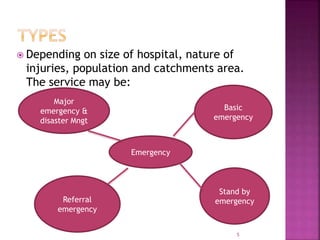
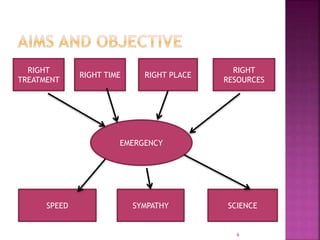
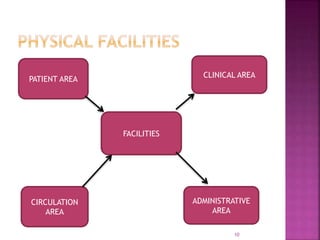
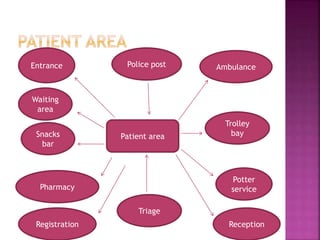
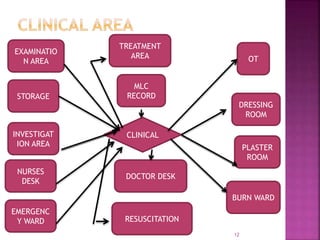
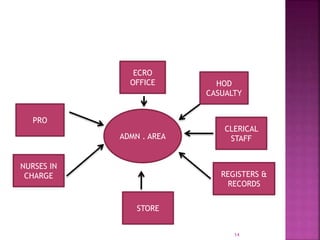
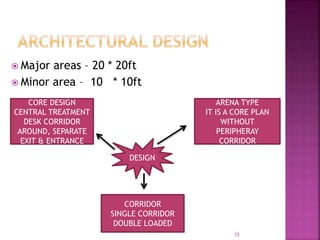
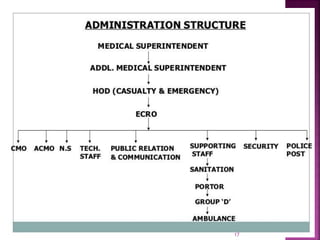
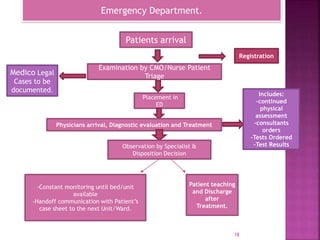
The document provides an overview of the emergency department (ED) in a hospital. It discusses that the ED acts as the front door and portal of entry for critical patients. The ED aims to provide immediate life-saving treatment and manage medical emergencies to prevent loss of life. It must be properly equipped and located for efficient patient care. Staff have defined roles to ensure the smooth functioning of the ED.