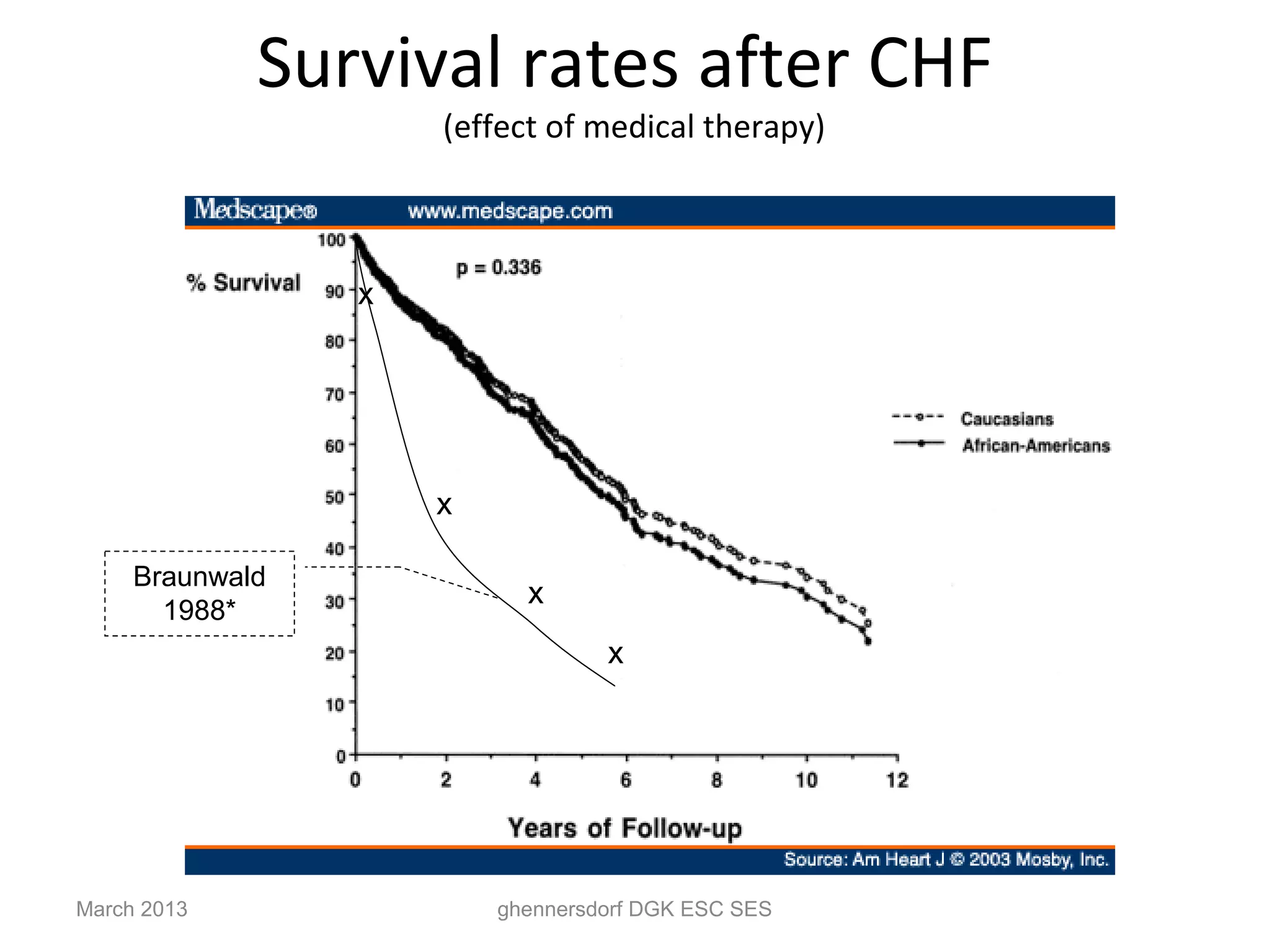
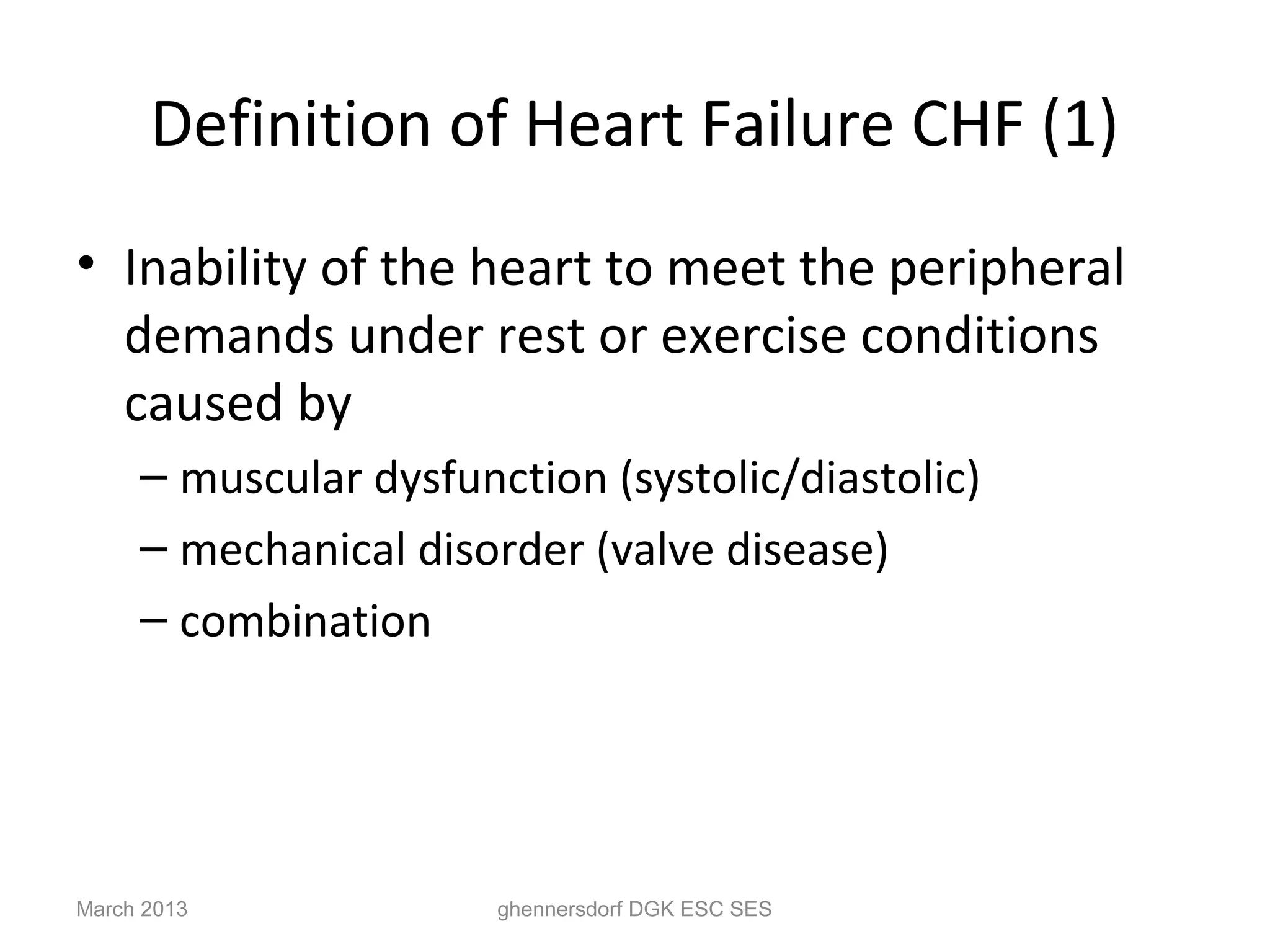
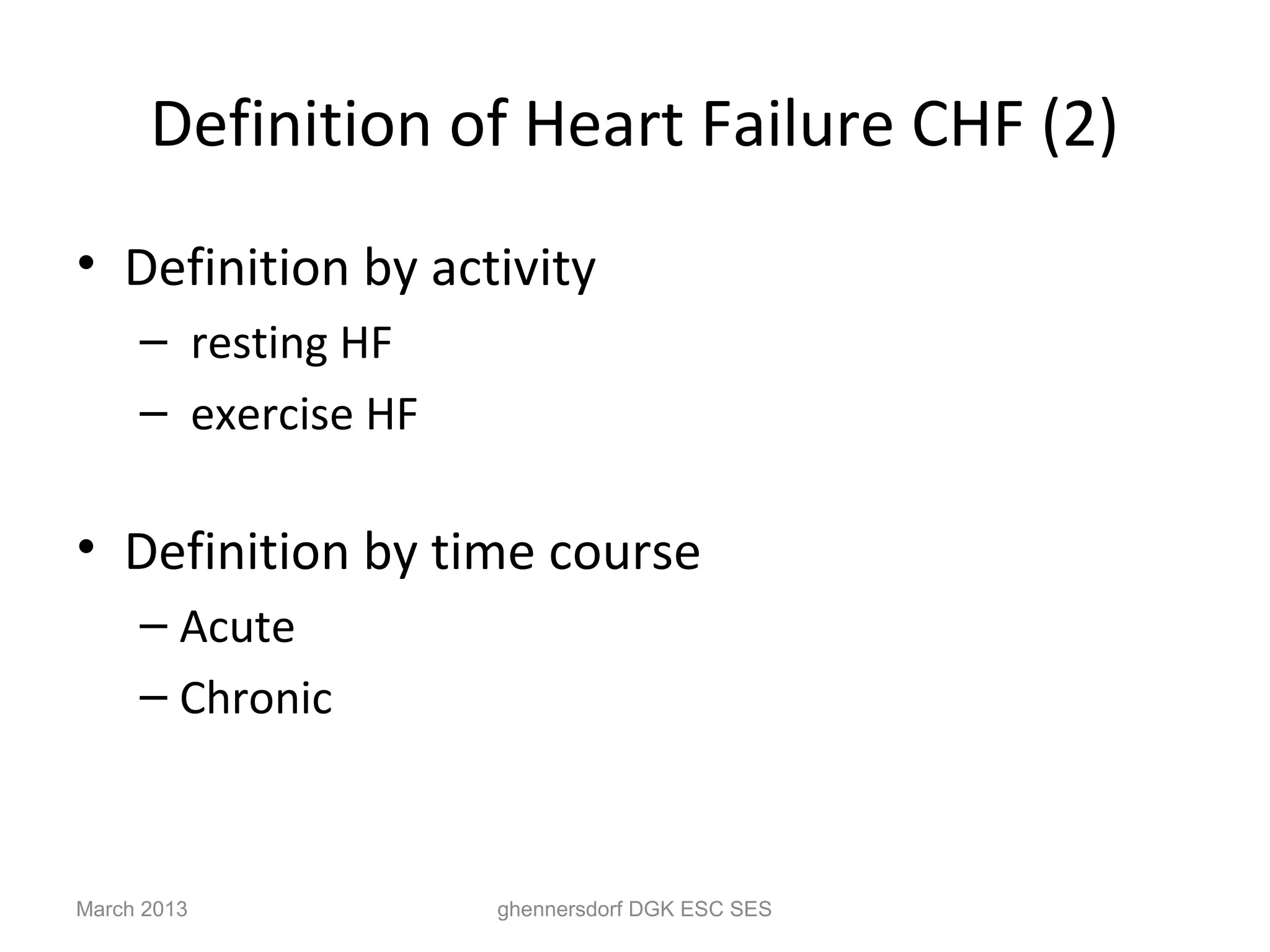
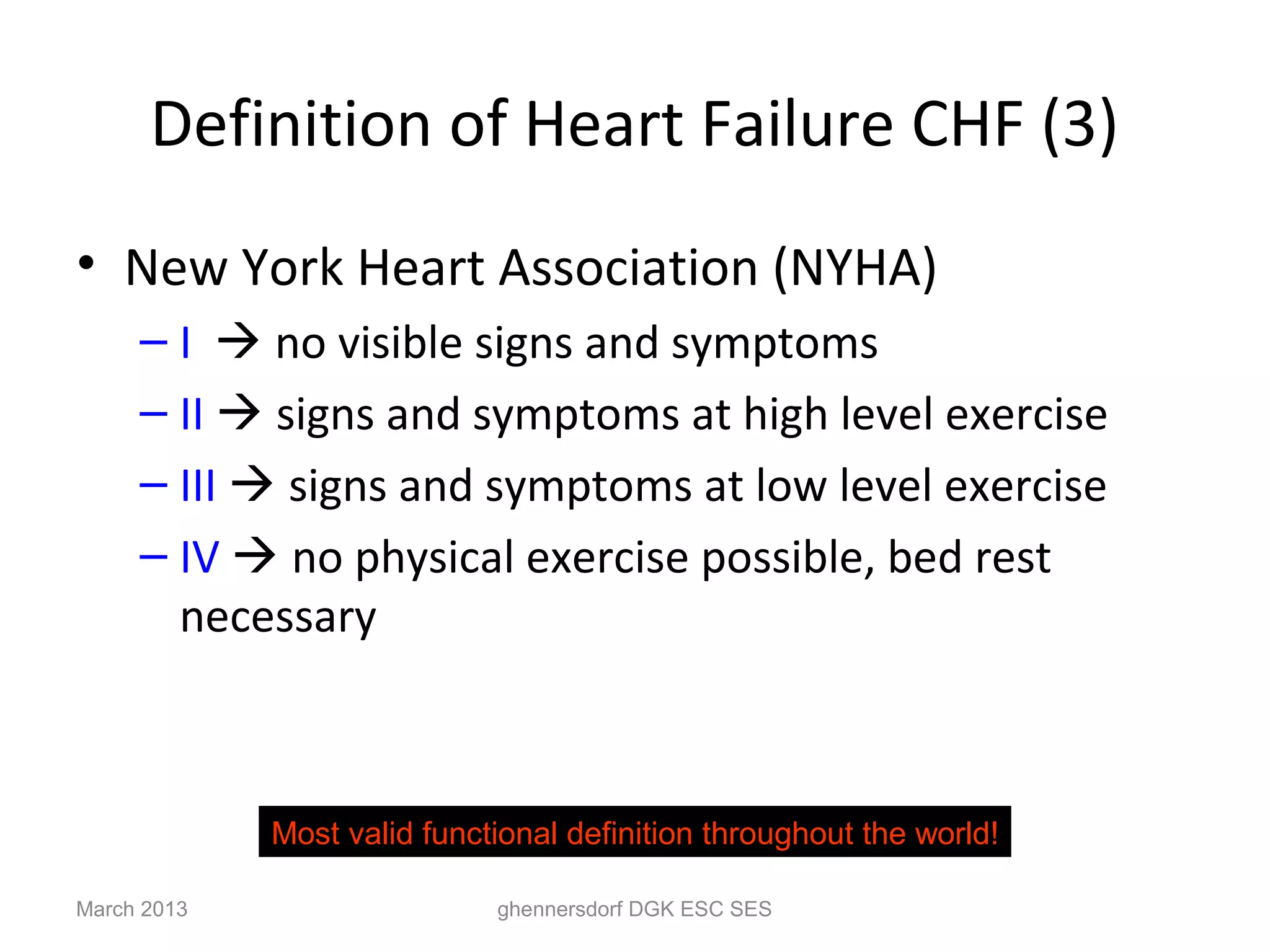
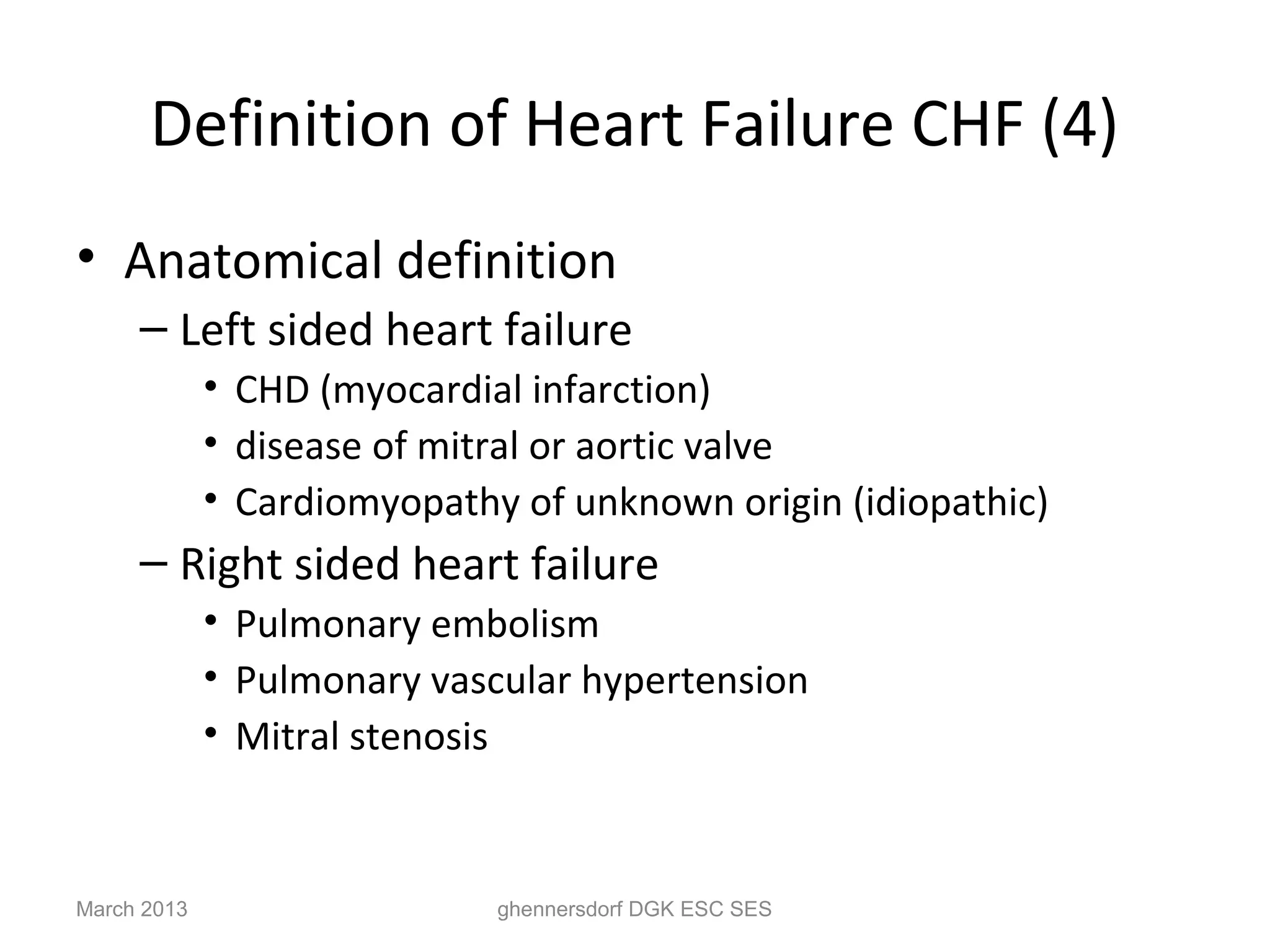
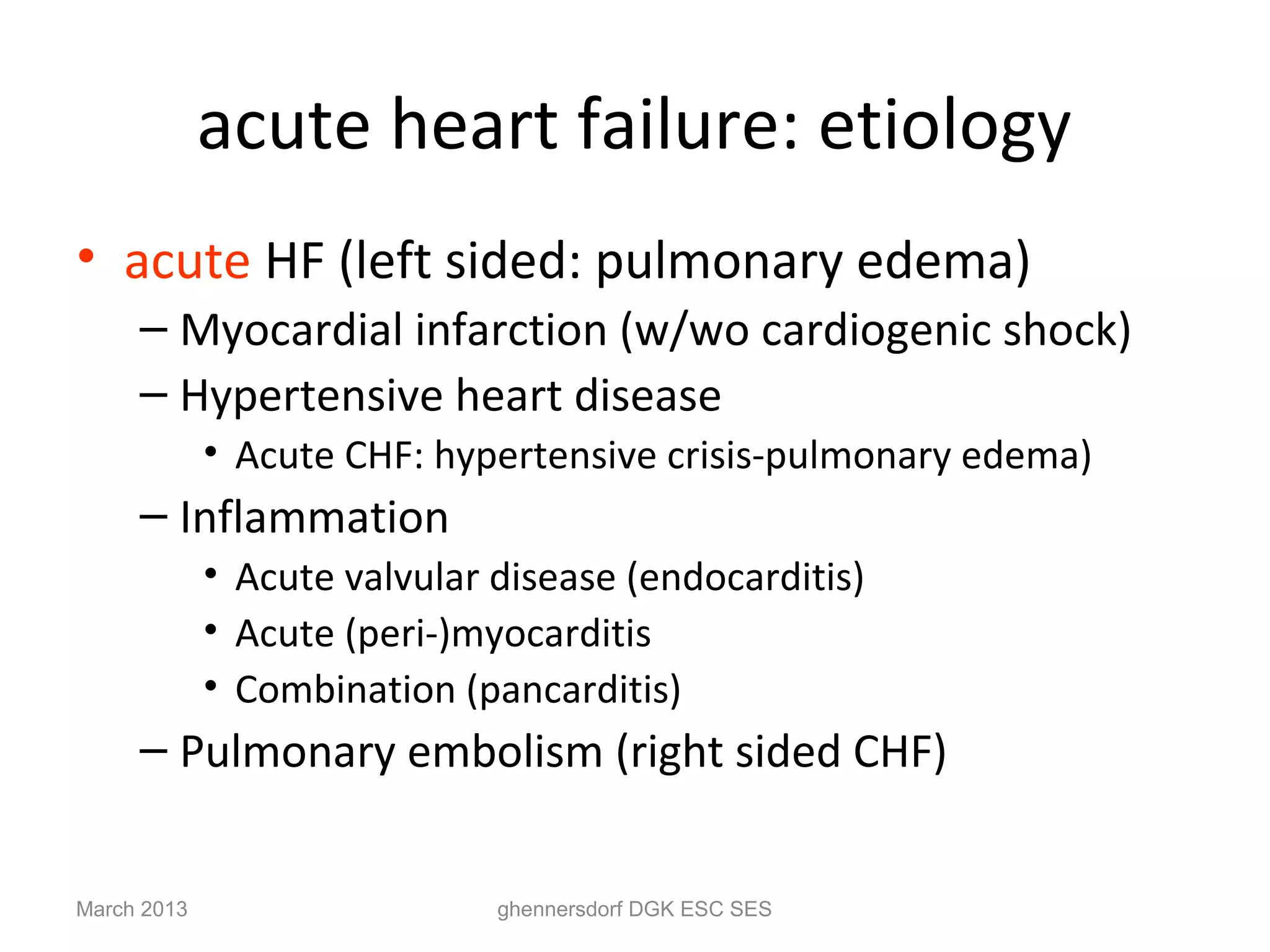
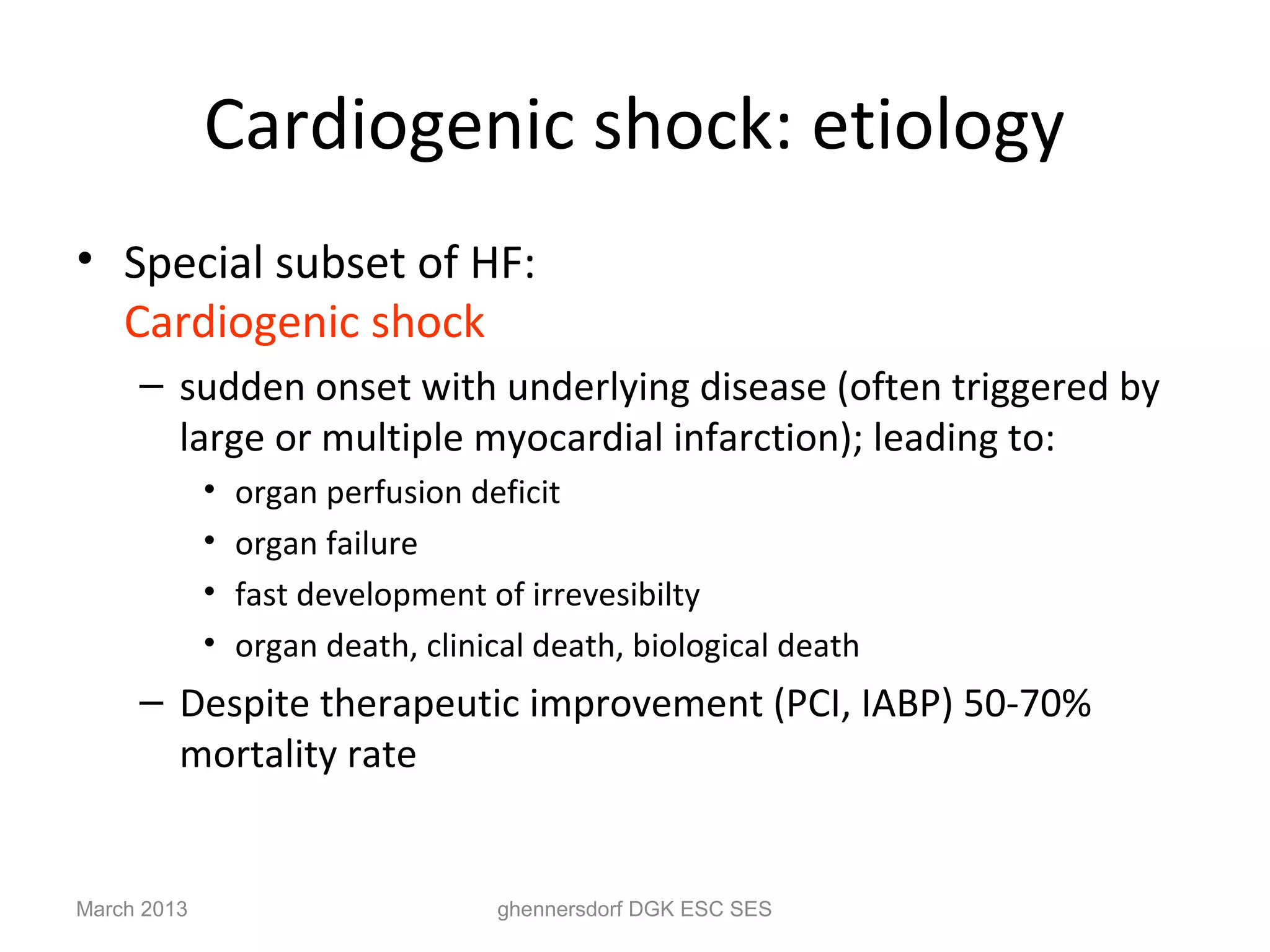
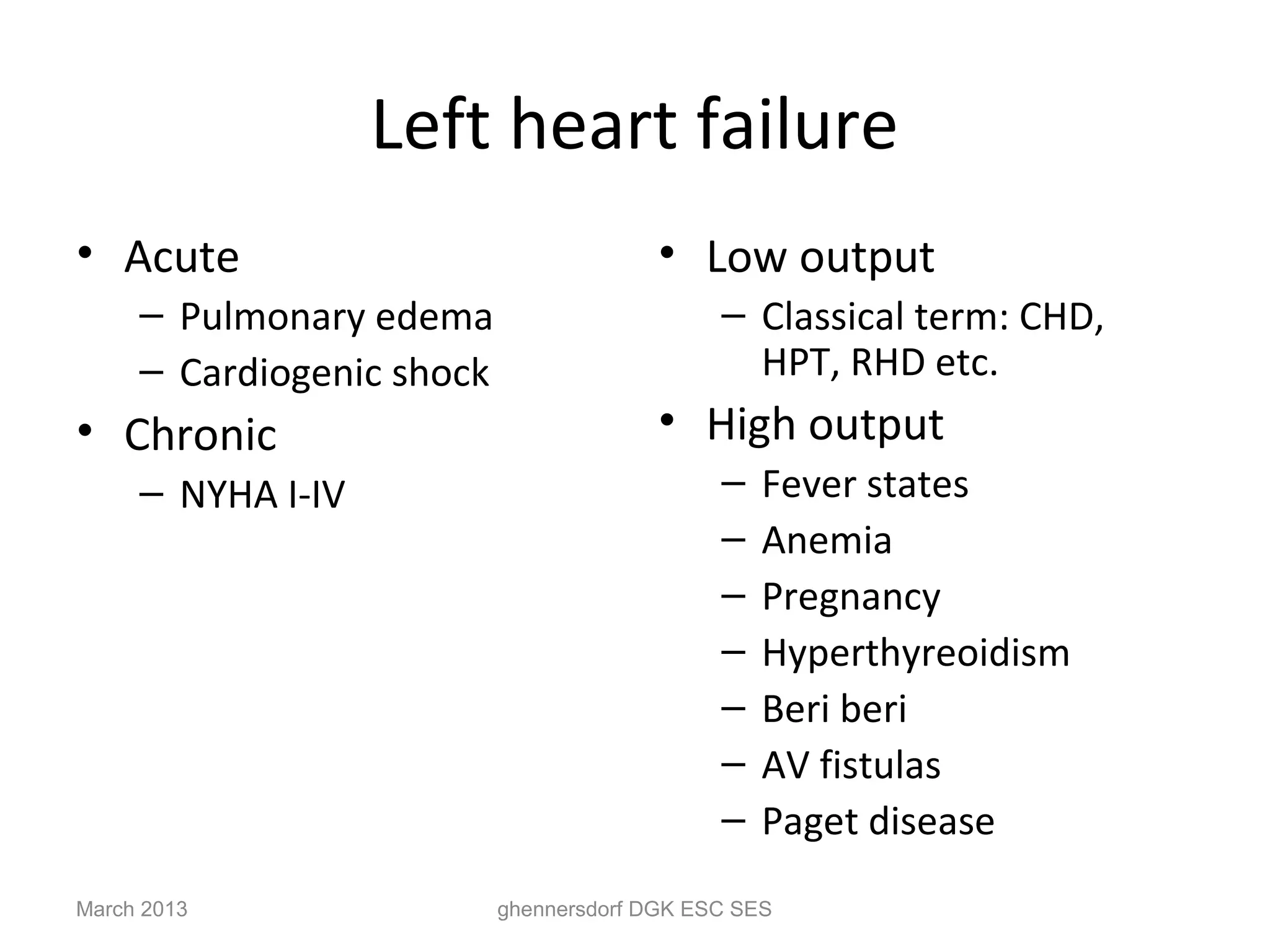
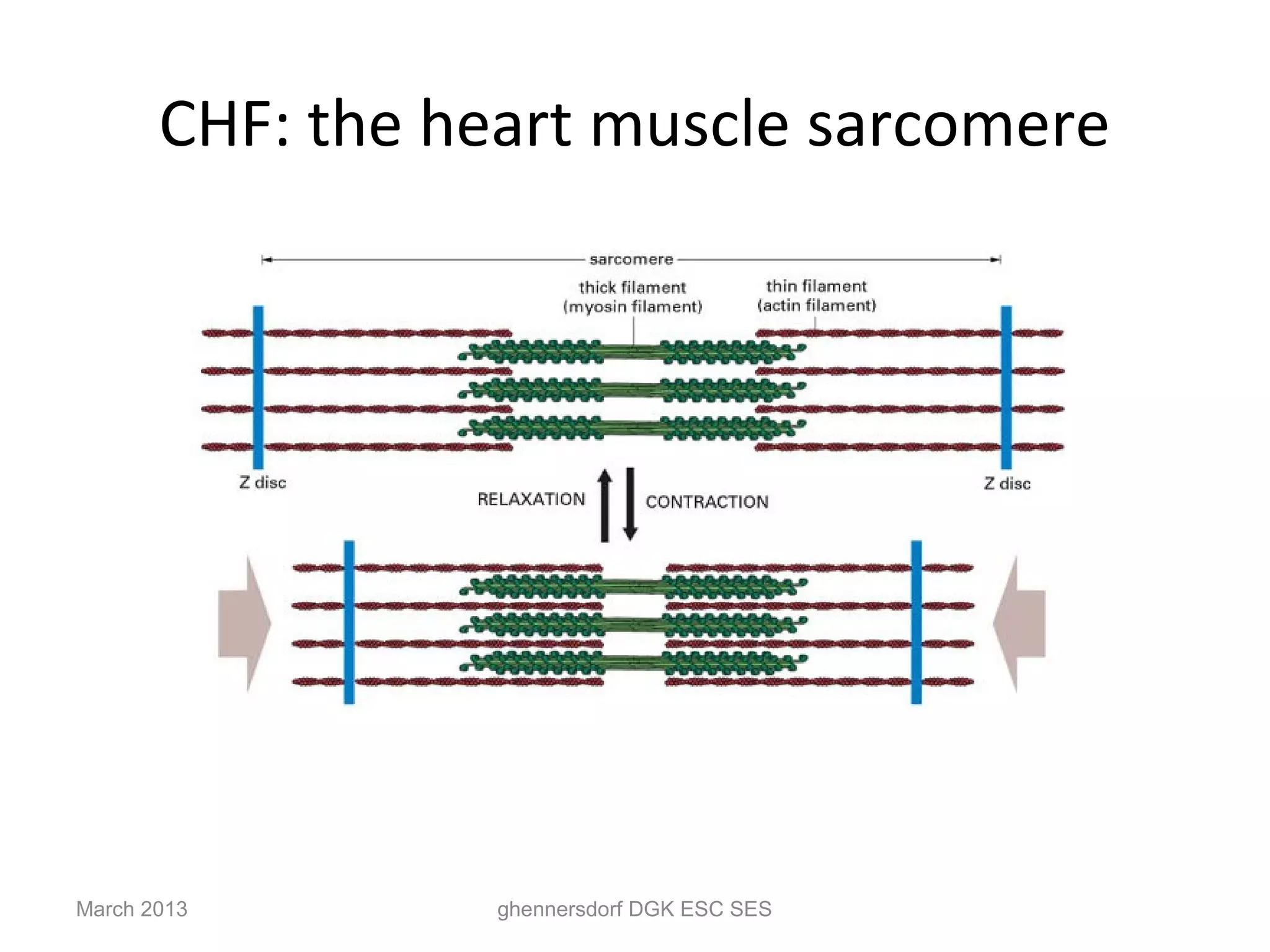
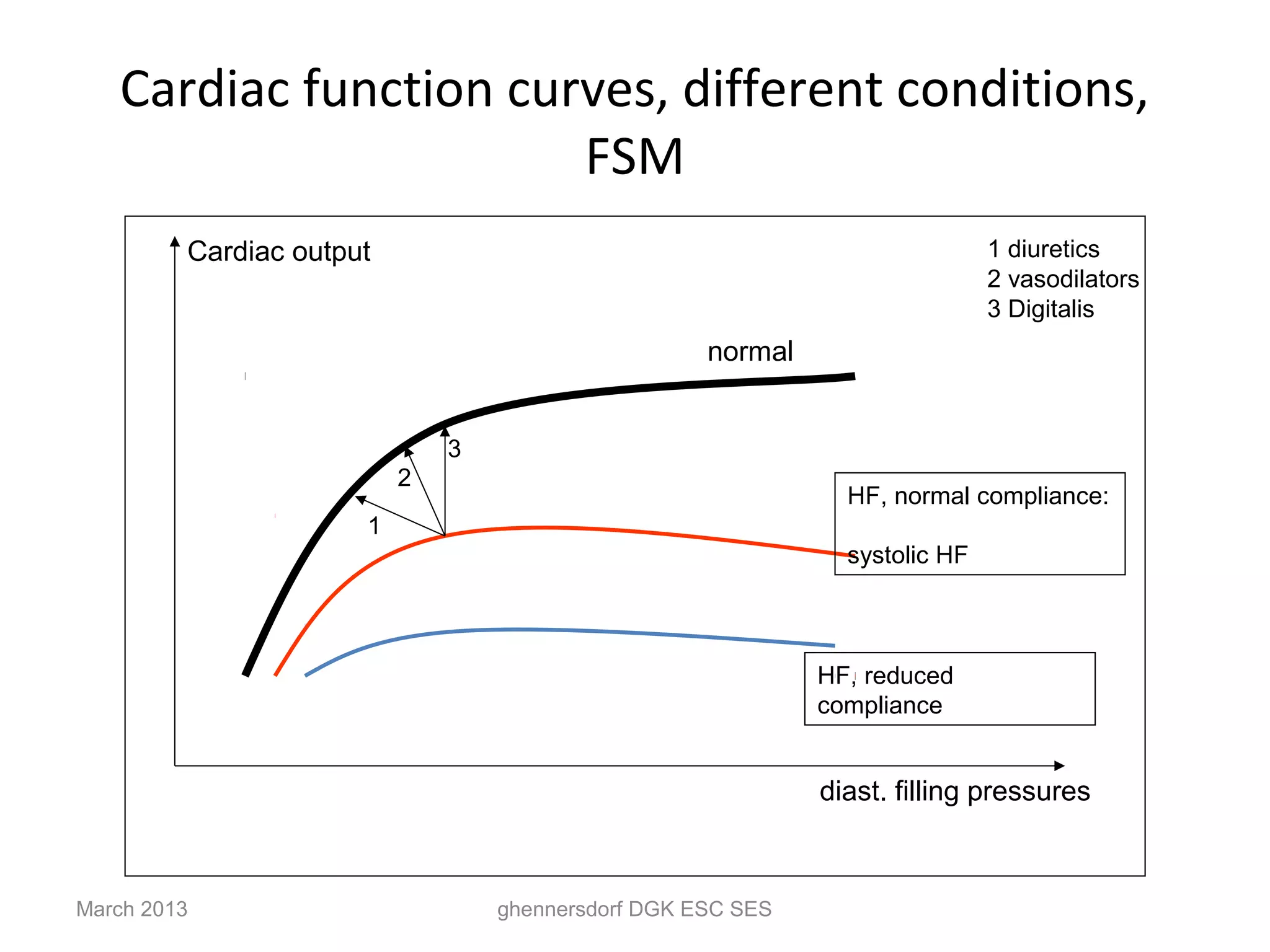
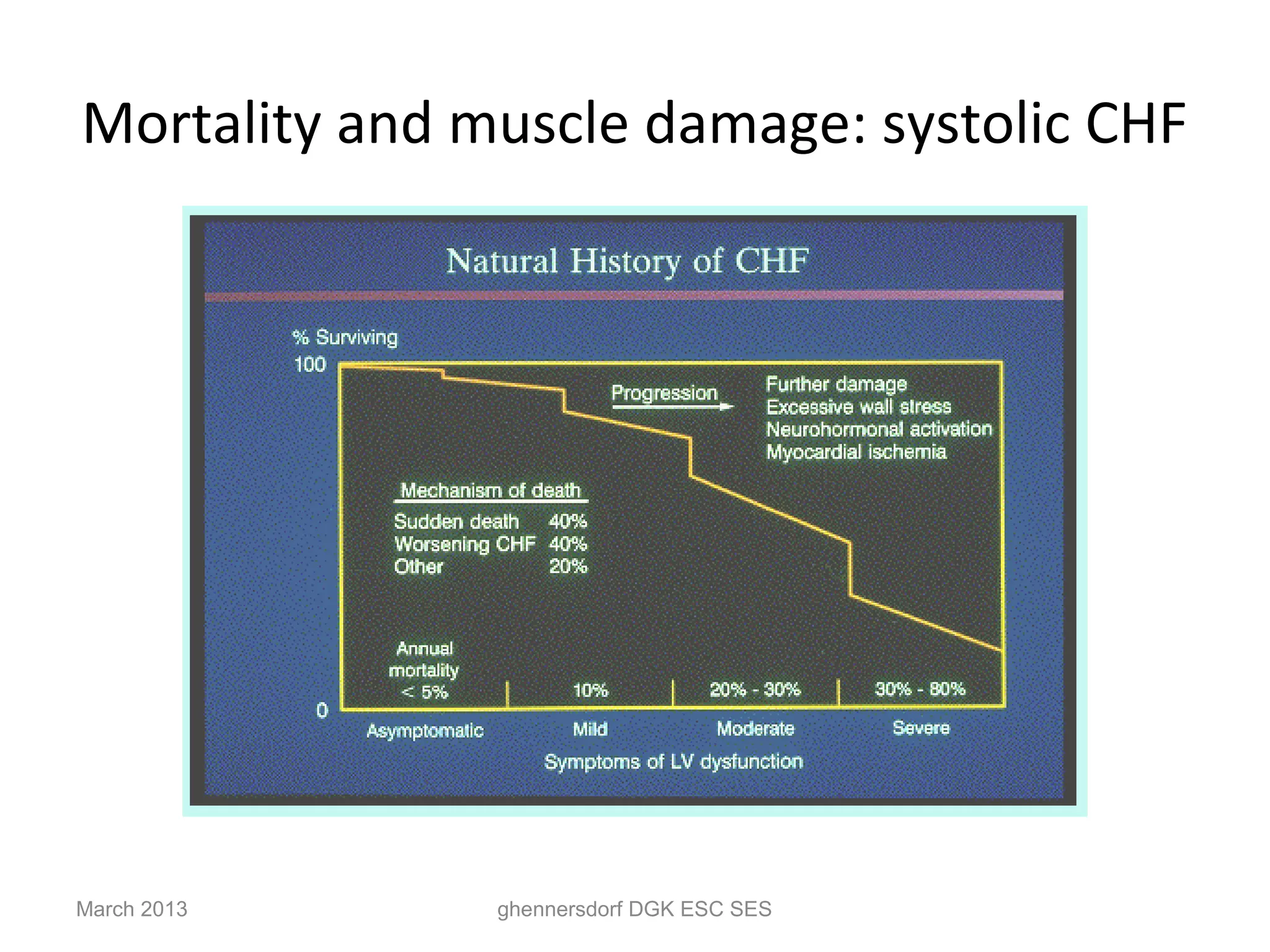
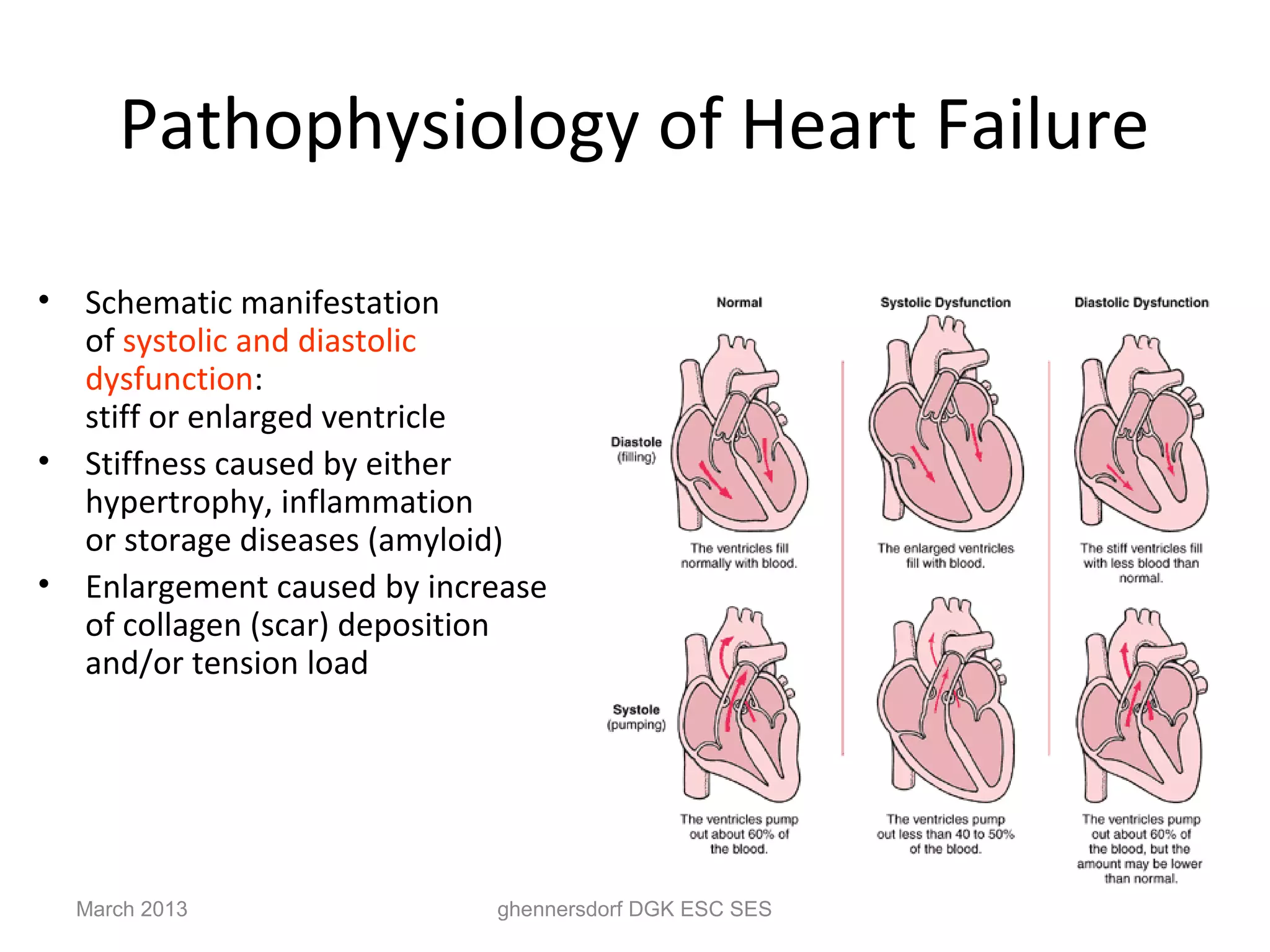
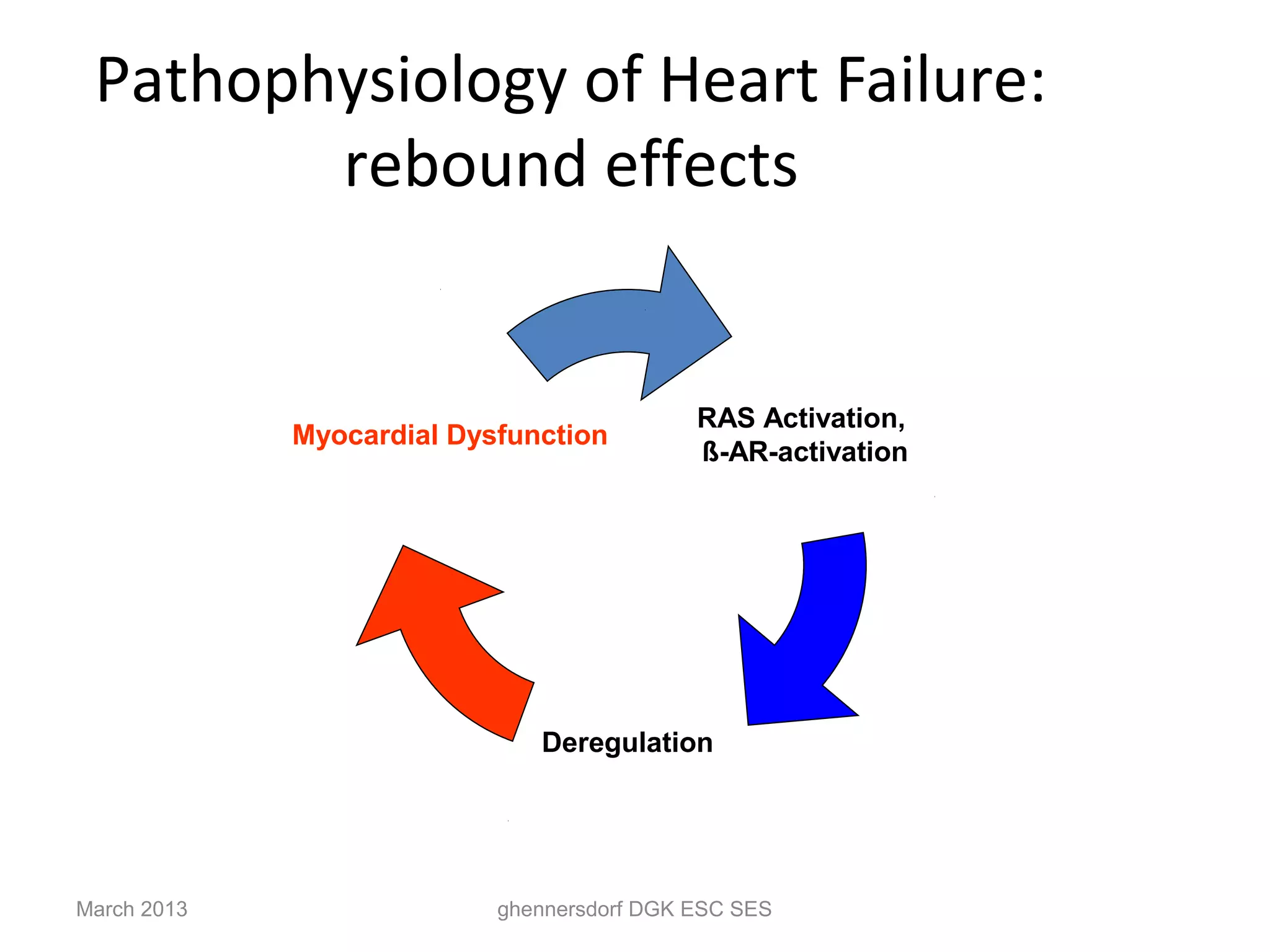
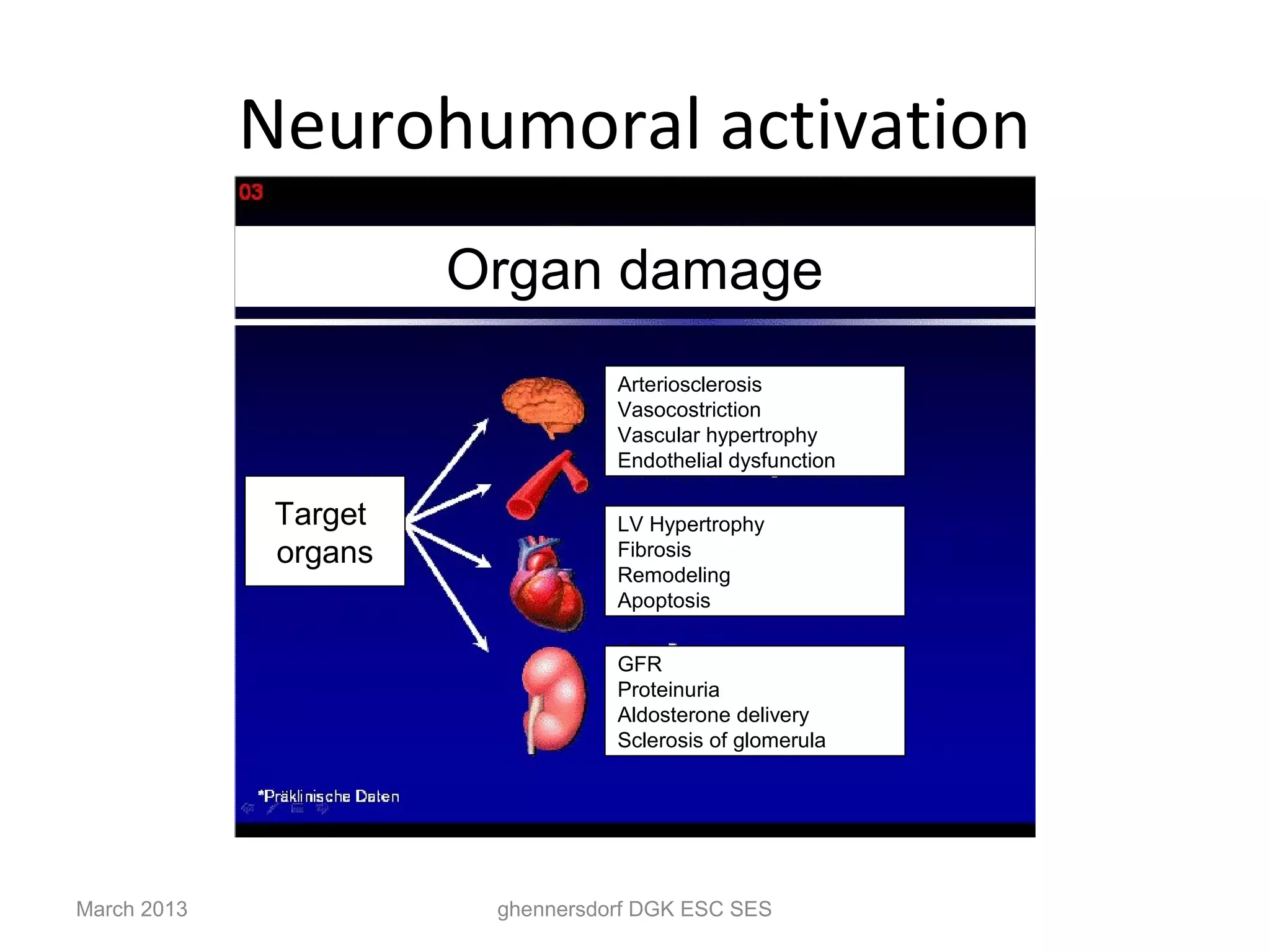
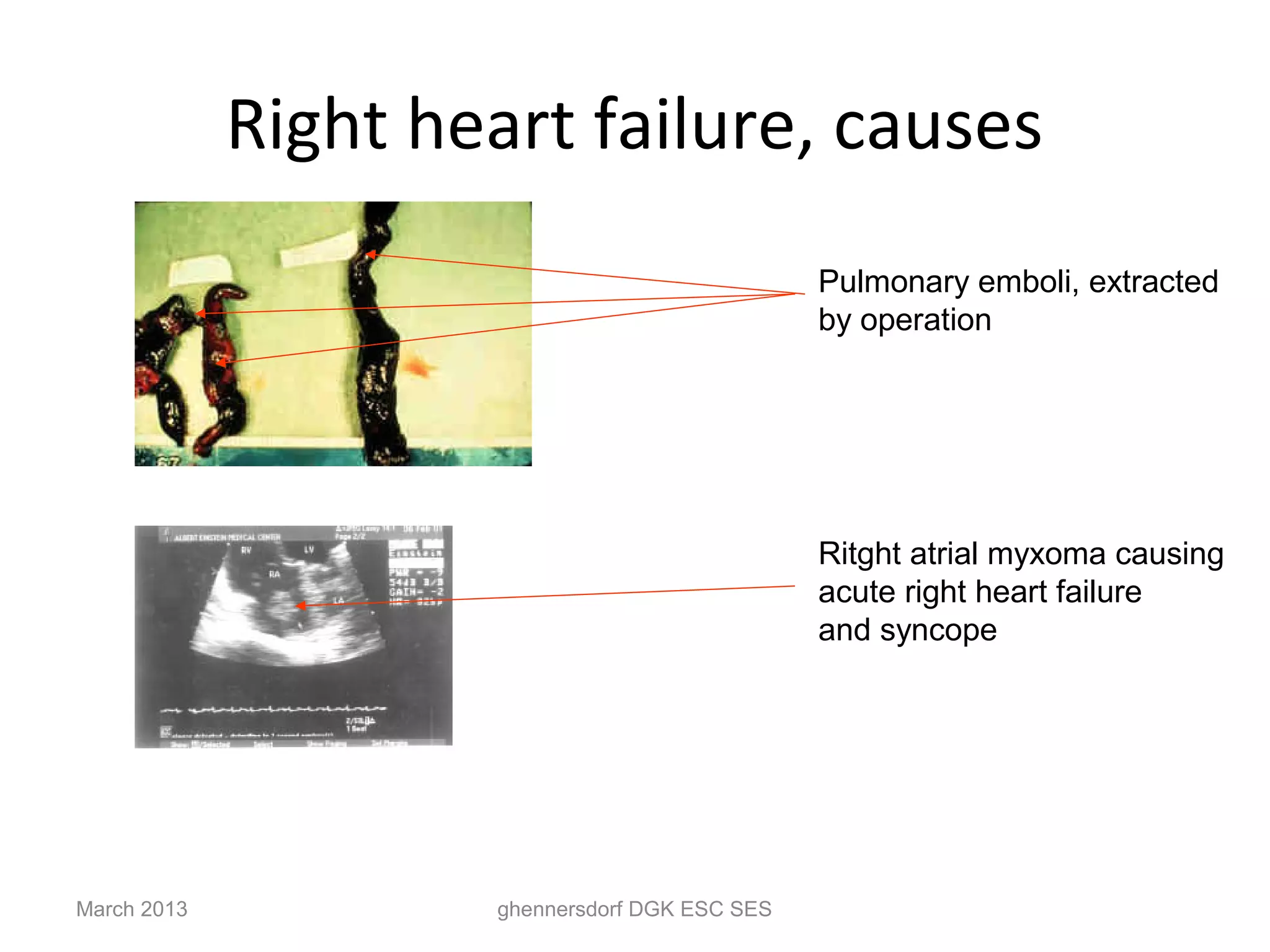
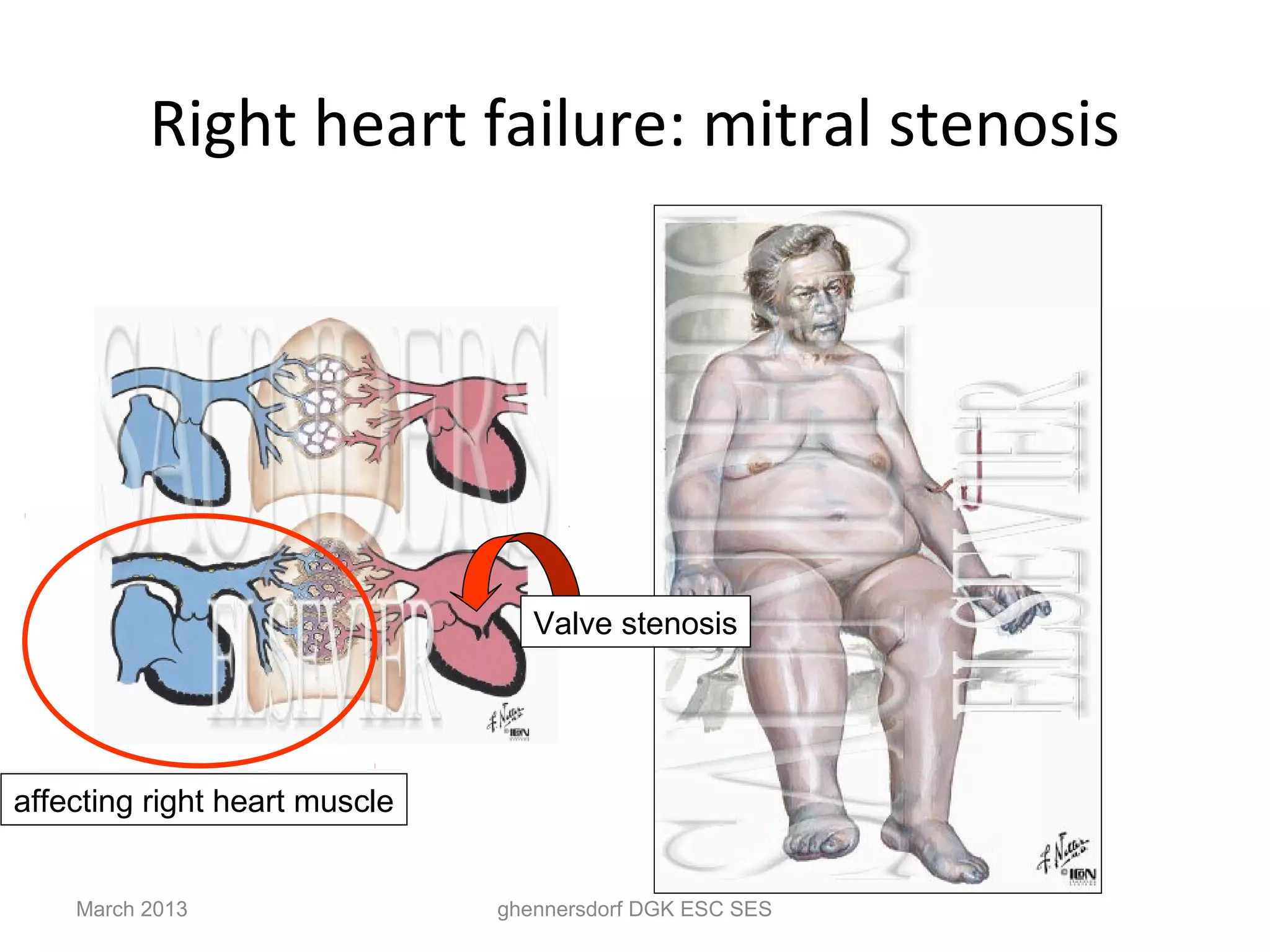
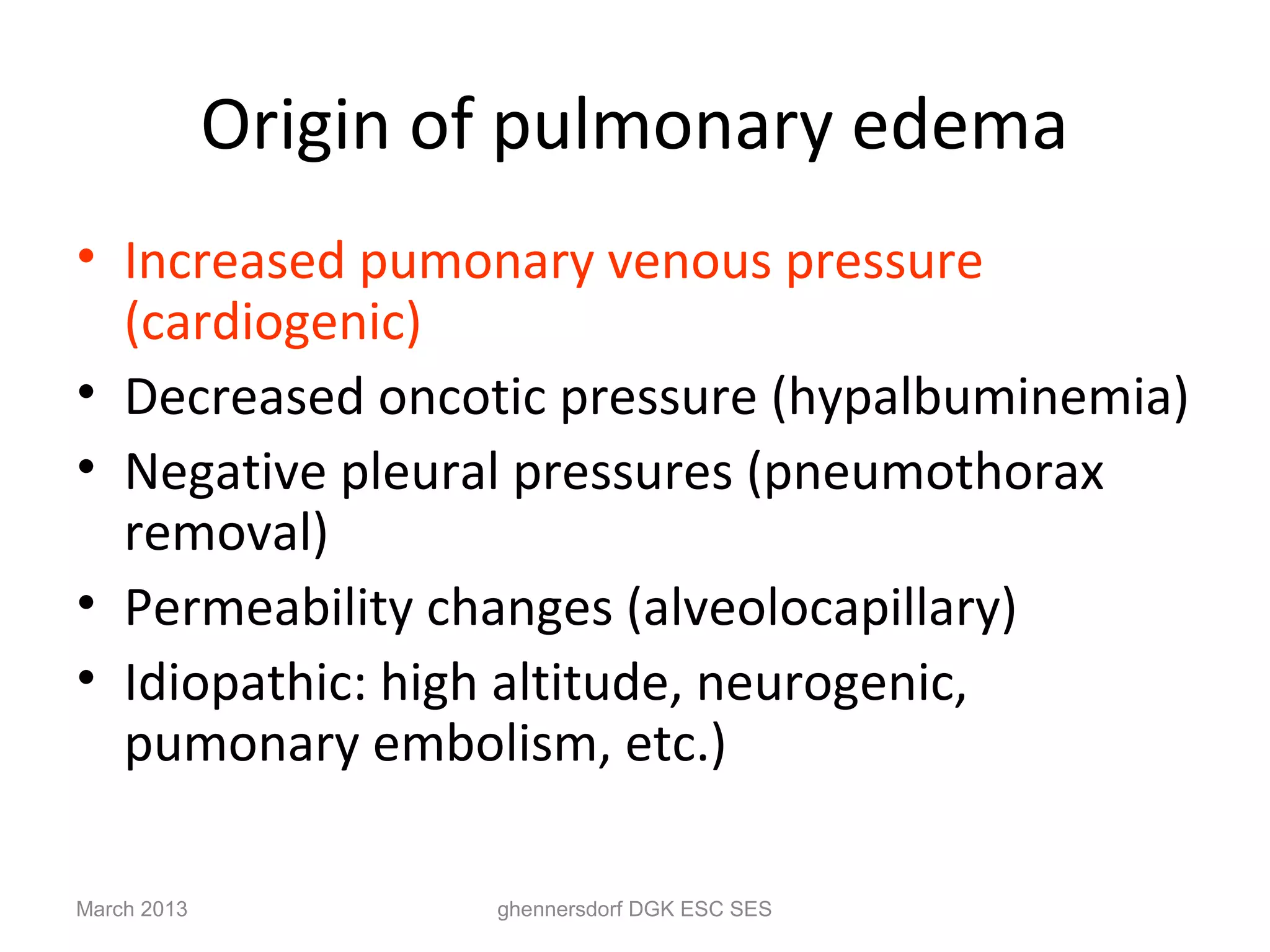
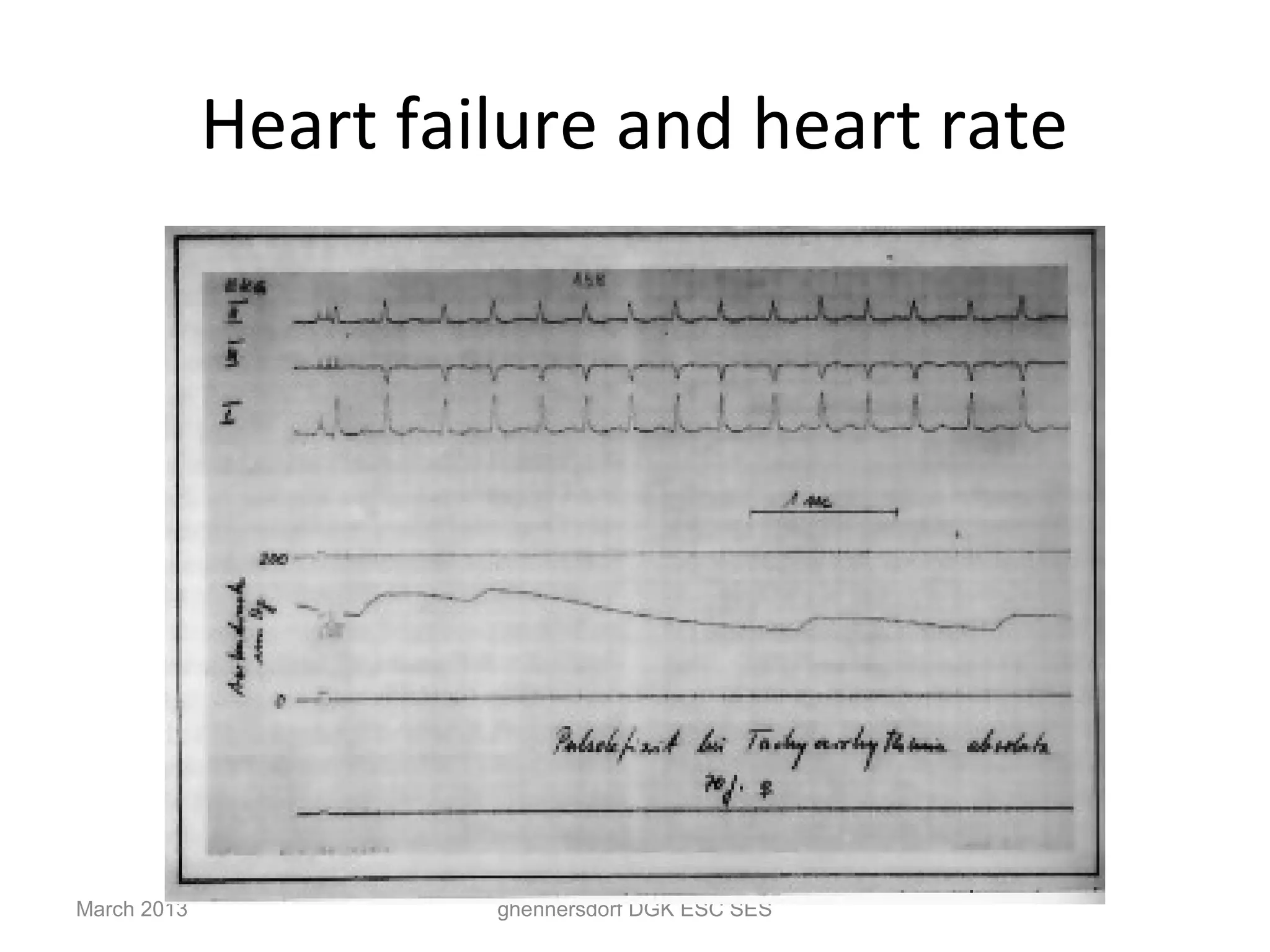
This document discusses congestive heart failure (CHF). It provides epidemiological data on CHF, showing it affects millions of people worldwide and costs billions of dollars annually. It defines CHF as the heart's inability to meet circulatory demands and classifies it based on location (left vs right heart) and time course (acute vs chronic). Causes of acute and chronic CHF include myocardial infarction, hypertension, valvular diseases, and cardiomyopathies. The pathophysiology of CHF involves systolic and diastolic dysfunction that can lead to ventricular hypertrophy, dilation, and neurohormonal activation causing further organ damage.