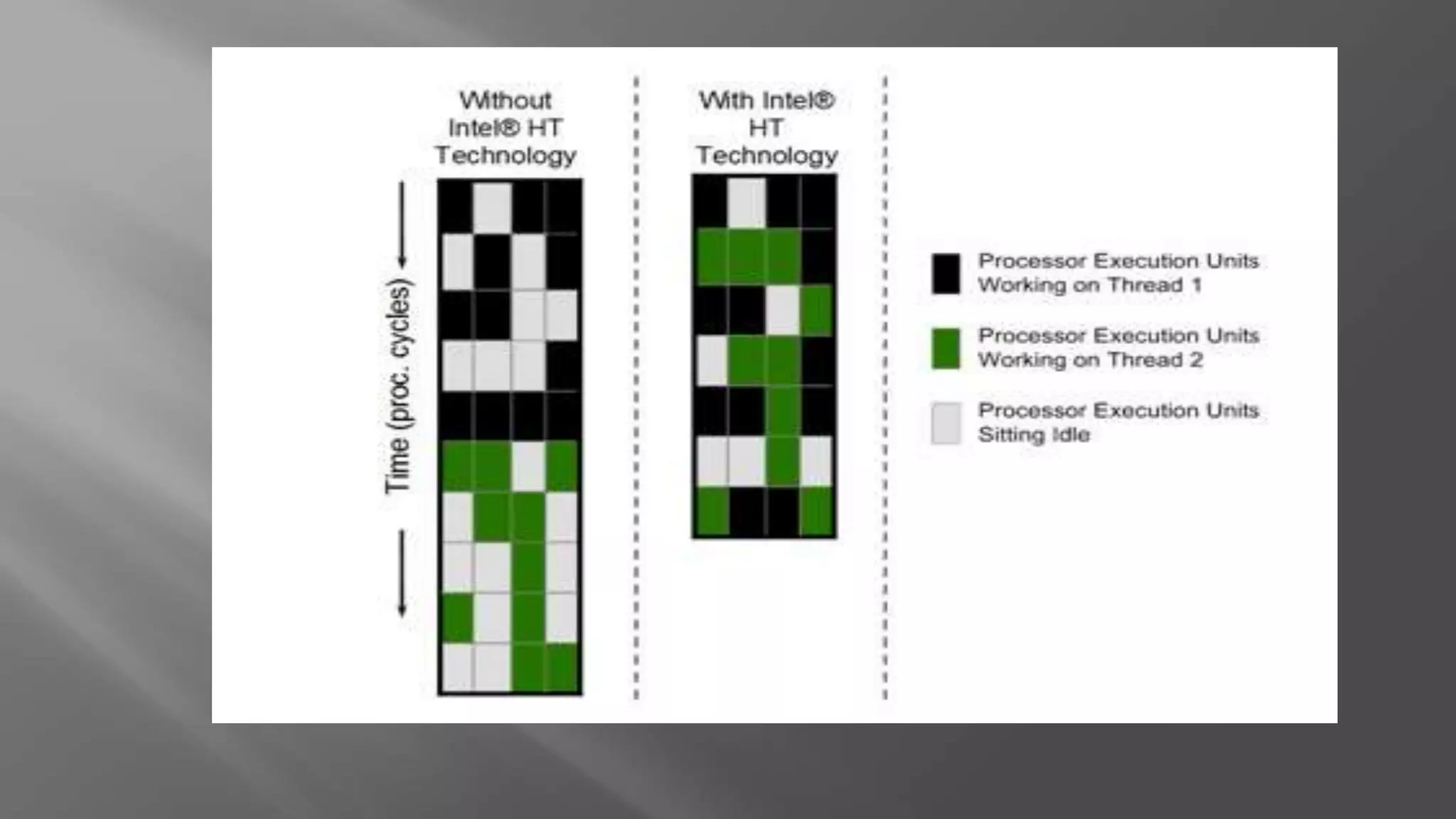
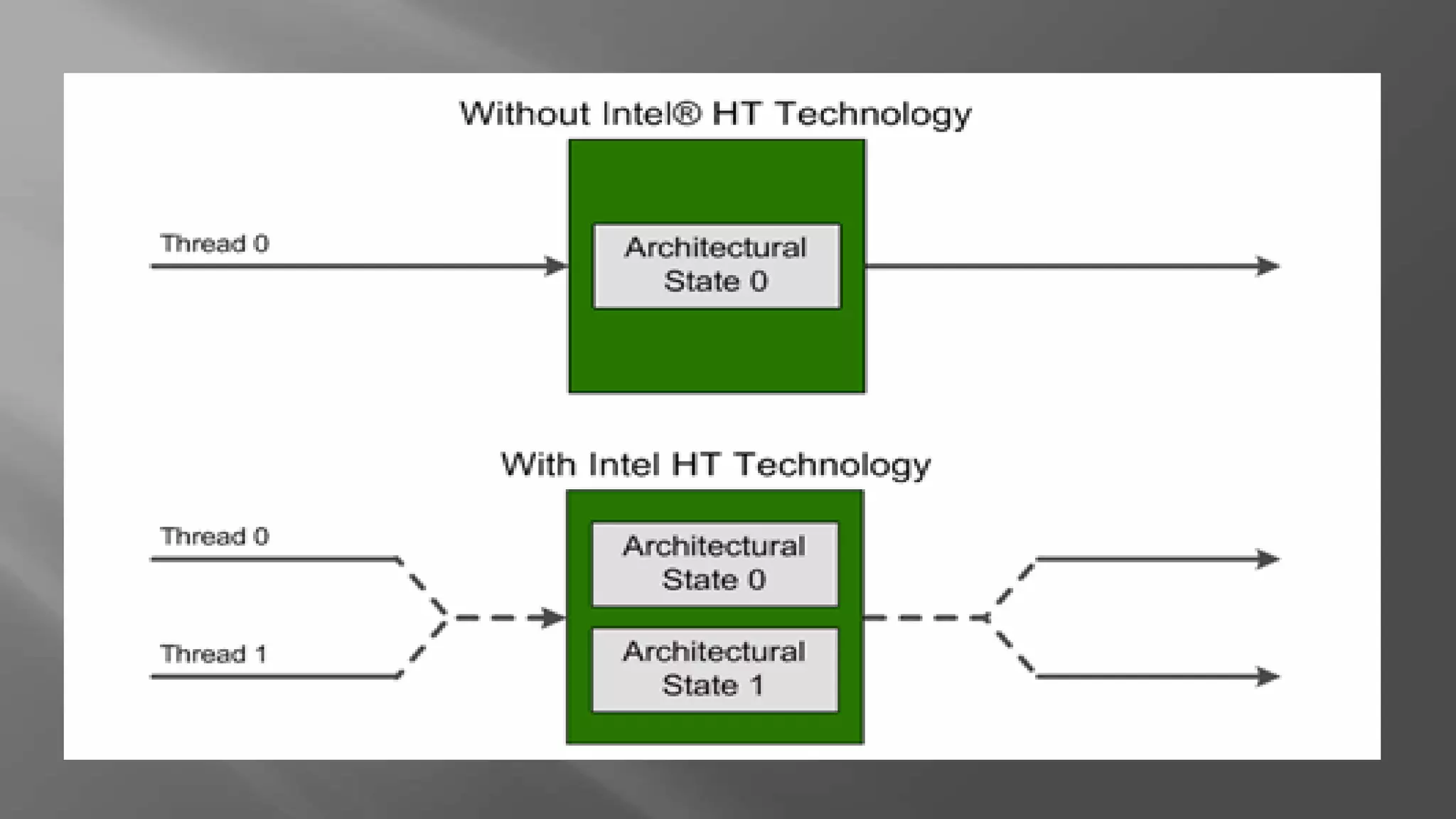
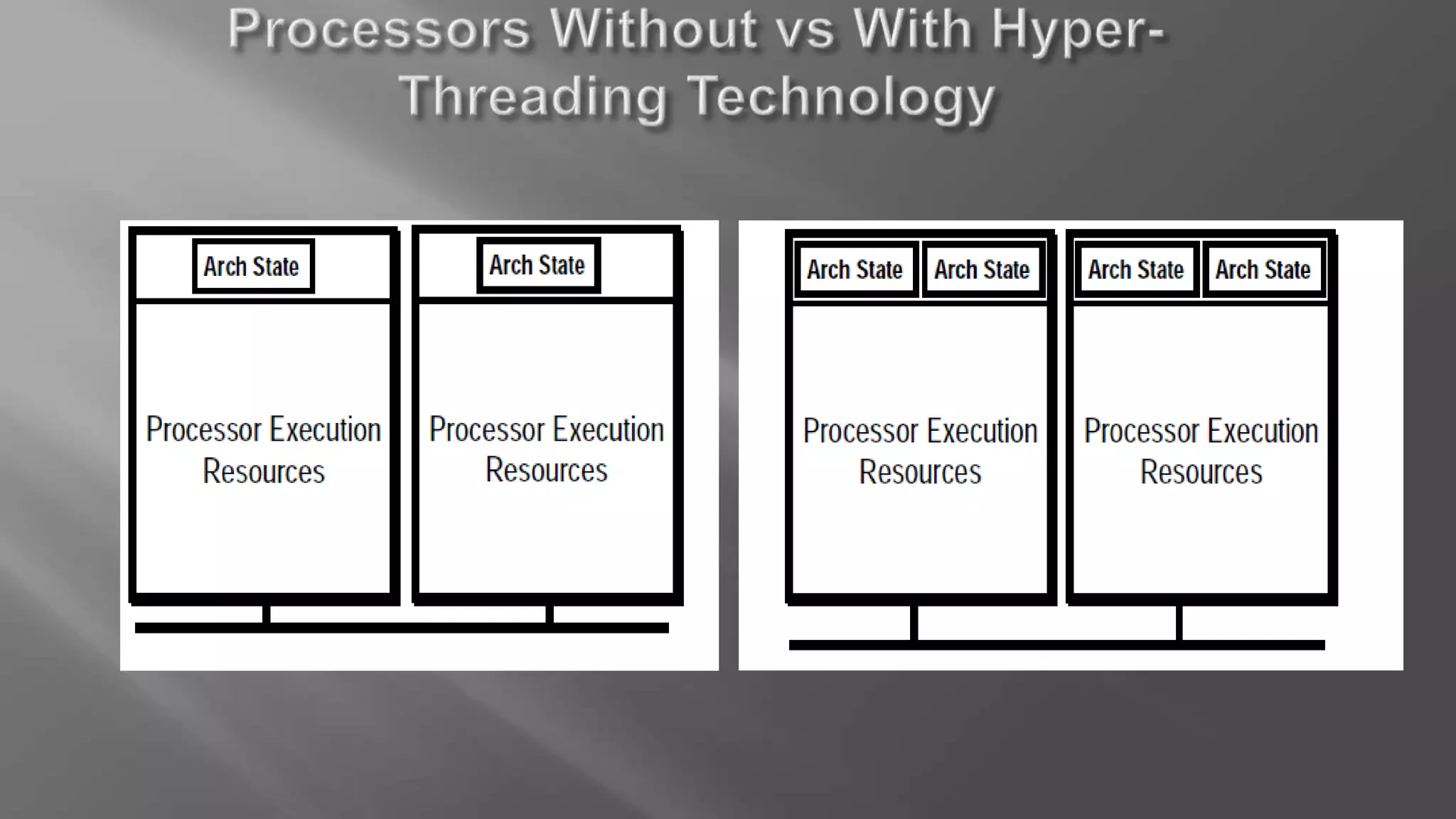
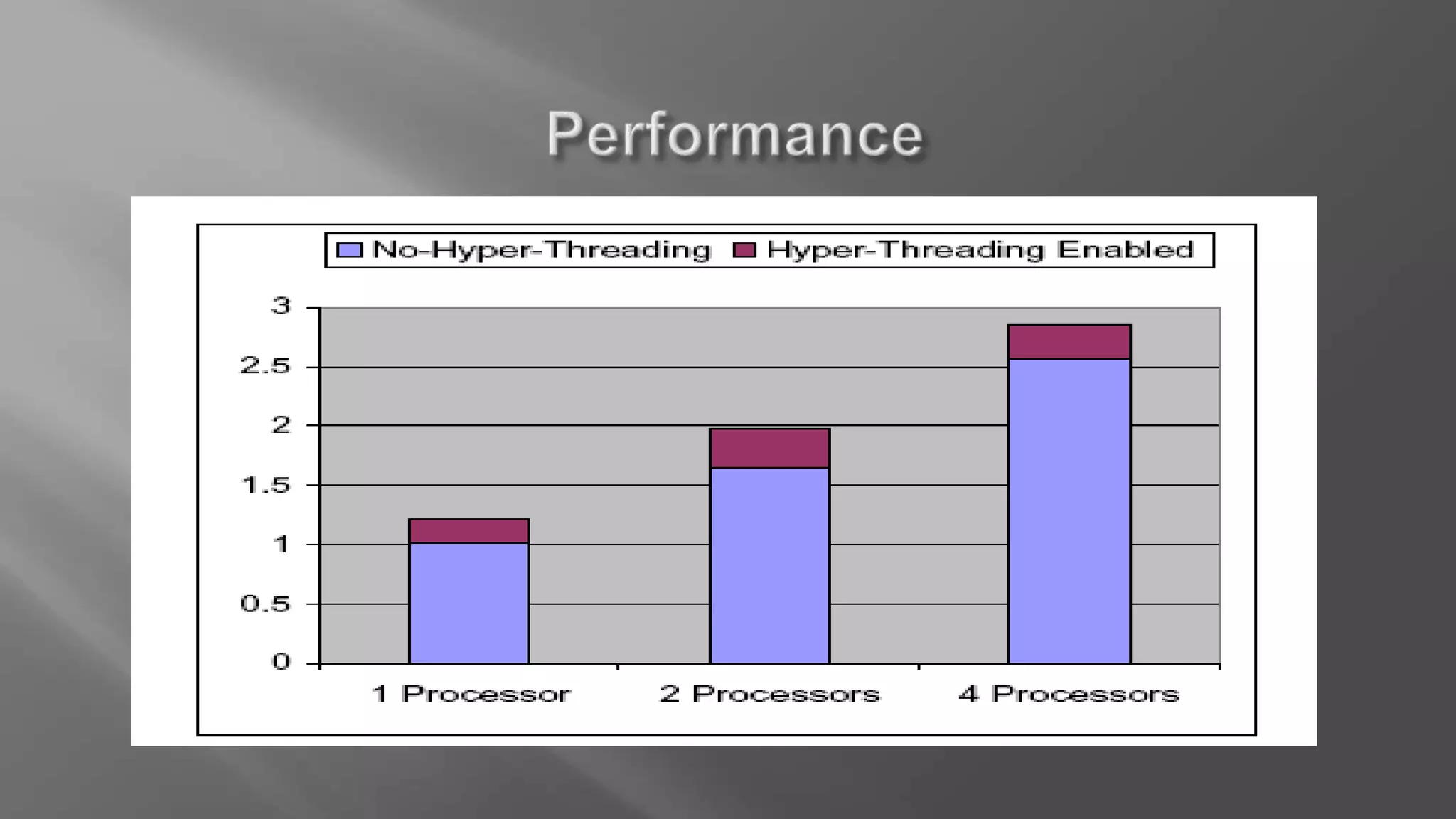
Hyper-threading is a technology that allows each core of a CPU to behave like two logical processors to the operating system. It improves performance by enabling simultaneous multi-threading, where execution units can process instructions from two threads at once to reduce idle clock cycles. This can boost system performance by up to 40% and helps keep systems responsive under heavy workloads.