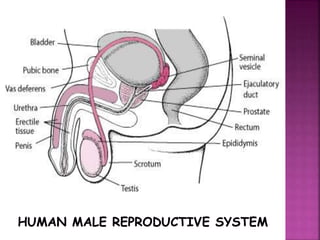
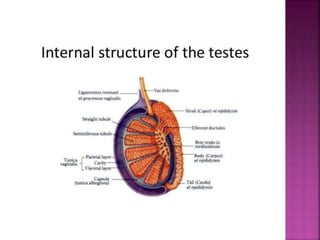
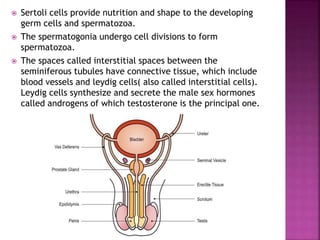
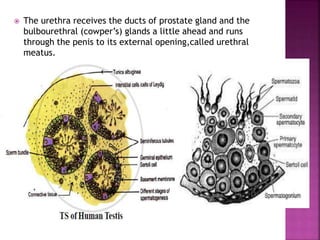
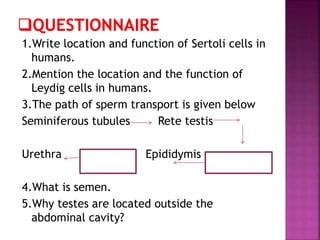
The male reproductive system consists of internal testes that produce sperm and external genitalia. The testes contain seminiferous tubules lined with Sertoli cells that nurture developing sperm and Leydig cells that produce testosterone. Mature sperm exit the testes into the epididymis and are transported via the vas deferens for ejaculation through the urethra, combining with seminal fluid from the seminal vesicles, prostate and bulbourethral glands to form semen. The testes are located outside the body in the scrotum to maintain a temperature slightly lower than normal body temperature which is necessary for sperm production.