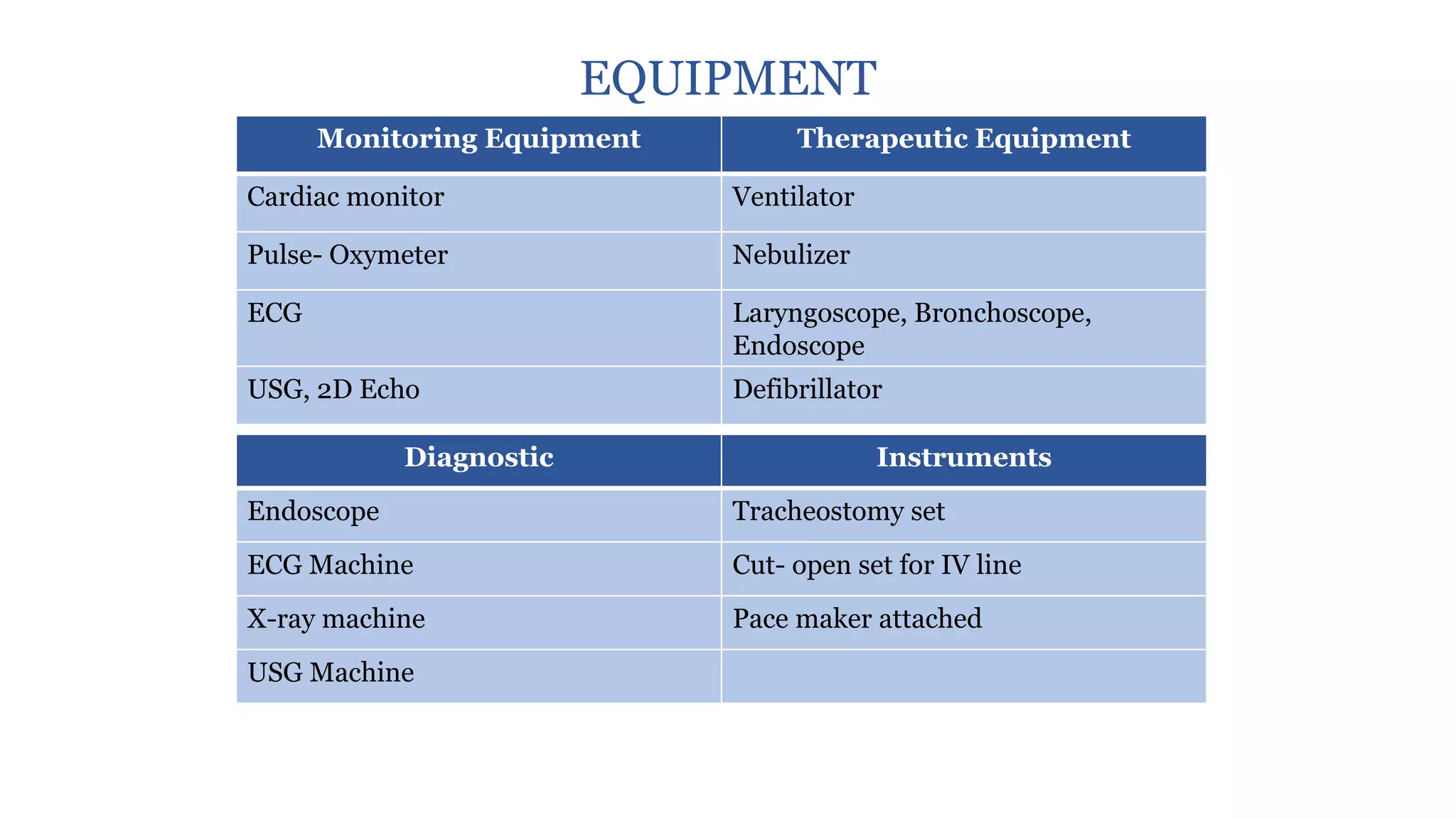
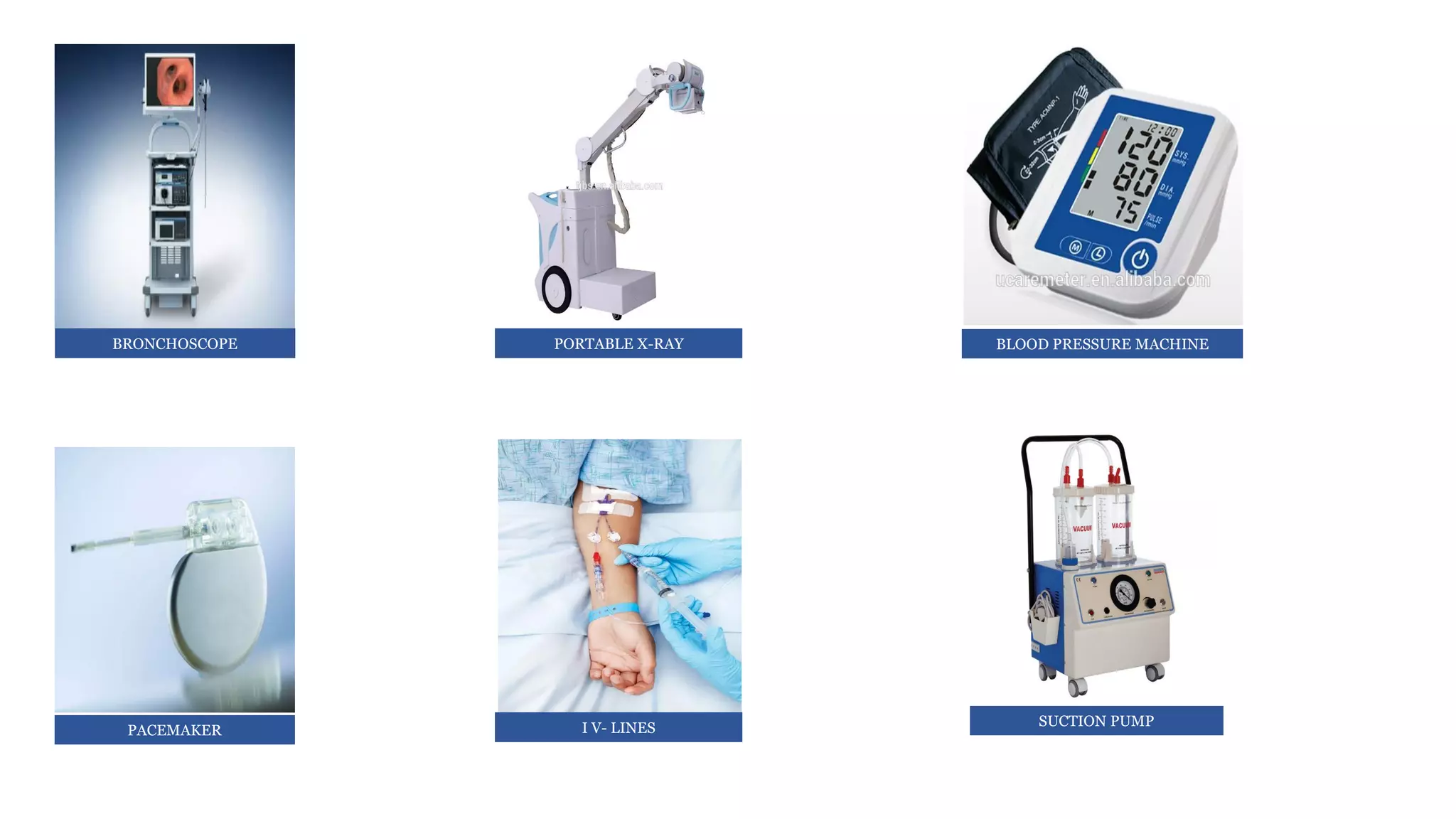
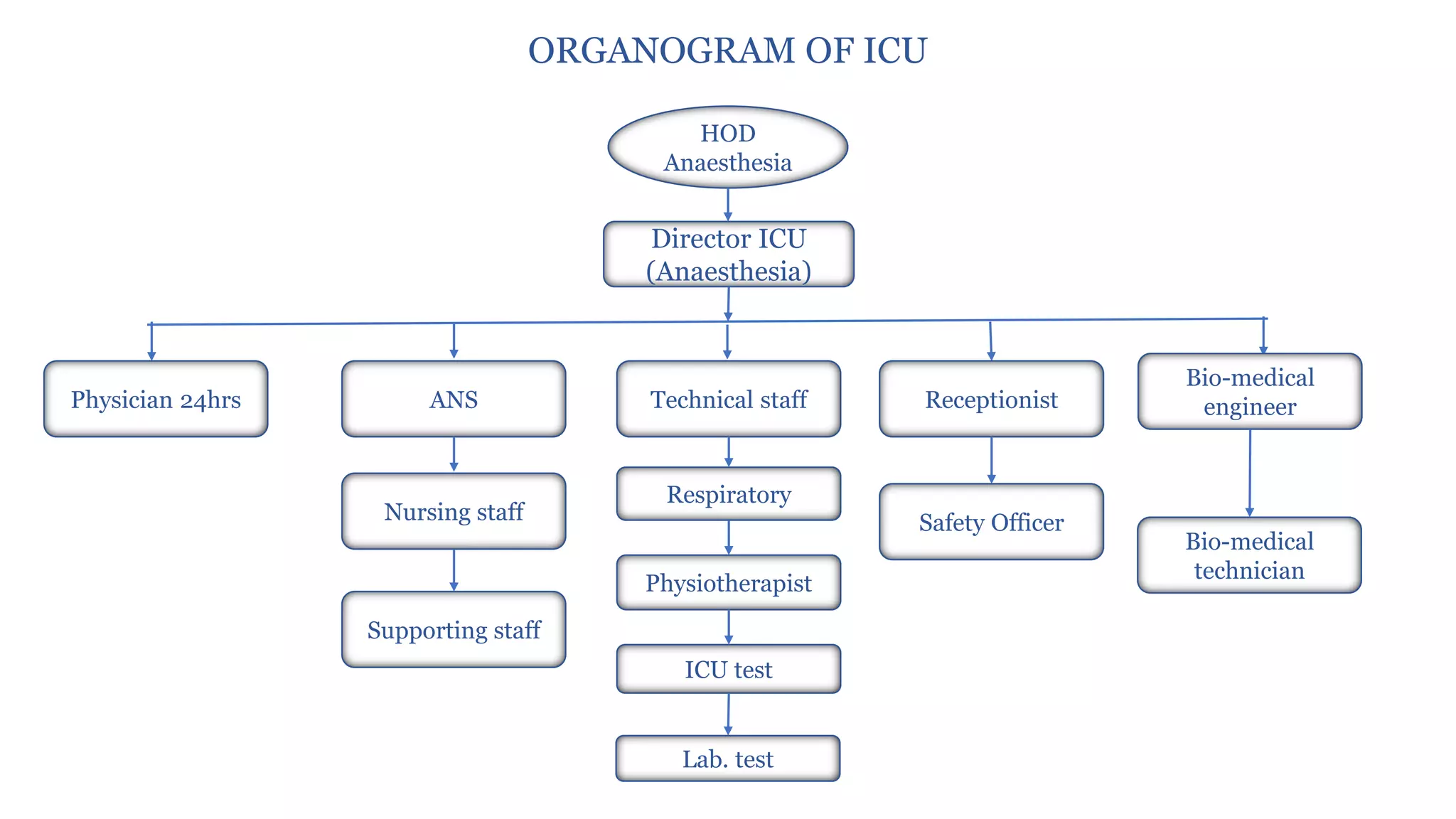
1:2
▪ Night 1:4
❑ICU Matron
❑Nursing orderly
➢ Medical Staff
❑Consultant: 1:4 beds
❑Resident: 24 hrs
➢ Technical Staff
❑Respiratory therapist
❑ECG/Echo technician
❑Lab technician
❑X-ray technician
➢ Ancillary Staff
❑Housekeeping
❑Dietician
❑Physiotherapist
❑Social worker
❑Pharmacist
❑Bio-medical engineer
❑Safety officer