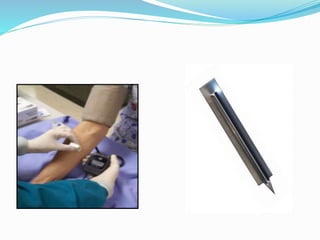
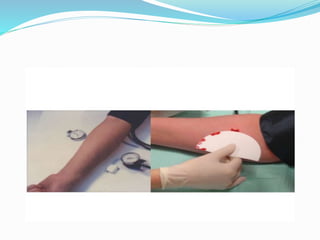
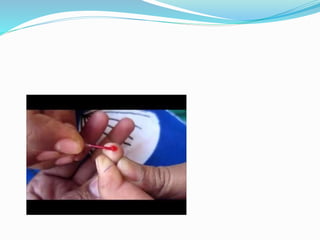
This document discusses various methods for measuring bleeding time and clotting time. The Ivy method, Duke method, and Template method are described for measuring bleeding time. The Ivy method involves making small punctures on the forearm and timing how long it takes for bleeding to stop. Prolonged bleeding time can indicate platelet or coagulation disorders. Clotting time is measured by timing how long it takes blood to form a clot after a finger prick. Prolonged clotting time suggests a deficiency in intrinsic coagulation factors. Normal ranges for bleeding time and clotting time are provided.