Genetic Material.ppt
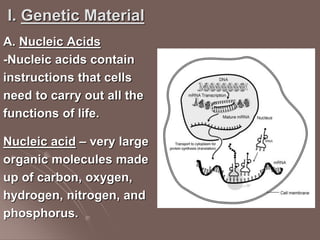
- 1. I. Genetic Material A. Nucleic Acids -Nucleic acids contain instructions that cells need to carry out all the functions of life. Nucleic acid – very large organic molecules made up of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and phosphorus.
- 2. 2 Types of Nucleic Acid : 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)- the genetic material that carries information about an organism. It is passed from parent to offspring. -DNA directs all cellular activities and is ONLY found in the nucleus of a cell. 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid) – a nucleic acid found in the nucleus and cytoplasm of cells that plays an important role in the production of proteins.
- 3. Nucleotides & Genetic Organization -Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides. Nucleotides have 3 basic parts : 1. A 5-carbon sugar. 2. A phosphate group. 3. A nitrogenous (nitrogen-containing) base. Levels of genetic organization : Nucleotide Gene DNA Chromosomes Genome smallest code for made tightly coiled the entire building our traits of many strands of DNA genetic block of genes make-up of a gene an organism
- 4. B. Composition of DNA Major parts of a DNA nucleotide : 1. A 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose. 2. Phosphates 3. Four different nitrogenous bases (rungs of the ladder) : a. Adenine (A) b. Thymine (T) c. Guanine (G) d. Cytosine (C)
- 5. Pairing the Nitrogenous Bases in DNA *Adenine always pairs (matches up) with thymine and guanine always pairs (is complementary to) with cytosine. -These nitrogenous bases make up four different possible nucleotides in DNA. -Many nucleotides (basic unit of nucleic acids) placed together make one DNA molecule.
- 6. C. Structure of DNA James Watson & Francis Crick – American biologist & British physicist who built the first accurate structural model of DNA (Nobel Prize in 1962). -Watson & Crick’s model of DNA was a double helix (twisted ladder), in which 2 strands were wound around each other.
- 7. Structure of DNA con’t. -The outside/sides of the ladder are made of deoxyribose sugar and phosphates. -The rungs of the ladder are the nitrogenous bases (connect to deoxyribose sugar in the outside/side of the ladder).
- 8. II. DNA Replication *Before cells divide, they make copies of their DNA. -DNA Replication ensures that each daughter cell will have all of the genetic information it needs to carry out its activities. -DNA replication is semiconservative, meaning that when DNA copies, each new strand has ½ of the original strand.
- 9. Major steps in DNA Replication : 1. DNA unwinds (untwists) exposing the nitrogenous bases. 2. DNA unzips – weak hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases break. *Hydrogen bonds are the weakest type of bond that occurs in molecules. 3. New complimentary strands form – nitrogenous bases floating in the nucleus of the cell pair up with the bases on each half of the DNA molecule. 4. Two new DNA molecules that are exactly alike are formed. -Both new strands are identical to the original strand of DNA.
- 10. III. The Function of Genes in DNA *Proteins determine the size, shape, and many other traits of an organism, ex : eye color, hair color, type of hairline, etc. -Each gene in a DNA molecule codes for the production of a particular protein. Gene – a small portion of the DNA molecule that codes for a particular trait/protein.
- 11. Order of Nitrogenous Bases -The order of the nitrogenous bases along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. -The order of the nitrogenous bases tells the cell which amino acids to put together to make a protein. If one amino acid is changed or out of place, a different protein is made. -Since DNA cannot leave the nucleus to make proteins at the ribosomes, RNA directs protein synthesis.
- 12. IV. RNA (ribonucleic acid) Major parts of an RNA nucleotide : 1. Ribose sugar (a 5-carbon sugar) 2. Phosphates 3. Four different nitrogenous bases : a. Adenine (A) b. Uracil (U) c. Cytosine (C) d. Guanine (G)
- 13. How RNA makes a protein -There are 3 major types of RNA. 1. mRNA – (messenger RNA) carries information from the nucleus to the rest of the cell. 2. tRNA – (transfer RNA) transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis. 3. rRNA – (ribosomal RNA) makes up a major part of ribosomes.
- 14. When making proteins : 1. mRNA carries DNA’s message to the ribosomes (site of protein synthesis) in the cytoplasm. 2. Ribosomes (like a decoder ring) translate (interpret) the RNA code into a protein.
- 15. V. Differences between DNA and RNA 1. RNA has uracil and DNA has thymine. 2. RNA is a single helix and DNA is a double helix. 3. RNA is very small and DNA is very large. 4. RNA can travel between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, DNA is only in the nucleus. 5. RNA has ribose sugar and DNA has deoxyribose.