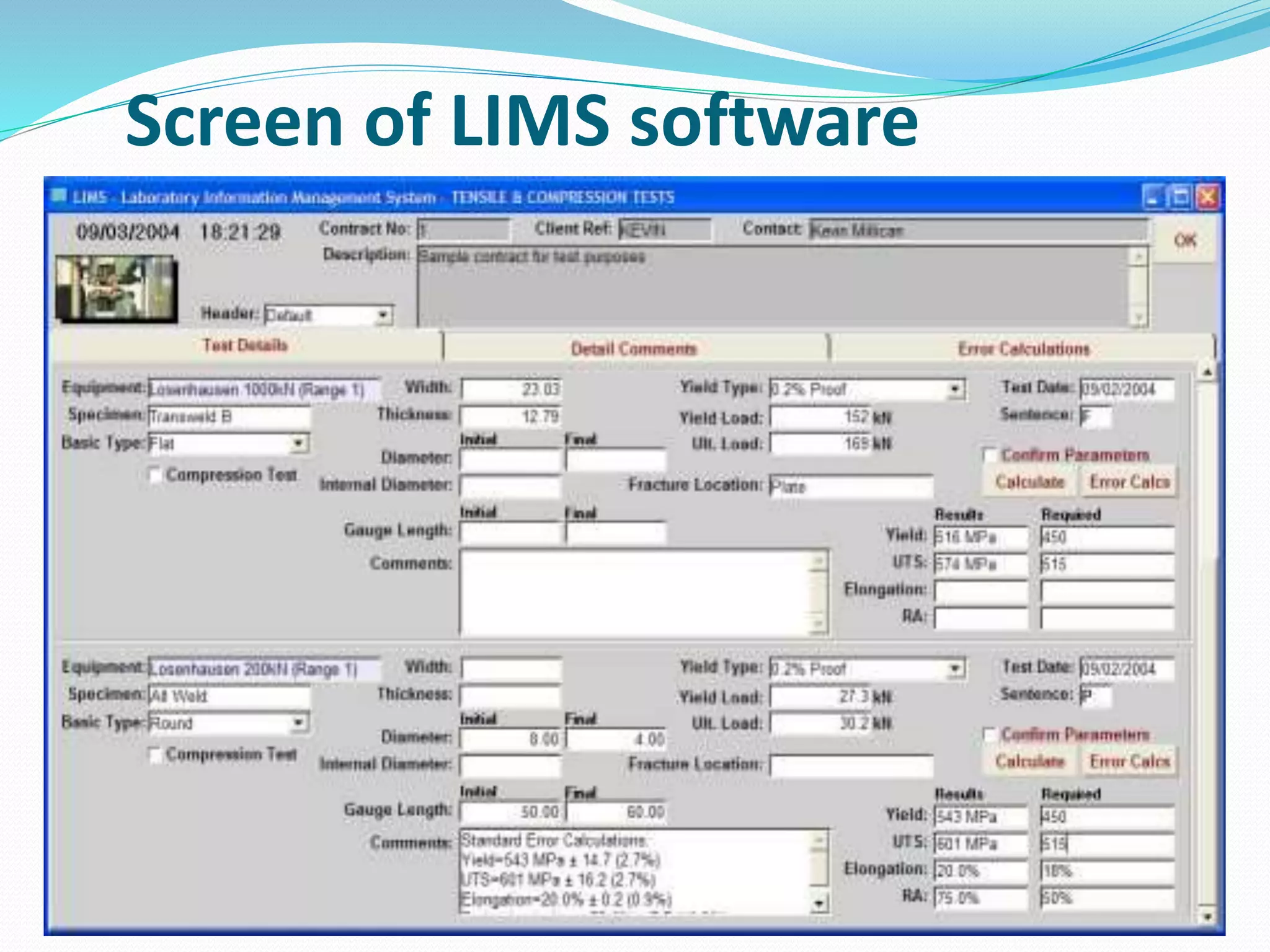
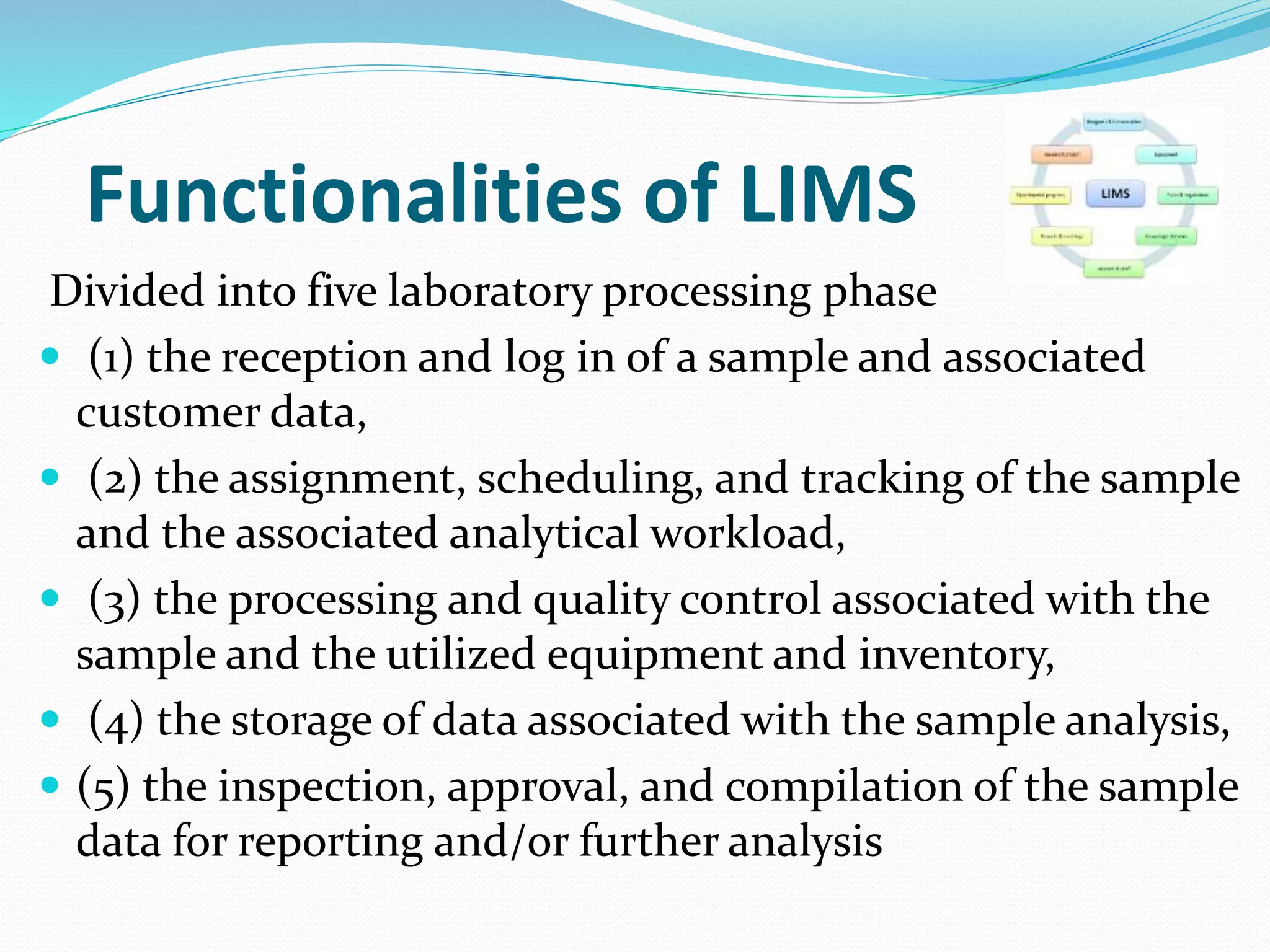
The document discusses Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS), detailing their objectives, functionalities, advantages, and disadvantages. LIMS enhances laboratory efficiency by managing samples and associated data, automating workflows, and improving data quality. Although LIMS systems can be costly and require training, they are increasingly adopted in laboratories to streamline operations and enhance data accessibility.