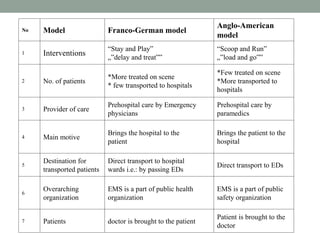
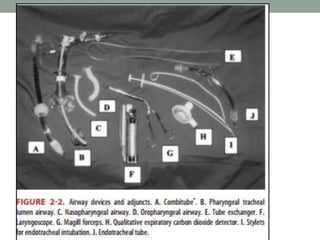
EMS provides emergency medical care to patients outside of hospitals. It focuses on preventing mortality and morbidity from sudden injuries or illnesses. Key components of EMS systems include personnel like EMTs and paramedics, equipment for patient care, transportation, communications, and facilities. EMS aims to bring appropriate care quickly to every patient regardless of ability to pay through coordinated public and private organizations. Ongoing training, quality improvement, and disaster preparedness help EMS systems effectively deliver prehospital emergency care.