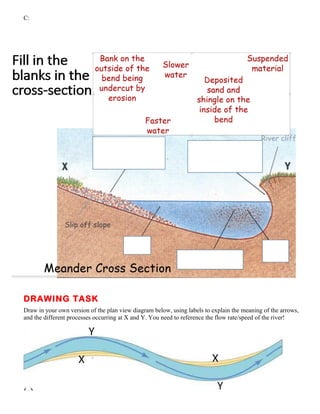
Meanders are bends in rivers that constantly change shape and position over thousands of years. Erosion by the flowing water carves the outer banks of bends while deposition builds up inner banks, causing the bends to grow wider and migrate downstream over time. Faster flow and deeper water on the outside of bends enhances erosion of the outer bank, while slower flow on the inside produces deposition building up point bars.