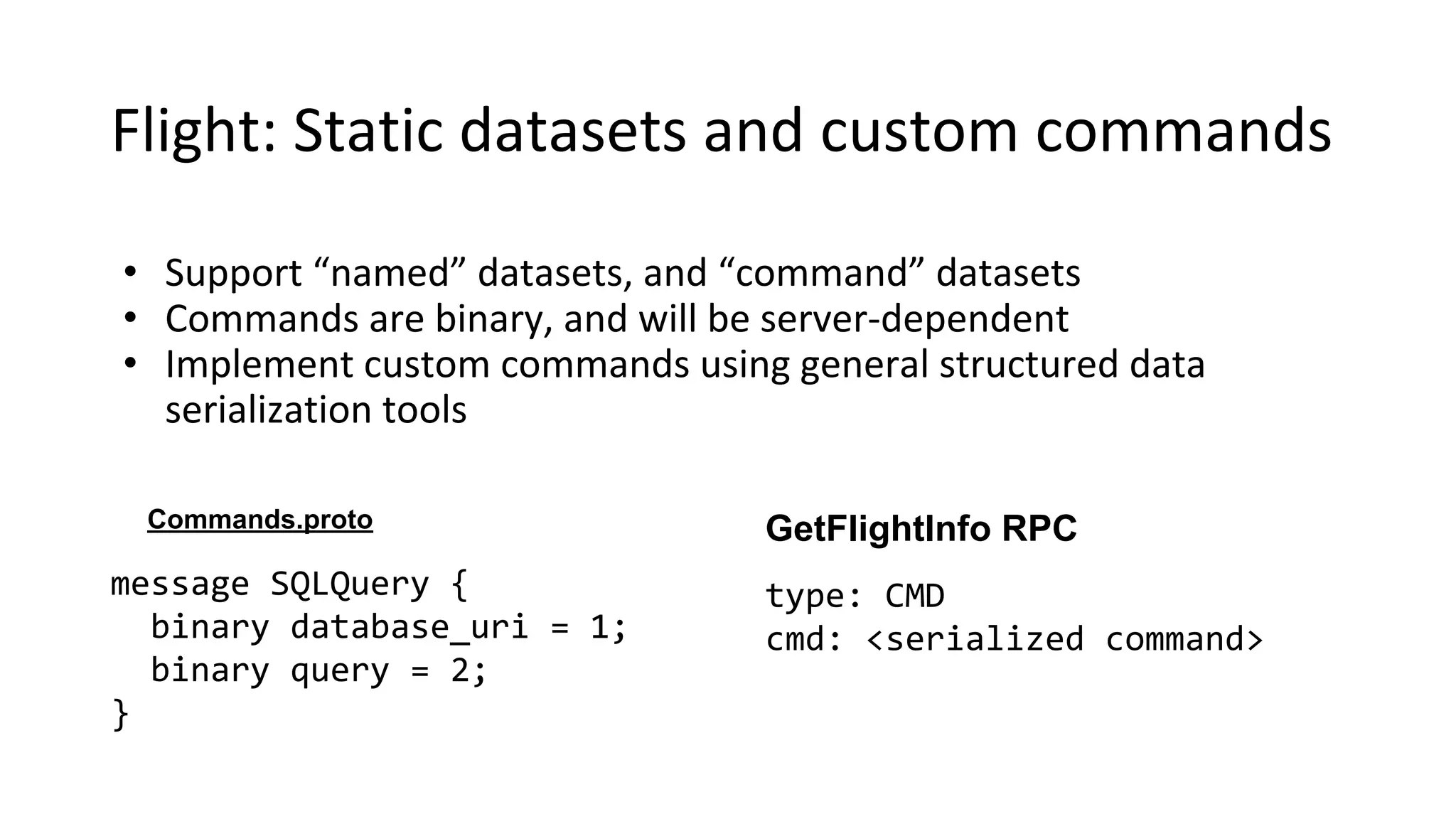
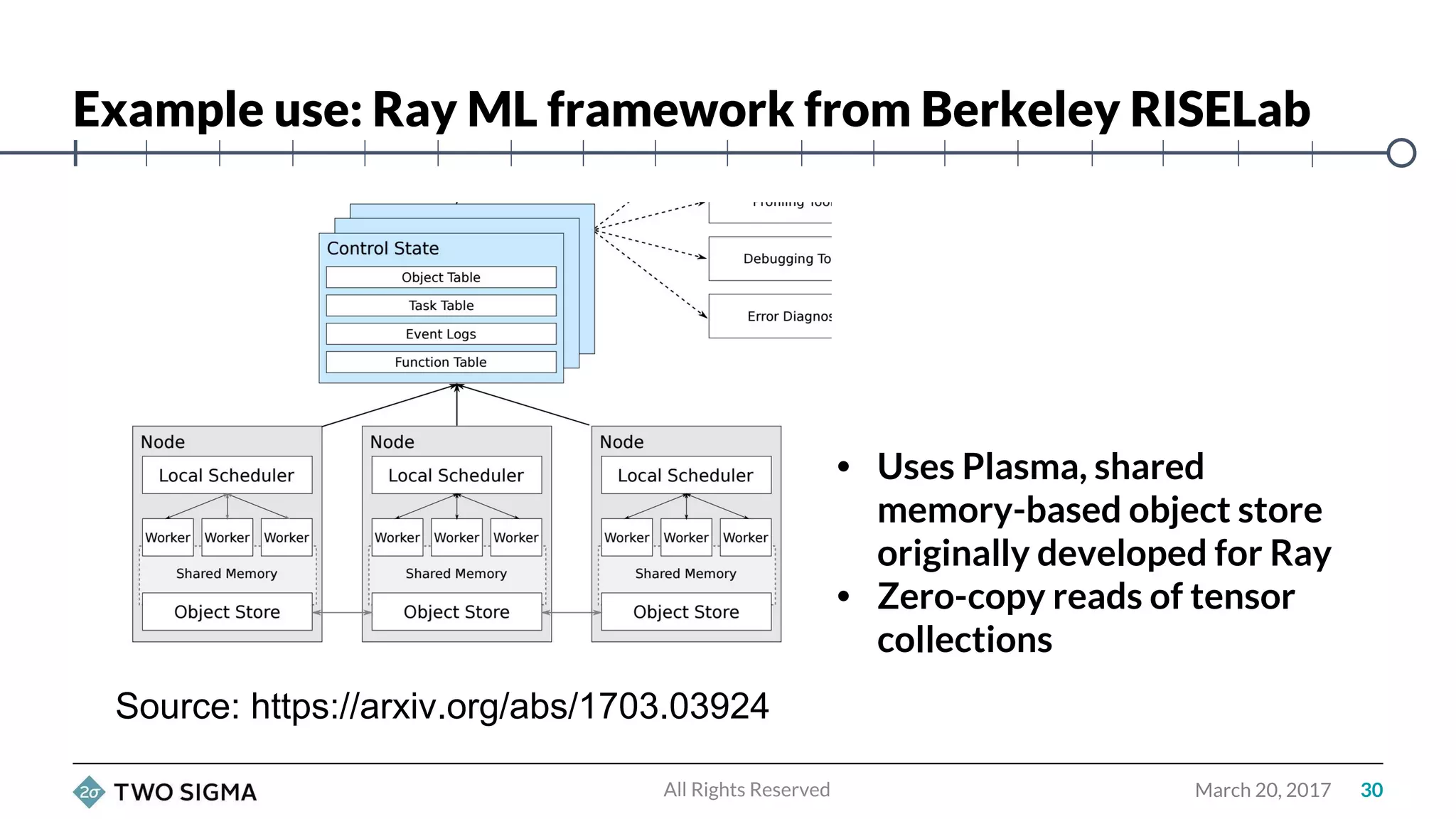
Wes McKinney is a leading open source developer who created Python's pandas library and now leads the Apache Arrow project. Apache Arrow is an open standard for in-memory analytics that aims to improve data sharing and reuse across systems by defining a common columnar data format and memory layout. It allows data to be accessed and algorithms to be reused across different programming languages with near-zero data copying. Arrow is being integrated into various data systems and is working to expand its computational libraries and language support.